The Cross-WLF viscosity model describes the temperature, shear rate, and pressure dependency of the viscosity.
The viscosity model is given by the following equation: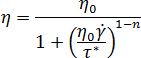
where:
-
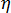 is the melt viscosity (Pa s)
is the melt viscosity (Pa s) 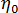 is the zero shear viscosity or the 'Newtonian limit' in which the viscosity approaches a constant at very low shear rates,
is the zero shear viscosity or the 'Newtonian limit' in which the viscosity approaches a constant at very low shear rates, 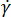 is the shear rate (1/s)
is the shear rate (1/s) 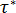 is the critical stress level at the transition to shear thinning, determined by curve fitting, and
is the critical stress level at the transition to shear thinning, determined by curve fitting, and 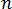 is the power law index in the high shear rate regime, determined by curve fitting.
is the power law index in the high shear rate regime, determined by curve fitting.
The zero shear viscosity is given by the equation: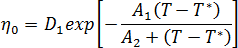
where
-
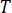 is the temperature (K)
is the temperature (K) 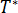 is the glass transition temperature, determined by curve fitting,
is the glass transition temperature, determined by curve fitting, -
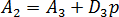
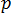 is the pressure (Pa), and where
is the pressure (Pa), and where-
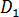 ,
, 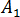 ,
, 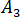 , and
, and 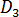 are data-fitted coefficients.
are data-fitted coefficients.
The glass transition temperature is given by the equation: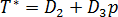
where 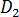 is a data-fitted coefficient.
is a data-fitted coefficient.