How to calculate and display the mass properties (volume, surface area, and centroid) of a model.
The Mass Properties tool provides two ways of specifying the object to measure:
- Solid – The surfaces you pick represent the boundaries of a closed, solid object.
- Shell Interior – The surfaces you pick represent the outside of a thin shell enclosing a hollow space (for example, modeling a bottle with a single surface of revolution). You specify the thickness of the shell.
Restrictions
To get accurate statistics on an object, the following conditions must be met:
- The surfaces must completely enclose a volume. The edges of surfaces must meet within the tolerance value set in the Mass Properties option window.
- The normals on all NURBS surfaces must point out of the solid, and, when moving along a face boundary in the increasing U direction, the face area must be to the left when viewed from outside the solid.
or
The normals on all NURBS surfaces must point into the solid, and, when moving along a face boundary in the increasing U direction, the face area must be to the right when viewed from outside the solid.
You can check the seam between two surfaces by placing a Deviation measurement on the seam. You can check the orientation of normals using the Reverse Direction tool.
Show the mass properties of a model
- Pick all the surfaces that make up the model. Make sure the surfaces completely enclose the volume of the object.
- Click the Mass Properties
 icon, or choose Evaluate > Mass Properties from the palette.
icon, or choose Evaluate > Mass Properties from the palette. When the Mass Properties tool completes its calculations, the Mass Properties window appears, containing the following statistics about the object.
Label Description Formula Units Current unit of measurement (default is either centimeters or millimeters, depending on which product you are using). Area Area of the picked surfaces. 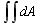
volume Volume enclosed by the picked surfaces, or volume occupied by shell surface with given thickness. 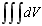
centroid X, Y, Z coordinates of the center of the object 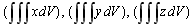
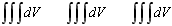 Note:
Note:If you are using a construction plane when you click the tool, the calculations use the X, Y, and Z axes of the current construction plane.
If you change the options of the Mass Properties tool, the window updates.
Tips and notes
- Using the Mass Properties tool with the Solid option on a group of surfaces with gaps does not produce an error.
In fact, the results are still meaningful if the gaps between surfaces are not too large.
- If the volume value is negative, some of the surfaces probably have normals pointing inward. Use the Surface Edit > Orientation > Reverse Surface Orientation
 tool or Surface Edit > Orientation > Set Surface Orientation
tool or Surface Edit > Orientation > Set Surface Orientation to find and reverse the surfaces so they have normals pointing out.
to find and reverse the surfaces so they have normals pointing out.