Use this tool to sculpt NURBS, polygons, and subdivision surfaces.
Mesh Tools > Sculpt Geometry Tool > 
Lets you specify the settings for the Sculpt Geometry Tool in the Tool Settings editor. There are attributes unique to the Sculpt Geometry Tool in the Sculpt Parameters sections. These unique attributes are described below.
Sculpt Parameters
These are descriptions of the attributes in the Sculpt Parameters section.
- Operation
-
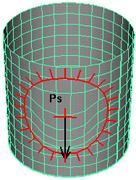
Select Push, Pull, Smooth, Relax, Pinch, Slide or Erase. A letter appears within the brush stamp to reflect the operation: Ps (Push), Pl (Pull), Sm (Smooth), Re (Relax), Pn (Pinch), Sl (Slide) or E (Erase).
To remove the letters from the brush stamp, open the Sculpt Surface Tool Settings window, click the Display section, and turn off Draw Brush Feedback.
When the Operation is set to Smooth, the Max Displacement and Reference Vector (X, Y, Z) options are respected. That is, the smoothing will be constrained based on what Reference Vector option is set and limited by the Max Displacement value.
Tip:To select a brush operation from a marking menu, press your keyboard’s u key while dragging the mouse.
- Auto smooth
-
When Auto Smooth is turned on, the surface is automatically smoothed for every brush stroke when using either the Push or Pull sculpting operations. The amount of smoothing is based on the Smooth Strength value. The Auto Smooth option is only available when either the Push or Pull sculpting operations are selected.
- Smooth strength
-
Specifies the amount of smoothing the Sculpt Surface Tool applies to the surface for each Push, Pull, or Smooth stroke you perform. The Smooth Strength value ranges from 1 to 10. The higher the Smooth Strength value entered, the more smoothing takes place for each brush stroke.
- Brush strength
-
Determines how much the selected Sculpt Surface Tool affects the surface for each stroke you perform. The Brush strength value ranges from 1 to 100. The higher the value entered, the more influence the tool has on each brush stroke. This option is only available when the Pinch of Slide sculpting operation is selected.
- Reference vector
-
In the Sculpt Parameters section, select the Reference Vector. The Reference Vector controls the direction the vertices move when you push or pull. The brush arrow represents the reference vector.
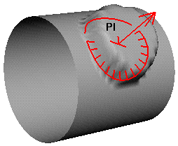
- Normal
-
The vertices move in the direction of the surface normal.
- First normal
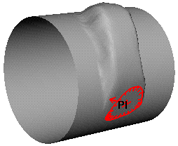
-
The vertices move in the direction established by the surface normal at the beginning of the stroke.
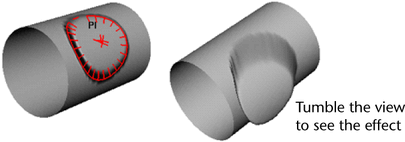
- View
-
The vertices move parallel to the camera view direction.
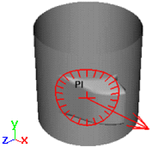
- X Axis
-
The vertices move in the direction of the X axis only. They do not move along the Y or Z axis.
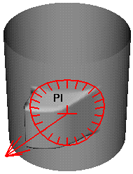
- Y Axis
-
The vertices move in the direction of the Y axis only. They do not move along the X or Z axis.
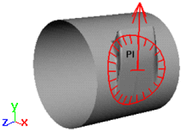
- Z Axis
-
The vertices move in the direction of the Z axis only. They do not move along the X or Y axis.
- U
-
U moves CVs in the direction of the U isoparm when sculpting NURBS surfaces.
- V
-
V moves CVs in the direction of the V isoparm when sculpting NURBS surfaces.
 Tip:
Tip:To avoid overlapping isoparms when you sculpt along the U or V isoparms of NURBS surfaces, use a softer brush shape and keep the displacement small.
- Max displacement
-
Type the maximum possible depth or height of the brush stroke, or use the slider to select it. (The actual displacement of the brush stroke is based on how hard you press with the stylus and on the Opacity value.)
- Seam/Pole tolerance
-
Set how close the vertices must be along an edge, and how close the edges on the same surface must be to each other before they are detected as common. This is most commonly used to detect poles on surfaces like spheres.
- Flood
-
Applies the Operation to all selected control vertices.
- When Operation is Push or Pull, Flood applies the maximum displacement to all selected control vertices.
- When Operation is Smooth, Flood smooths all selected control vertices.
- When Operation is Erase, selected control vertices are restored to their last saved state.
Reference Surface
Turn the following on or off:
- Update on each stroke
-
To “bake” or update the surface automatically on each stroke, turn on Update on each Stroke. For a description of reference surfaces, see Reference surface. To update the reference surface manually, click Update.
Tip: Turn Update on each stroke off when Operation is Slide.
Erase Surface
Turn the following on or off:
- Update on each stroke
-
To update the erase surface automatically on each stroke, turn on Erase Surface > Update on each Stroke. To update the erase surface manually, click Update.