Mold cooling accounts for more than two-thirds of the total cycle time in the production of injection molded thermoplastic parts. An efficient cooling circuit design reduces the cooling time, which in turn increases overall productivity. A well designed circuit achieves uniform cooling, improving part quality by reducing residual stresses and maintaining dimensional accuracy and stability.
The primary factor governing production costs is cycle time, and the cycle time is governed by the material's ejection temperature.
- Surface finish
- Residual stresses
- Crystallinity
- Thermal bending
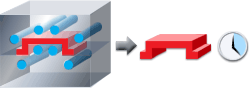
The following diagram shows how an effectively cooled part (left) leads to a correctly molded part in a shorter period of time (right).
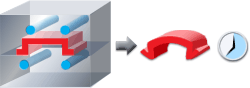
The following diagram shows how a poorly cooled part (left) leads to a low quality part in a longer period of time (right).
Cooling system components
A cooling system typically consists of the following items:
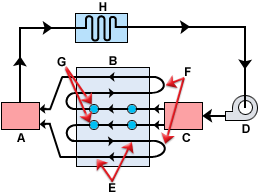
- A - Collection manifold
- B - Mold
- C - Supply manifold
- D - Pump
- E - Cooling channels
- F - Hoses
- G - Baffles
- H - Temperature controller