The Smoke Visibility capability computes the distance a lighted sign can be seen from within a smoke-filled environment. The flow computed by Autodesk Simulation CFD and a correlation developed by the United States NRC evaluate this distance based on the resultant air flow, location of the fire, and properties of the fire load.
This information helps architectural designers determine the location and placement of exit signs in enclosed environments. As smoke fills a room, the visibility of signs that point to exits is vital for safe evacuation.
Simulating smoke visibility
Because smoke visibility is derived from the flow results computed by Autodesk Simulation CFD, it can be enabled either before running or after the solution is complete.
Basic analysis considerations
Flow:
- Assign a Scalar boundary condition (value = 1) to indicate the location of the fire (smoke emission source). This can be on either a solid surface or a wall surface. The scalar value represents the mass concentration of the combustion products throughout the analysis region.
- Set up other boundary conditions, materials, mesh distributions, etc.
- On the Physics tab of the Solve dialog, click the Advanced button, and enable General Scalar. Specify a non-zero value for the diffusion coefficient.
- In many smoke visibility analyses, air movement is driven at least in part by natural convection. To enable material properties to vary with temperature, select Variable on the Environment dialog.
Thermal:
- Specify the air temperature at all inlets. This is required.
- Specify known heat generation boundary conditions on lighting, electronics, and equipment. Do not specify temperatures on components that will be solved for in the simulation.
- Specify film coefficients (as needed) to exterior surfaces to simulate heat transfer with the surrounding environment. (External wall surfaces that do not have an applied heat transfer boundary condition are treated as perfectly insulated.)
On the Solve dialog, enable both Flow and Heat Transfer.
To enable Smoke visibility prior to running an analysis:
- On the Control tab of the Solve dialog, click the Results quantities button.
- Check the Smoke visibility box.
- To define the characteristics of the environment, click the Parameters button adjacent to the Smoke visibility check box.
To enable Smoke visibility for a completed analysis:
- Follow the preceding procedure to enable the Smoke visibility result quantity.
- On the Control tab of the Solve dialog, leave the Continue From field at the last iteration.
- Set the Iterations to run to be 0, and click Solve.
The analysis will appear to start, but will not solve any additional iterations. The smoke visibility results are then computed and made available for visualization.
Smoke visibility parameters
These parameters define the substance being burned, the type of fire (smoldering or flaming), and the sign illumination type:
Extinction coefficient
The extinction coefficient characterizes the mode of combustion:
|
Type of Combustion |
Specific Extinction Coefficient (ft2/lbm) |
|
Smoldering combustion |
21000 |
|
Flaming combustion |
37000 |
Sign visibility constant
The sign visibility constant characterizes the visibility of the sign:
|
Type of Situation |
Constant |
|
Illuminated sign |
8 |
|
Reflecting sign |
3 |
|
Building components in reflected light |
3 |
Combustion particulate yield
The combustion particulate yield is the particulate content of the smoke based on the burning fuel. It is an important parameter for characterizing the translucency of the smoke.
Combustion particulate yield for several combustible materials
|
Combustible Material |
Particulate Yield |
|
Wood (red oak) |
0.015 |
|
Wood (Douglas fir) |
0.018 |
|
Wood (hemlock) |
0.015 |
|
Fiberboard |
0.008 |
|
Wool (100%) |
0.008 |
|
Acrylonitrile-Butadiene-Styrene (ABS) |
0.105 |
|
Polymethylemathacrylate (PMMA; PlexiglasTM) |
0.022 |
|
Polypropylene |
0.059 |
|
Polystyrene |
0.164 |
|
Silicone |
0.065 |
|
Polyester |
0.09 |
|
Nylon |
0.075 |
|
Silicone Rubber |
0.078 |
|
Polyurethane Foam (Flexible) |
0.188 |
|
Polyurethane Foam (Rigid) |
0.118 |
|
Polystyrene Foam |
0.194 |
|
Polyethylene Foam |
0.076 |
|
Phenolic Foam |
0.002 |
|
Polyethylene (PE) |
0.06 |
|
Polyvinylchloride (PVC) |
0.172 |
|
Ethylenetetrafluoroethylene (ETFE; TefzeTM) |
0.042 |
|
Perfluoroalkoxy (PFA; TeflonTM) |
0.002 |
|
Fluorinated Polyethylene-Polypropylene (FEP; TeflonTM) |
0.003 |
|
Tetrafluoroethylene (TFE; TeflonTM) |
0.003 |
Assessing smoke visibility results
The Smoke visibility output quantity indicates how far away a sign is visible at every location in the model. The visibility distance near the burn source is typically very small because of heavy smoke. The visibility distance away from the burn source is usually significantly higher, indicating a reduced smoke concentration, and greater visibility.
