| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Fixture Units | The number of piping components in the system. |
| Flow | Cumulative flow for the system, based on the flow for individual components in the system. |
| Reynolds Number | This value is calculated using the following formula: |
| Relative Roughness | This value is calculated using the following formula: |
| Flow State | This value is determined by the value of the Reynolds Number. A Reynolds Number less than 2,000 is considered laminar flow. A Reynolds Number greater than 4000 is considered turbulent flow. Numbers between 2,000 and 4,000 are unpredictable, and no loss calculation is made. There are two types of turbulent flow: transition and complete turbulence. |
| Friction Factor | Friction factor used in the Darcy-Weisbach equation is calculated based on the following flow states: Laminar Flow  Turbulent Flow |
| Velocity | This value is calculated using the following formula: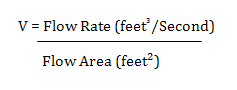 |
| Friction | This value defines the pressure loss for a specific length unit of pipe. |
| Pressure Drop | This value defines the total pressure drop for the entire length of pipe. |