The 13th user material constant is used to define the response of the composite after a fiber failure when instantaneous degradation is used. Specifically, this value is a fraction used to define the damaged elastic moduli of the fiber constituent after fiber constituent failure occurs
The fiber post-failure stiffness is a fraction used to define the damaged elastic moduli of the fiber constituent after fiber constituent failure occurs. Specifically, it is the ratio of the failed fiber constituent moduli to the unfailed fiber constituent moduli. For unidirectional materials, a value of 0.01 would specify that after a fiber failure occurs at a particular integration point, all six of the fiber constituent moduli ( 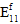 ,
,  ,
, 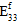 ,
, 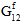 ,
, 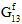 ,
, 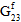 ) are reduced to 1% of the original undamaged fiber constituent moduli at the integration point in question. For woven materials, a value of 0.01 would specify that after a fiber failure occurs at a particular integration point, three of the fiber constituent moduli (
) are reduced to 1% of the original undamaged fiber constituent moduli at the integration point in question. For woven materials, a value of 0.01 would specify that after a fiber failure occurs at a particular integration point, three of the fiber constituent moduli ( 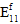 ,
, 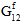 ,
, 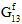 ) are reduced to 1% of the original undamaged fiber constituent moduli at the integration point in question. The fiber post-failure stiffness value must be greater than 0, and less than or equal to 1.
) are reduced to 1% of the original undamaged fiber constituent moduli at the integration point in question. The fiber post-failure stiffness value must be greater than 0, and less than or equal to 1.
The value of the 13th user material constant can have a pronounced effect on the predicted progressive failure response of a multilayer composite structure since this constant is largely responsible for the rate at which local loads are redistributed after a localized fiber constituent failure occurs. Consequently, as the value of the thirteenth user material constant is reduced from 1.0 toward 0.0, a local fiber failure is more likely to precipitate a cascade of localized fiber failures. Depending upon the magnitude of the fiber failure cascade, the result may be discernible as a noticeable softening of the overall structural response, or it may cascade without arresting and result in a global structural failure.