The Cooling quality result shows you where heat tends to stay in a part due to its shape and thickness.
The part is considered to be located in the center of a block of metal, or a theoretical mold, without any cooling circuits and held there for a fixed period of time. The result shows the way heat will leave the hot part naturally and flow towards the extremities of the block.
This result is derived from the cooling time variance and temperature variance results.
Using this result
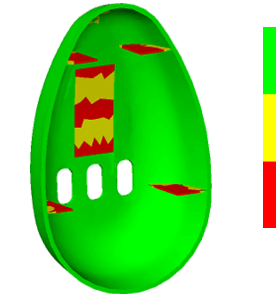
The Cooling quality result graphically depicts a part with green, yellow, and red areas. The green areas indicate a high amount of cooling; the yellow areas indicate a medium amount of cooling; and the red areas indicate a low amount of cooling. This result is a combination of the Cool analysis Temperature variance result, which is mainly affected by shape, and Cool analysis Cooling time variance result, which is mainly affected by thickness.
The following graphic result shows that most of the part can be cooled effectively, but there could be problems with the thin center and the thin ribs.
Things to look for
If cooling quality is low in a thin area of the part due to the Temperature variance result or Cooling time variance result being significantly lower than the average, hesitation or a short shot may occur, and the result will show a red area. Thicker walls or a higher melt temperature may be necessary.
For the same reason, the cooling quality may be low in an area where weld lines are more obvious and the part is structurally weaker.
In areas where the cooling quality is low due to the temperature or cooling time variance being significantly higher than normal, surface defects and warpage can occur unless significant cooling is introduced to your mold design or the product redesigned. Ensure the temperature at the flow front is always within the recommended temperature range for the polymer you are using.
- Cooling time variance results that are significantly shorter or longer than the average time to freeze
- Temperature variance result values that are too low or too high
When a part has a yellow or red Cooling quality result, examine the Cooling time variance and Temperature variance results to investigate the cause.