In some situations, exploring and optimizing the design of the bulb itself must precede understanding the thermal performance within a fixture.
Geometry
There are two primary modeling strategies for simulating the thermal performance of an individual bulb: in an air column and enclosed in a can. In both cases, it is better to omit the details of the socket as their geometric complexity does not significantly influence the thermal performance of the design.
Air Column
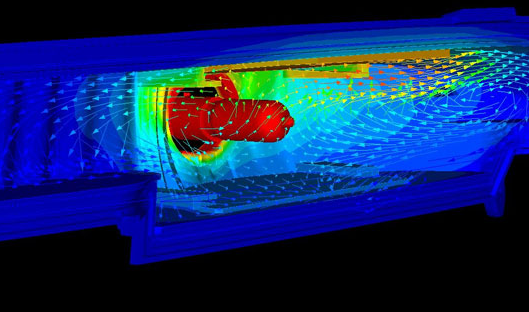
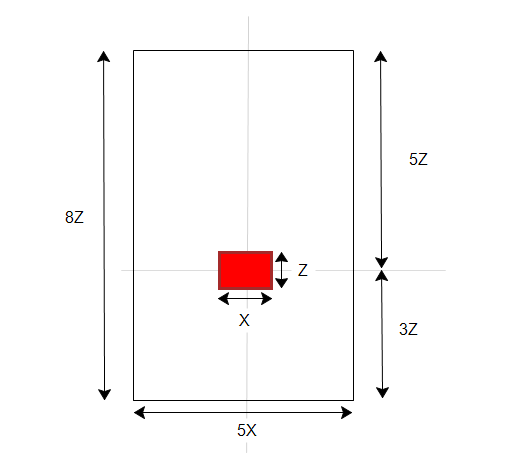
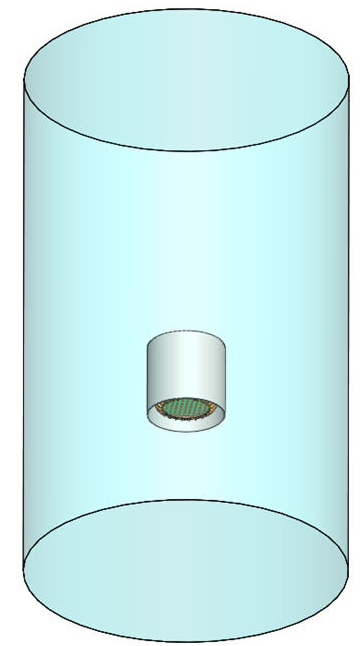
Construct a cylindrical enclosure around the bulb, and center it horizontally within the enclosure. The size of the enclosure should be based on the size of the device, as shown below.
|
|
To model different orientations of the bulb, modify the orientation of the air cylinder instead of the bulb. This allows Summary entities (Points, Planes, XY plots) created for one orientation to be used for comparing results from other orientations in the Decision Center.
Can Enclosure
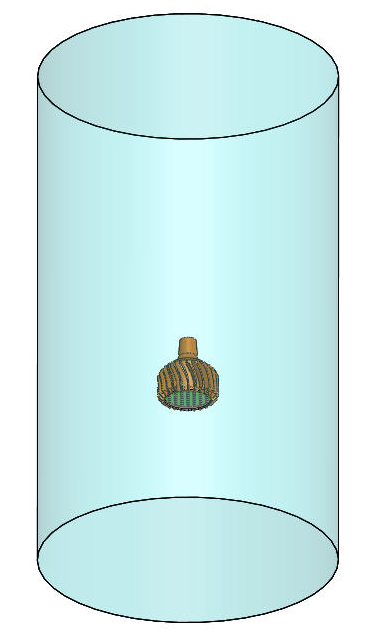
A can restricts the airflow around the bulb, and can better predict installed performance.
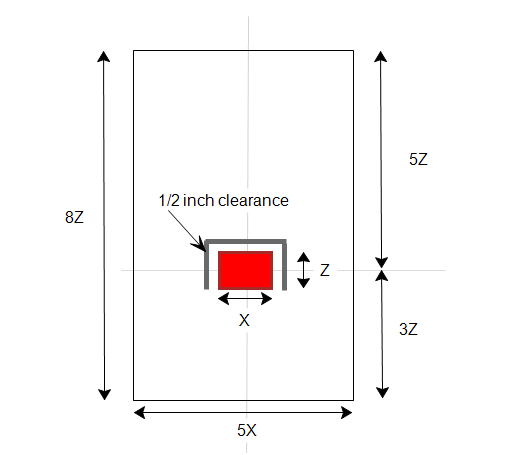
- Construct a cylinder around the bulb with a half inch clearance.
- Construct a cylindrical enclosure around the bulb, and center it horizontally within the enclosure. The size of the enclosure should be based on the size of the device, as shown below.
|
|
Boundary Conditions
- To define openings at the top and bottom of the air volume, assign Static Gage Pressure = 0 to both surfaces.
- Bottom face (inlet): Static Temperature = ambient temperature.
- Heat loading is specific to the lighting type. Click for LED. Click for fluorescent.