This material model is available for 2D, brick and tetrahedral elements. The Blatz-Ko material model involves strong coupling between volumetric and non-volumetric parts, such as the bulk modulus, cannot be determined separately as with other hyperelastic material models. The Blatz-Ko material properties are listed below. In addition to these properties, it may be necessary to define some Isotropic Material Properties.
Click the Curve Fit button on the Element Material Specification dialog to use the Curve Fitting routine. This routine calculates the material constants using measured stress-strain data.
The potential function of the material is as follows:
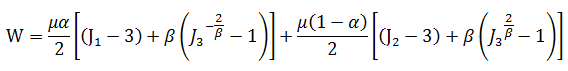
where
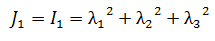
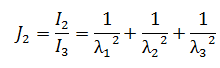
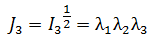
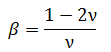
Shear modulus
The shear modulus (μ).
Alpha
Alpha (α) is a material constant introduced during the derivation of the strain energy form. This value is derived using the curve fit algorithm based on the stress-strain curves. α=1 is suggested for a rubber-like material. For example, µ=200711.2 Pa, α=1, and β=13.3 are suggested for polyurethane rubber in the Blatz-Ko's paper.
Poisson's Ratio
The Poisson's Ratio (ν) of the material.