Transform node
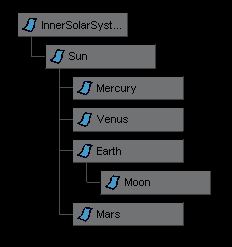
A node that contains an object’s transformation attributes—values for its translation, rotation, scale, and so on. It also holds information on parent-child relationships it has with other nodes. InnerSolarSystem, Sun, Moon, and all other boxes shown in the example are transform nodes.
Shape nodes
Holds an object’s geometry attributes or attributes other than the object’s transform node attributes. A shape node is the child of a transform node. A transform node has only one shape node.
Auxiliary nodes
There are several nodes, such as unitConversion, which are hidden to reduce clutter in the editors. They are not normally useful to see or edit; however, if you need to you can show these nodes. (You can also hide nodes that are normally shown if you want to further reduce clutter.)
Hidden nodes
Any object hidden using Display > Hide. Maya hides the default cameras (top, front, side, and persp) by default.
Underworld nodes
A pair of nodes below a shape node. When you create a curve-on-surface, Maya creates an underworld transform node and shape node for the curve-on-surface below the surface’s shape node. The CV positions of underworld nodes have UV coordinates on the surface rather than coordinates in world or local space.
Rendering nodes
Materials and textures each have nodes containing attributes that control their look. Texture placement nodes have attributes that control how a texture is fitted onto a surface.
Lights are of course nodes too, with attributes controlling their properties.
Utility nodes
Utility nodes provide extra functions you can use for example in a shader network, or a character rig. For example, multiply/divide nodes let you alter inputs and outputs between other nodes.
Script nodes
Script nodes are a way of storing a MEL script in a Maya scene file:
You can set a script node to execute its “payload” in response to various events:
- When the node is read from a file.
- Before or after rendering a frame.
- Before or after rendering an animation.
- When a file is closed or de-referenced.