Styles control the display and design characteristics of drawing objects.
You can use styles to efficiently manage object appearance. When you create a new object, you can apply a predefined style for its display. Later, you can apply a different style. Also, you can create new styles to suit the needs of different users and different project stages. If you change a style definition, the changes are applied automatically to all objects using that style.
The object styles in AutoCAD Civil 3D have general attributes, such as object color, visibility of components, linetypes, and fill patterns.
Similarly, label styles work with text format, data content, location, and graphic elements, such as leader lines and Point Identification Boxes.
Within your design process, object and label styles should be created with specific purposes in mind, such as representing objects at different approval stages, or displaying the right information for different types of users. Before you create object styles, experiment with editing styles for different objects to learn the available controls.
Styles for each object type are managed on the ToolspaceSettings tab. The General collection contains styles that can be used by more than one object type (called Multipurpose styles) as well as shared label styles. All AutoCAD Civil 3D objects have a Basic style that can be used as is, or as the basis for building new styles. If you want to customize some attributes of a style, you can create a new style, or make changes to an existing style and save it with a new name. Groups of styles can be collected and saved as a drawing template (.dwt) file. All drawings created from a specific .dwt will share the same styles. The controls for creating styles are standardized as much as possible across all features to make the process easier.
For objects, you can add labels by using the Annotate tab to access the Add Labels dialog box or feature-specific label menus.
You can create sets of label styles for alignments, profiles, and sections in order to manage multiple labels easily. After the set is defined, it can be applied to or removed from an object in a single operation.
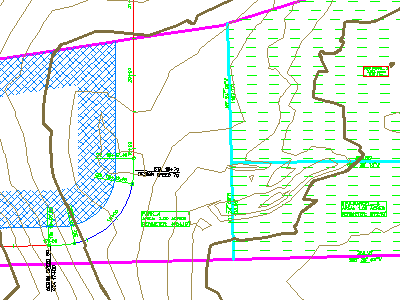
Object styles for a surface, plots, and an alignment, showing stylization
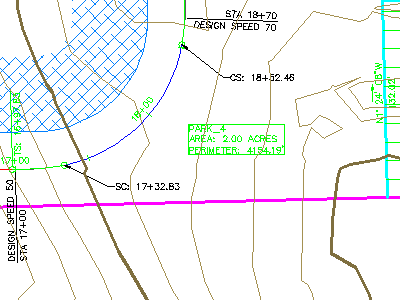
Label styles, including two alignment labels in a dragged state
Label Styles
Label styles are used to control and manage the display of labels and expressions for a class of objects.
Labels are associated with many objects, and their content is updated whenever the object itself is changed. Labels are also controlled by styles. You can modify the label styles in the same way that you modify the object styles: right-click a style name on the Toolspace Settings tab, and then click Edit.
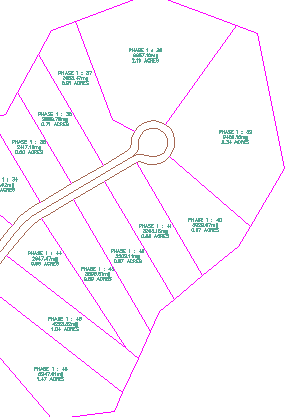
Plot area labels appear in the drawing as they appear in the preview of the Label Style Composer
You can create and save label sets for alignments, profiles, and sections, which allows you to apply multiple label types in one operation. For example, an alignment label set could include labels for major chainages, minor chainages, and geometry points.
Labels can include text, blocks, lines, ticks, and leaders. You can create labels and preview their appearance in the Label Style Composer dialog box, as shown in the following illustration:
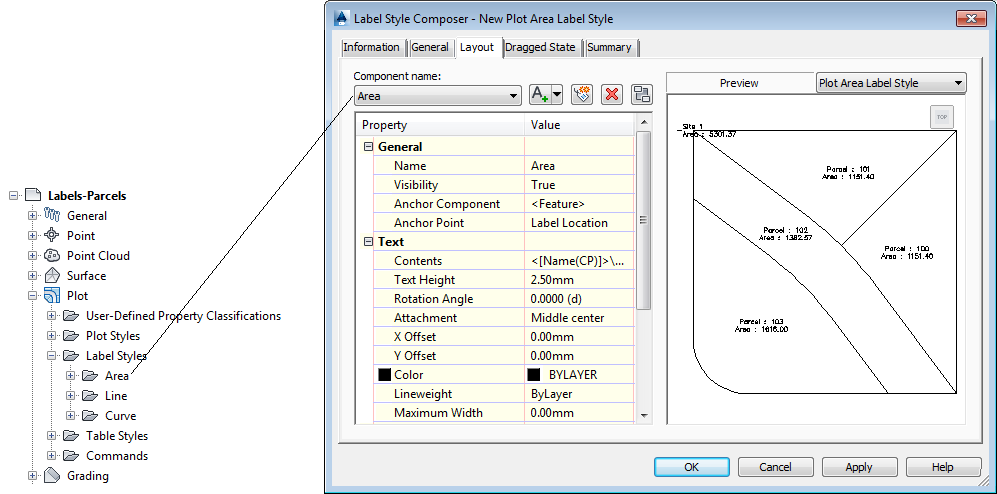
Previewing customized label style for plot area
The General Label Styles are used by lines, curves, feature lines, and corridors. This collection also contains Note label styles, which are not specific to an object.
For information about managing label styles, see Label Styles.
Table Styles
Table Styles are used to control and manage the display for the tables associated with a class of objects.
AutoCAD Civil 3D provides automated data tables for points, surfaces, plots, alignments, and quantity takeoff. As shown in the following illustration, these tables provide a concise display of object data as an alternative to using object labels. The table styles control the data properties and the displayed components of the table.
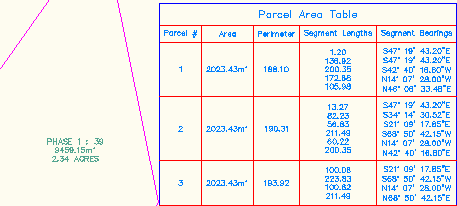
Example data table for plots
Data properties include the data format, order of columns, text style, and whether the table title and column headers are repeated if the table is split. Display components include the borders, separators, fill, and text. You can control the visibility, color, linetype, and scale of each component.