In addition to interactive rendering, most Alias products have tools that generate effects and renderings. These are located in the Render menu and include all the global settings for render output, editors, and rendering features.
Software rendering provides different features and additional details to image creation than can be achieved with Hardware Shade. There are three methods of rendering: Raycasting, Raytracing, and Hidden Line Rendering.
 |
 |
 |
|
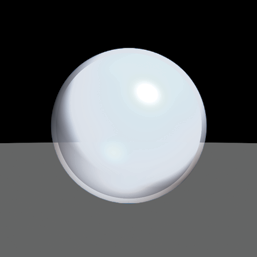
Raycasting Produces smooth shaded renderings that include basic shadows. Raycasting is faster than raytracing, but does not produce reflections or refraction (although you can simulate these using clever shaders). |
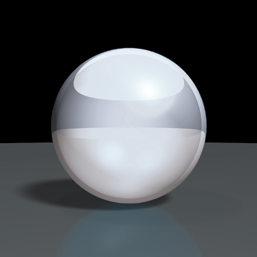
Raytracing Produces smooth shaded renderings that include optical effects (reflections and refraction) and smooth shadows. It creates more realistic renderings, but is slower than raycasting. |
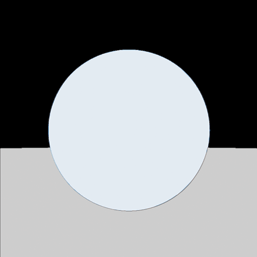
Hidden Line Rendering Produces outline renderings of objects that are filled with flat, unshaded color. |
Renderings can be launched using Render and Direct Render. Before launching a rendering, however, you need to set up Render Globals. In this editor, you establish the quality settings that are used by Direct Render and Render. For Render, the output format and image resolution are also defined in Render Globals.
Render
Choose the render method from the option box. Choosing Render opens a browser where you name your file. The default location is your current project in your My Documents\Autodesk\Alias\user_data (Windows) or Documents/Autodesk/Alias/user_data (Mac) directory.
Direct Render
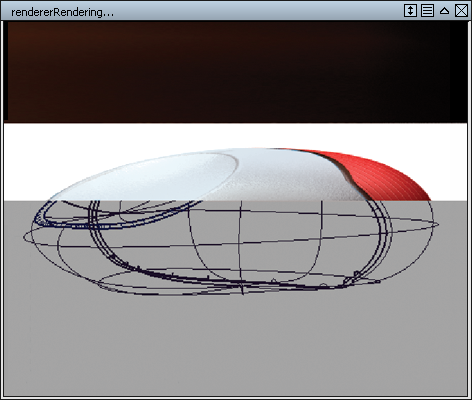
Direct Render calculates the image directly on top of the active window. Using the right mouse button in the Direct Render window opens the options to re-render and save the image to your clipboard.
Ambient Occlusion
Ambient occlusion renders shading based on an omni-directional light source to create general areas of shadow on your model. The feature set is located in Render Ambient Occlusion.
Ambient Occlusion.
When calculated, the results are immediately visible on your Hardware Shaded geometry, adding incredible realism to your interactive display. The shadows are applied to the geometry and are saved with your file. However, when you move geometry in the 3D scene, the ambient occlusion does not update interactively. In order to update, the ambient occlusion needs to be deleted and re-calculated.
Ambient occlusion is also used with software renderers, adding a global illumination-like quality to your renderings. Once again, the shadows are "baked" onto the geometry, so if you use the animation functionality in Alias, you will not be able to combine ambient occlusion with moving parts.
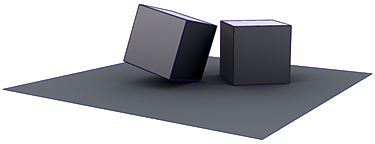
Hardware Shade with ambient occlusion. |

Raytraced rendering with ambient occlusion. |