A surface is a three-dimensional geometric representation of an area of land, or, in the case of volume surfaces, is a difference or composite between two surface areas.
Surfaces are made up of triangles or grids, which are created when AutoCAD Civil 3D connects the points that make up the surface data.
To use a surface in your drawing, you can create an empty surface and then add data to it. You can also import existing files containing surface information, such as LandXML, TIN , or DEM files.
Points or contours are usually a primary part of the original surface information and are supplemented with breaklines and boundaries.
Boundaries define the visible area of a surface. Only the area within the boundary is included in calculations, such as for total area and volume. You can also define masks to hide or show parts of a surface for editing or presentation purposes, while still including that area in calculations.
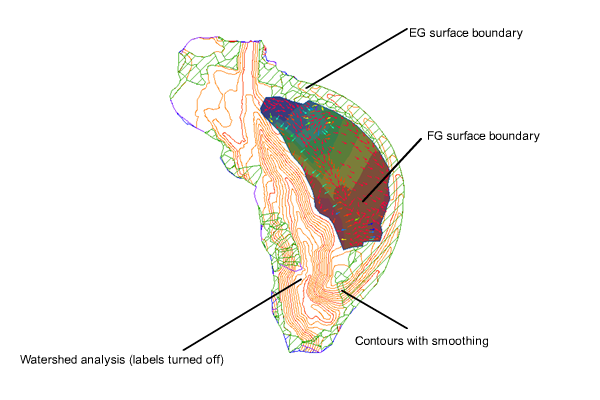
Surfaces displaying boundaries, contours, and level analysis
Breaklines are used on TIN surfaces to define linear features that triangles cannot cross, such as retaining walls or streams. Breaklines affect triangulation of the surface.
You can define different sets of contours, for example, for different intervals. Smoothing is provided for the surface object as a whole, which gives better results than simply smoothing the contours. In AutoCAD Civil 3D, the build process for surfaces is incremental. Whenever data is added or corrected, the surface is updated. Each surface has a definition list. This list contains all the operations performed on the surface. By turning the operations on and off, you can return a surface to a previous state or modify it to support different types of analysis.
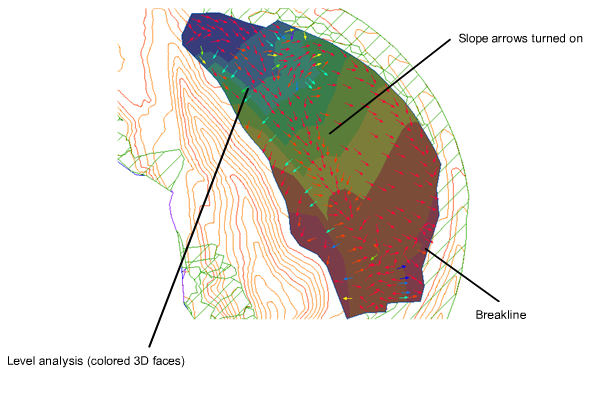
Surfaces displaying slope arrows level analysis