Transform > Array  is a new tool that lets you create arrays of objects, either linearly or radially, from duplicates of an original set of objects. A rich set of options allows you to create various patterns. This tool is useful when modeling objects such as grills, speakers, wheels, and so on.
is a new tool that lets you create arrays of objects, either linearly or radially, from duplicates of an original set of objects. A rich set of options allows you to create various patterns. This tool is useful when modeling objects such as grills, speakers, wheels, and so on.
Create an array of similar objects from an original
- Choose Transform > Array
 .
. - Select (or box-select) the objects to duplicate.
- Click the Build button in the view window.
The array is built.
Note: If Number is 1 along both axes, you only see the original objects. - Adjust the options in the control window.
If Auto Update is on, the array updates automatically. Otherwise click the Update button.
Options
- Plane
- Choose whether to create the array in the XY, XZ or YZ plane.
- Mode
-
Linear – The array consists of rows and columns arranged in a rectangular pattern. The original object is located in the lower left corner.
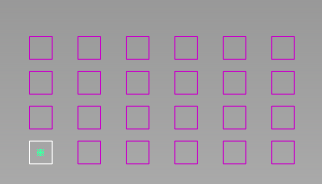 Radial – The array consist of "spikes" arranged radially around the original object. There is an option (Grow Radially) to increase the number of duplicates as the distance to the object increases, to create the appearance of concentric circles.
Radial – The array consist of "spikes" arranged radially around the original object. There is an option (Grow Radially) to increase the number of duplicates as the distance to the object increases, to create the appearance of concentric circles.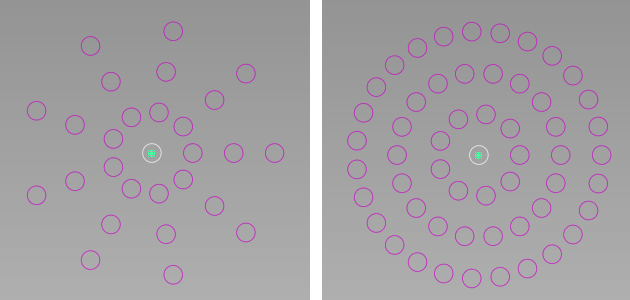
Left: Grow Radially = off; Right: Grow Radially = on
Axis 1/Axis 2 or Radial/Angular
These sections control the two directions of the array. For a linear array, both these sections have identical options. Axis 1 is horizontal and Axis 2 is vertical. For a radial array, Radial is in the direction of the radius, and Angular is in the direction of the circumference.
- Number
- This value specifies the number of duplicates in each direction (horizontal/vertical for a linear array; radial/angular for a radial array).
- Spacing/Angle
- Spacing specifies the distance between the rows and columns, in the current units. For a radial array, Angle specifies the angle between the columns, or "spikes".
- Offset
- Offsets each row (column) in the array by this distance from the previous row (column).
- Scale
- This is a relative scale factor applied to the original object to produce the last duplicate in each row or column. The sizes of intermediate duplicates are interpolated.
- Stagger
- Check on to set the Offset to half the Spacing value for alternating rows (or columns), creating a "stagger" effect, or "brick pattern".
The following options only appear in the Angular section when creating a radial array.
- Fit to Circle
- Check on to adjust the Angle so that the specified number of columns (spikes) fill a 360 degree circumference evenly. For example, if Number is 6, Angle is set to 60.
- Rotate Duplicates
- Check on to rotate duplicates around their local pivot by a relative value of Angle with respect to their orientation in the previous column (spike).
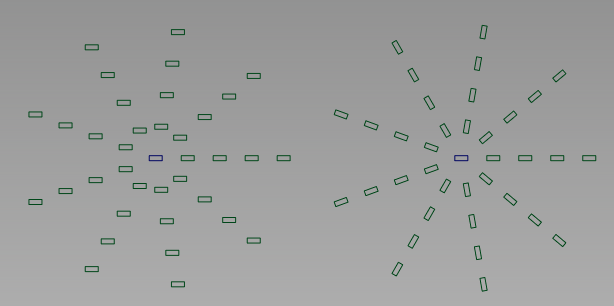
Radial array with 9 spikes and Angle = 40. Left: Rotate Duplicates is OFF; Right: Rotate Duplicates is ON.
Control Options
- Auto Update
- When checked, duplicates update automatically when values in the control window are changed.
- Create History
- When checked, the duplicates have construction history so that modifying the original objects causes the duplicates to update accordingly.
- Scale Position
- Check on to scale the distance between duplicates along with their size when Scale is different from 1.0. For a scale greater than 1.0, this option reduces overlapping.
- Grow Radially
- This option is only available in Radial mode. When checked, the number of duplicates increases as the radius of its "row" increases. This technique helps create the appearance of concentric circles, rather than spikes.
Example
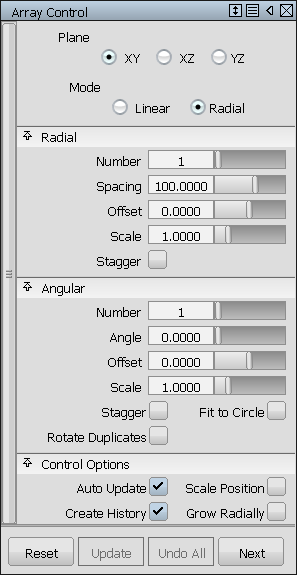
Below, the Array tool is used to create a grill array from a single hexagonal curve. The array of curves is then projected onto a surface. The surface is trimmed, and draft surfaces are built around the holes.
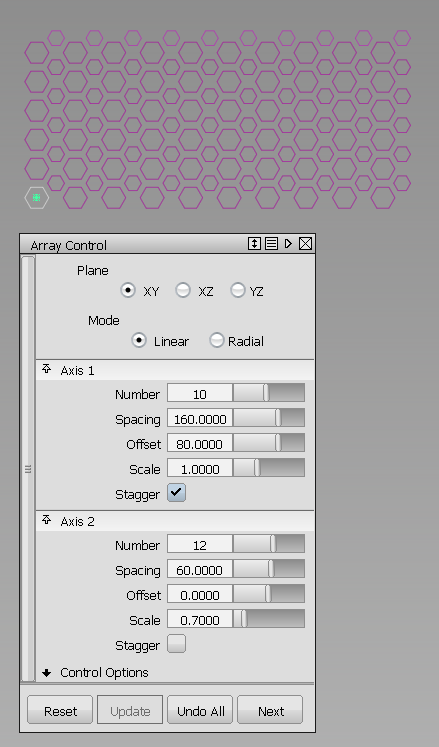
Option settings to create the grill array.
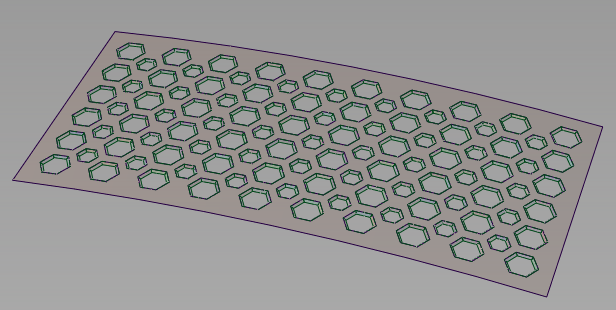
Finished grill after projection, trimming, and draft.