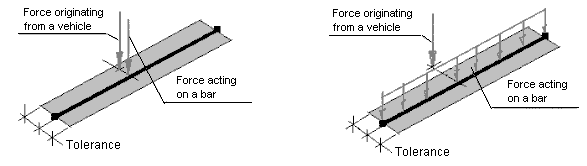
Moving load tolerance is a parameter assigned to a defined moving load analysis case.It determines the conditions for generating loads that originate from a vehicle, on bars. The tolerance defines the maximum distance from a bar, for which a concentrated force determined in a vehicle definition is applied directly to a bar without distributing the forces on the bars. (See the following images: the left image shows a force that falls within the range, which determines the maximum distance from a bar; however, on the right, a force applied beyond this range is shown and this force is being distributed on the structure bars.)
Introduction of the tolerance parameter resulted from problems which might have occurred when generating loads that originated from a vehicle on bar grillage. If a concentrated force originating from a vehicle was acting outside the grillage contour, it was not applied to the bars. This type of problem occurred particularly for arc bridge models with a curved vehicle route. This new parameter lets you increase the tolerance of generating forces acting on bars. The default parameter value is used according to the tolerance assumed for structure generation, that is,1.0 mm.
The Moment originated from force eccentricity option works for concentrated loads caused by a vehicle, applied to bars. It is not used for vehicle loads composed of linear or planar loads. It is of no significance, either, when applying loads to planar structures. When this option is selected, Robot generates a load of a concentrated force and concentrated moment from the force acting on the eccentricity.
This option is directly connected with the Tolerance parameter previously described. The moment originating from the eccentricity of F concentrated force is generated only if the concentrated force is positioned at a distance from a bar less than the assumed tolerance (TOL < e). The F concentrated force and the concentrated moment M = F*e are applied to a bar. (See the following image.)
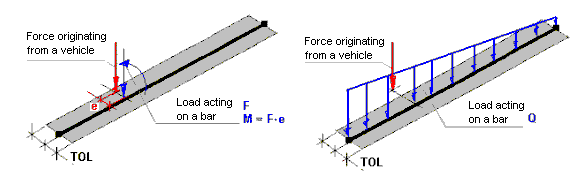
If a concentrated force is positioned at a distance greater than the tolerance assumed, then Robot uses a general algorithm of distributing a concentrated force acting on a bar in the form of a linear load without considering the moment originating from the force eccenticity. Moments originating from forces on eccentricity are generated for any direction of forces and eccentricity. In particular, Robot generates moments bending a bar caused by the forces acting along the bar.