Duplicates one or more objects and places the copies at equal distances along one or more curves, creating "stitch patterns".
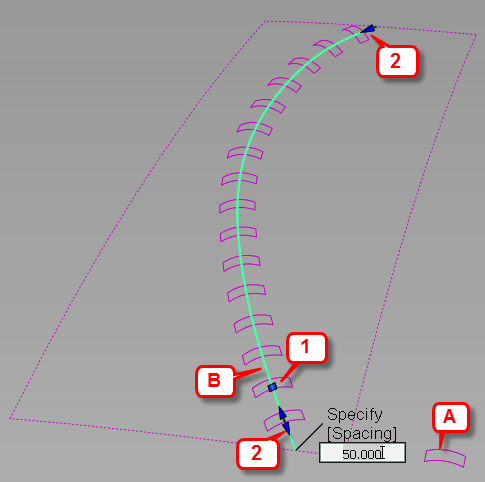
A: Stitch object. B: Target curve. 1: Spacing manipulator. 2. Range (Start/End) manipulators.
Through the option window and manipulators, you control the spacing, range, position, and orientation of the duplicates.
Create and place duplicates (stitch pattern)
- Choose Transform > Path Array


- Select the stitch objects. They can be curves, surfaces, or meshes.
- Click the Build button in the lower right corner of the view window.
- Select the target curves. They can be free curves, curves-on-surface, surface edges, trim edges, or isoparms (including precision lines).
- Duplicates of the stitch objects appear along the length of the curves. The pivot points of the duplicates are placed along the curves and used to calculate spacing.
- Range arrow manipulators appear at the start and end of the last target curve.
- A Spacing/Number manipulator also appears, with a Specify label that you can click to toggle between Spacing and Number adjustments. Clicking the numerical value below the label lets you enter an exact value.
- Modify the spacing, range, and orientation of the duplicates through the control options. You can also use the manipulators to modify the spacing and range directly on the model.
The duplicate objects have history and update as the options are modified.
Note: Only duplicates along the last selected target curve are affected. - Select additional target curves if desired.
Set the range, spacing or number of duplicates with the manipulators
Some of the options in the control window have a corresponding manipulator on the model.
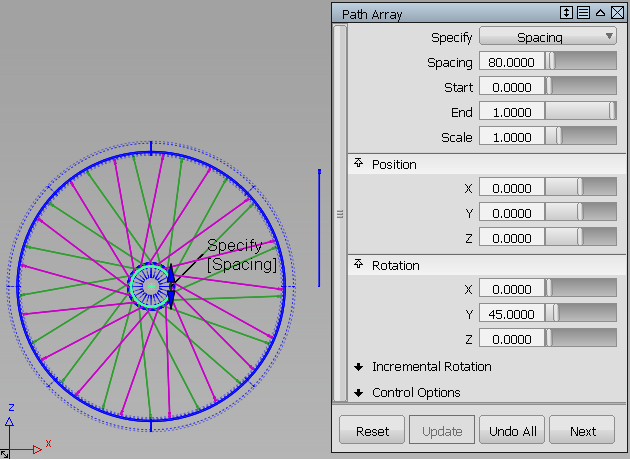
An example
In the following image, a spoke (two surfaces, shown to the right of the bicycle wheel) is duplicated and placed along a circular path curve (inner rim). The operation is repeated twice to create two sets of spokes: one rotated by 45 degrees around Y (in pink), and the other rotated by 315 degrees around Y (in green).