Internally, a material is defined by four shaders from different classes: Color, Transparency, Reflectance and Displacement. Each class of shader controls a different aspect of a material's behavior. There are many types of shader in each class, each type being defined by its own set of parameters.
- A Color shader is used to define the color of a surface at any point in space. It may be as simple as a plain color which specifies all parts of the surface to have a uniform color, or it may define complex surface patterns such as marble or wood. Every material must have a color shader.
- The behavior of a surface in the presence light is represented by a reflectance shader which defines how much light is reflected by the surface towards the viewer. Shaders of this class may be thought of as defining a surface’s “finish”, and are used to model properties such as matte, metal, and plastic.
- A transparency shader is used to define how transparent or opaque a surface is, and thus how much light is able to pass through it. Transparency shaders range from a simple uniform transparency to more complex regular or irregular eroded patterns that would be more difficult to represent using modelling techniques. A material without a transparency shader is completely opaque.
- Small surface perturbations can be supported by means of displacement shaders. Typically, a displacement shader will give an otherwise smooth surface an irregular or indented appearance. Displacement shaders are used to represent features that would be difficult, impossible, or inefficient if conventional modelling techniques were used. For example, rough metal castings and the regular indentations produced by pressed sheet metal can be simulated.
Normally, the Material Editor displays a selection of the most important parameters from all shaders within the Materials tab. If the user profile is set to Developer on the Interface node in the Options Editor (see Presenter Page ), then all four shaders can be edited and changed individually.
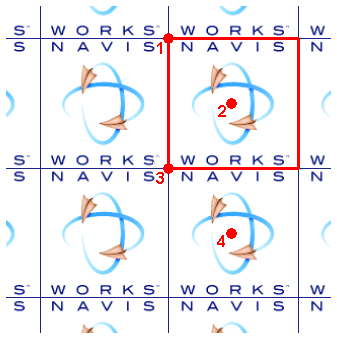
Some shaders are described as “wrapped”. These define a flat, two dimensional material, like wallpaper. Wrapped materials need a texture space shader to define how they should be applied to (wrapped around) a three dimensional object. Materials that include a wrapped shader can also include a texture space shader. A special type of texture space shader, called a layout shader, can be used to transform (rotate, stretch, offset) the two dimensional material before it is applied to the three dimensional object. Transforms are based around an origin point, which by default, is the top left corner of the image (refer to the diagram below, where the image is inscribed in the red square, which is then repeated. The default origin is Point 1). Selecting the Offset Center check box will reposition the origin to the center of the image (Point 2). Finally, in Developer profile, you can edit the Decal Mode, choosing from either Default or Normalized. Selecting Normalized will move the origin to the lower-left corner of the image (Point 3, with the Offset Center option cleared). With both Normalized and Offset Center selected, the origin will be repositioned in the center of the repeated image, directly below (Point 4).
In the Presenter window, materials that include a wrapped shader also have a layout texture space shader associated with them. Normal texture space shaders are associated with objects.