Filtering, iso surfaces, and results plane are useful for effectively displaying smoke visibility. In the following images, the darker regions correspond to lower values of smoke visibility, and are close to the burn source:
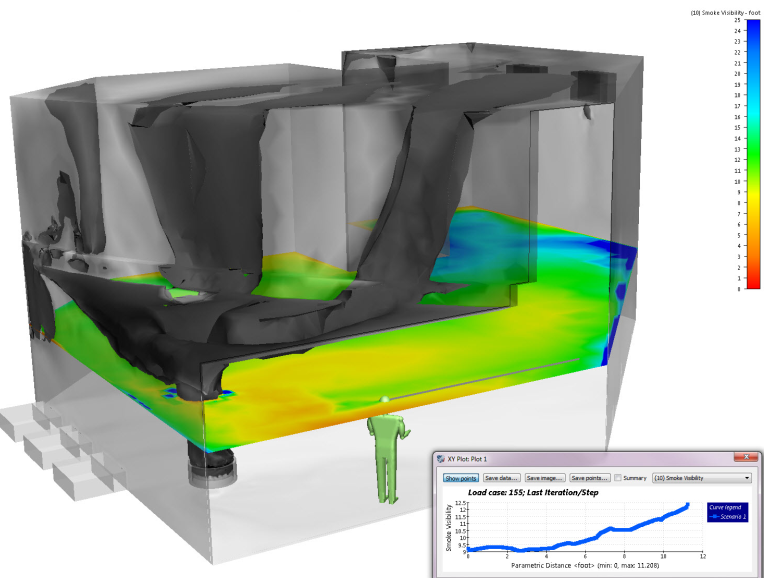
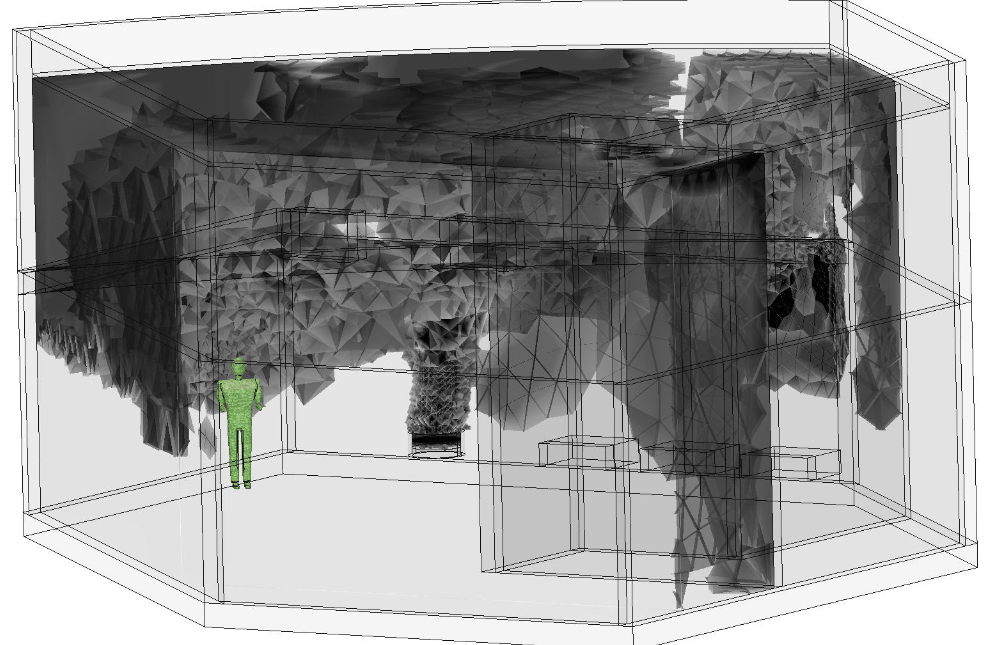
To view the mass concentration of the fuel, display Scalar as the output quantity.
References
Klote, J., J. Milke, Principles of Smoke Management, 2002