This dialog is used to view/edit the properties of the selected thermoplastics material.
The Rheological Properties tab of the Thermoplastics material dialog is used to specify the rheological (flow-related) properties of the thermoplastics material.
Dialog elements
- Default viscosity model
- In order to simulate material viscosity properties accurately during a flow simulation, a mathematical viscosity model is required.
Matrix, Cross-WLF and Second Order are the viscosity models used for thermoplastics. For materials in the Autodesk Simulation Moldflow database, the appropriate default viscosity model has been selected.
In cases where you need to view the viscosity model, click View viscosity model coefficients to display the coefficients.
In cases where you need to specify the default viscosity model, select the model from the drop-down list.
- Juncture loss method coefficients
- Bagley correction constants,
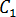 and
and 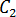 , specific for each resin. If the specific data does not exist, typical values can be used to evaluate whether juncture loss is significant to the application.
, specific for each resin. If the specific data does not exist, typical values can be used to evaluate whether juncture loss is significant to the application. Juncture loss is a calculation of the hydraulic loss that occurs when the melt passes through a large change in path diameter, such as from the end of the runner to the gate. The software calculates this loss using the Bagley correction constants,
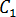 and
and 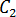 , for the material.
, for the material. If juncture loss data is not available for the material that you selected, you can use typical values for the juncture loss coefficients.
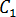 values range from 0.00001 to 10 (typically 0.0001), while
values range from 0.00001 to 10 (typically 0.0001), while 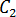 values range from 2.5 to 1 (typically 2). If analysis results show that juncture loss is siginificant to your application, it is strongly recommended that you have the material characterized by Autodesk Moldflow Plastics Labs for juncture loss coefficients.
values range from 2.5 to 1 (typically 2). If analysis results show that juncture loss is siginificant to your application, it is strongly recommended that you have the material characterized by Autodesk Moldflow Plastics Labs for juncture loss coefficients. - Transition temperature
- The transition temperature is the polymer freeze temperature. At this temperature, the melt-to-solid transition occurs.
The transition temperature corresponds to the glass-transition temperature (Tg) for amorphous materials and to the crystallization temperature (Tc) for semi-crystalline polymers.
- View/edit test information...
- Click this button to view the source of this material data, the date that the data was last modified, the date of testing and the test method that was used for the data.
For more information about Autodesk Simulation Moldflow materials data and material testing methods, see Material testing and data fitting.
- Moldflow Viscosity Index
- A single point reference viscosity level (in Pa. sec.) at the designated temperature and a shear rate of 1000 1/sec. For example, VI(240)125 means that the material has a viscosity of 125 Pa.s at a shear rate of 1000 1/s and a temperature of 240C.Note: Autodesk uses the same temperature to calculate the Viscosity Index for all polymers in a generic family (for example, PP) to make it easier to compare materials.
- Melt mass-flow rate (MFR)
- MFR is an ISO standard measure which describes how easily a given melt flows. The higher the value the more readily it flows.
MFR is identical to the ASTM standard, melt flow index (MFI).
To measure the MFR, the material is first heated in a barrel at a known temperature. A known weight is then applied to the top of the piston to drive the melt through a capillary die at the end of the barrel. MFR is the mass of the material that passes through the die in a given time interval under the specific conditions of temperature and pressure.
- Temperature is the temperature that was used to melt the material for the MFR measurement.
- Load is the mass that was applied to push the material through the barrel for the MFR measurement.
- Measured MFR is the mass-flow rate of the specific melt. It is measured in grams per 10 minutes (g/10 min), and represents the mass of the melt that passes through the die in 10 minutes.
- Extension viscosity
- Specifies whether extension viscosity data is available for this material. If the option is selected, a button is displayed which allows you to view or edit the extension viscosity model coefficients.Note: The extension viscosity model, if selected, is only used for 3D Fill+Pack analyses.