Access
Ribbon:
Sketch tab
 Constrain Panel
Constrain Panel
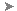 Constraint Settings: Relax Mode tab
Constraint Settings: Relax Mode tab
![]()
 Options
Options Sketch tab: Constraint Settings: Relax Mode tab
Sketch tab: Constraint Settings: Relax Mode tab
Enable Relax Mode
Sets the default behavior for Relax Mode.
 or by pressing F11 in the 2D sketch environment.
or by pressing F11 in the 2D sketch environment. For more information refer to Relax Mode
Constraints to remove in relax dragging
Lists the constraint glyphs to show or hide.
- Select All
-
Places a check mark in each active check box.
- Clear All
-
Removes all check marks. No constraint glyphs are shown.
The following lists the constraint types and their definitions:
 Perpendicular
Perpendicular -
Causes selected linear geometry to lie at right angles to each other. Linear geometry includes lines, ellipse axes, spline handles, text edges, and imported images.
 Tangent
Tangent -
Causes curves, including ends of a spline, to be tangent to other curves. One curve can be tangent to another even if they do not physically share a point.
 Coincident
Coincident -
Causes two points to be constrained together, or causes one point to lie on a curve. In a 3D sketch, can also cause points and lines to be constrained to surfaces.
-
 The yellow coincident dot represents the presence of the constraint. To show the coincident constraint glyphs, hover over the coincident dot.
The yellow coincident dot represents the presence of the constraint. To show the coincident constraint glyphs, hover over the coincident dot. -
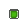 The green coincident dot means the Coincident constraints are checked on to remove in relax dragging in Relax Mode.
The green coincident dot means the Coincident constraints are checked on to remove in relax dragging in Relax Mode.  Collinear
Collinear -
Causes selected linear geometry to lie on the same line. In addition to lines, this includes ellipse axes, spline handles, text edges, and imported images.
 Horizontal
Horizontal -
(2D sketch only) Causes selected linear geometry or pairs of points to lie parallel to the X axis of the sketch coordinate system. In addition to lines and pairs of points, this includes ellipse axes, spline handles, text edges, and imported images.
 Parallel
Parallel -
Causes selected linear geometry to lie parallel to each other. In addition to lines, this includes ellipse axes, spline handles, text edges, and imported images. In a 3D sketch, the parallel constraint is parallel to X, Y, or Z part axes unless you manually constrain to selected geometry.
 Smooth (G2)
Smooth (G2) -
Causes a continuous curvature between a spline and another line, arc, or spline.
 Concentric
Concentric -
(2D sketch only) Causes two arcs, circles, or ellipses to have the same center point.
 Equal
Equal -
(2D sketch only) Causes selected arcs and circles to resize to the same radius or selected lines to resize to the same length.
 Vertical
Vertical -
(2D sketch only) Causes selected linear geometry or pairs of points to lie parallel to the Y axis of the coordinate system. In addition to lines or pairs of points, this includes ellipse axes, spline handles, text edges, and imported images.
 Symmetric
Symmetric -
(2D sketch only) Causes selected lines or curves to become proportionally constrained around a selected line. Segments constrained to the selected geometry also reorient when the constraint is applied.
 Fix
Fix -
Causes points and curves to be placed in a stable position relative to the sketch coordinate system. If the sketch coordinate system moves or rotates, fixed curves or points move or rotate with it.
Preserve dimensions with equations
Select this option to prevent the dimension from changing when you drag a line that is controlled by an equation.