3D spherical coordinates specify a location by a distance from the UCS origin, an angle from the X axis in the XY plane, and an angle from the XY plane.
Spherical coordinate entry in 3D is similar to polar coordinate entry in 2D. You specify a point using th efollowing syntax:
X < angle from X axis < angle from XY plane
In the following illustration, 8<60<30 indicates a point 8 units from the origin of the current UCS in the XY plane, 60 degrees from the X axis in the XY plane, and 30 degrees up the Z axis from the XY plane. 5<45<15 indicates a point 5 units from the origin, 45 degrees from the X axis in the XY plane, and 15 degrees up from the XY plane.
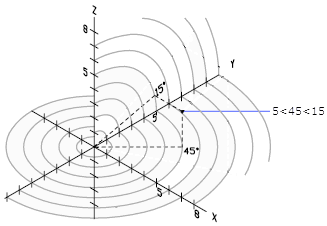
Absolute and Relative Spherical Coordinates
As with 2D coordinates, you can enter absolute coordinates, which are based on the origin, or you can enter relative coordinates, which are based on the last point entered.
To enter relative coordinates, use the @ sign as a prefix. For example, @4<45,30 specifies a point 4 units from the previous point, at an angle of 45 degrees from the positive X axis in the XY plane, and at an angle of 30 degrees from the XY plane.