This option generates forces resulting from prestressing tendons. The load from prestressing tendons is replaced with the equivalent external load.
The tendon assumes the parabolic shape according to the specified values of eccentricities. (The loss of prestress and when a tendon does not extend over the whole beam length are not considered.) Open the Forces due to Beam Prestress dialog by clicking Loads menu > Special Loads > Prestress Forces.
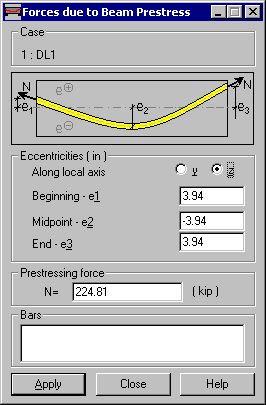
The following parameters can be specified in this dialog:
- Case - A load from a prestressing tendon is assigned after a load case is selected. The name of the case is displayed in the Case field.
- Eccentricities [in] - The Along local axis y/z option specifies the local axis of a bar section. Eccentricity values are defined along this axis. (It will also be the axis that determines the direction of the equivalent external load). The Beginning e1, Midpoint e2, and End e3 fields define the tendon profile (a parabola). You can enter both positive and negative values.
- Prestressing force - Specifies the value of the prestressing force. (It can be only a positive value.)
- Bars - Specifies the bars to which the defined load is applied. You can select any number of bars by highlighting them in the drawing area or by entering their numbers in the field). Note: You cannot define a load on a bar chain. On every bar you select, the load is defined and generated separately.
The equivalent load is generated after you specify the previous parameters and click Apply.
The equivalent load is defined as bar forces (concentrated and distributed) in the bar's local coordinate system. The following displays how the values of the equivalent load are calculated.
The following designations are used:
-
Data defined by the user:
N - Prestressing force
e1 - Eccentricity at the bar beginning
e2 - Eccentricity at the bar midpoint
e3 - Eccentricity at the bar end
L - Length of the bar to which the load is applied
-
Calculated load:
M1 - Concentrated moment at the bar beginning
M2 - Concentrated moment at the bar end
F1 - Shear force at the bar beginning
F2 - Shear force at the bar end
q - Uniform load
N1 - Axial force at the bar beginning
N2 - Axial force at the bar end
-
Calculated force values:
q = 8 * N * e / (L * L)
Where: e = | (e1 + e3) / 2 - e2 |
The sense of the load q depends on the following:
- For a convex parabola - (e1 + e3) / 2 > e2) - It is compatible with the sense of the axis selected with the Along local axis option.
- For a concave parabola - (e1 + e3) / 2 < e2 - It is opposite to the sense of the axis selected with the Along local axis option.
When the z axis is selected (Along local axis option):
My1 = N * e1
Nx1 = N
Fz1= - q * L / 2
My2 = - N * e3
Nx2 = - N
Fz2= - q * L / 2
When the y axis is selected (Along local axis option):
Mz1 = - N * e1
Nx1 = N
Fy1= - q * L / 2
Mz2 = N * e3
M = -N
Fy2= - q * L / 2.