With the Free Surface modeling capability, you can dynamically simulate the interface between liquids and gases. This ability is essential for modeling flow phenomena such as waves, sloshing, and spilling. These are flows that occur in nature as well as in a wide range of engineering applications.
The Free Surface formulation in Simulation CFD is based on the Eulerian Volume of Fluid (VOF) approach. The advection of the free surface is solved with this equation:
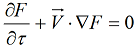
F is the Fill Fraction, and is used to determine which elements are filled with fluid and which elements are empty.
When F = 0, the element is empty.
When F = 1, the element is filled with liquid.
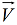 is the liquid velocity field, and is solved for by the incompressible Navier-Stokes equations.
is the liquid velocity field, and is solved for by the incompressible Navier-Stokes equations.
On the free surface (fluid-gas interface), the static gage pressure = 0. Gas-filled regions are simulated by empty elements. These empty elements are omitted from the flow solution.
Free Surface simulations are always run as time dependent, hence the time term in the governing equation.