Save time and control the drawing size by inserting references to a set of objects that have been combined to form a block.
How Blocks are Stored and Referenced
A block is one or more objects combined to create a single, named object. Whenever you create a block or insert a drawing as a block, all block information (including geometry, layers, colors, and linetypes) is stored in a behind-the-scenes table of definitions. Every block you insert is actually a reference to a block definition.
The following illustration shows a progression from an empty drawing, through creation of a block definition, to insertion of two block references in the drawing. (The second image represents a block definition that is saved in the block table, even though the geometry was removed from the drawing area as it was saved.)
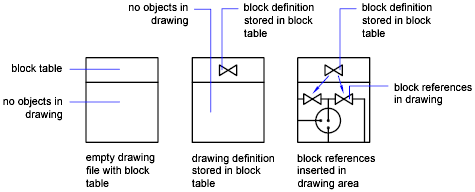
- If you redefine a block definition, all references in that drawing are updated automatically.
- You help control the drawing size by inserting references instead of object geometry.
You remove a block reference by erasing it. However, the corresponding block definition remains. To reduce the size of a drawing, you must also remove any unused block definitions by purging them.
Block Insertion Methods
A block can be composed of objects drawn on several layers with various colors, linetypes, and lineweight properties. Although a block is always inserted on the current layer, the block reference preserves information about the original layer, color, and linetype properties of the objects that are contained in the block. The layer on which you create the drawing objects and certain property settings affect whether objects in an inserted block retain their original properties or inherit properties from the current layer, color, linetype, or lineweight settings.
When you insert a block, you create a block reference and specify its location, scale, and rotation. Several insertion methods are available:
-
Block reference in the current drawing is inserted in the same drawing.
When you create a block, its definition is automatically saved in the block table and is available for referencing. You specify whether the original geometry remains, is converted to a block, or is removed from the drawing area.
-
Drawing file is inserted as a block.
When you insert one drawing file into another drawing, the information from the inserted drawing is saved as a block definition in the block table of the destination drawing. Subsequent references to that block definition can display different position, scale, and rotation settings, as shown in the following illustration.
Xrefs (external references) in a drawing you insert may not be displayed properly unless the xref was previously inserted or attached to the destination drawing.
-
Block is inserted from a tool palette.
You can insert blocks from tool palettes by dragging the block tool into the drawing or by clicking the block tool and then specifying an insertion point.
When a block is dragged from a tool palette into a drawing, it is scaled automatically according to the ratio of units defined in the drawing to units defined in block. For example, if the unit of measurement is meters in the destination drawing and centimeters in the block, the block is inserted at 1/100 scale.
-
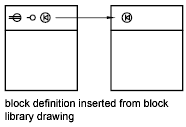
Block is inserted from a block library.
A block library is a drawing that typically contains block definitions of symbols with similar functions, which are stored together for easy accessibility and management. You can insert block definitions from a block library into your current drawing file.
-
Block is inserted from DesignCenter.
DesignCenter offers a quick, visual way to drag and drop blocks within the current drawing or from another drawing. Double-click the block names to specify the precise location, rotation, and scale of the blocks.
-
Block is inserted from the Insert drop-down.
All blocks in your drawing are automatically added in the Insert drop-down and are available for easy insertion. The blocks are saved in the current drawing.