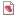
Poisson's ratios (3D fiber) are mechanical property values that indicate strain in a specific direction, caused by stress from another direction. These results are used in a subsequent Stress analysis.
- Overmolding Pack
Poisson's ratio (v12) (3D fiber) (overmolding) result
The Poisson's ratio (v12) (3D fiber) (overmolding) result indicates the strain in the second principal direction for the overmolded component, caused by stress in the first principal direction. This result is recorded for each tetrahedral element in the model, at the end of the analysis.
In general, vi,j=Poisson's ratio for transverse strain in the j-direction when stressed in the i-direction.
Poisson's ratio (v13) (3D fiber) (overmolding) result
The Poisson's ratio (v13) (3D fiber) (overmolding) result indicates the strain in the third principal direction for the overmolded component, caused by stress in the first principal direction. This result is recorded for each tetrahedral element in the model, at the end of the analysis.
In general, vi,j=Poisson's ratio for transverse strain in the j-direction when stressed in the i-direction.
Poisson's ratio (V23) (3D fiber) (overmolding) result
The Poisson's ratio (v23) (overmolding) result indicates the strain in the third principal direction for the overmolded component, caused by stress in the second principal direction. This result is recorded for each tetrahedral element in the model, at the end of the analysis.
In general, vi,j=Poisson's ratio for transverse strain in the j-direction when stressed in the i-direction.
Orthotropic assumption
The thermo-mechanical property calculation for fiber-filled composites is based on the orthotropic assumption, that fiber-filled material properties are different in three orthogonal principal directions. Under this assumption, there are 9 independent mechanical constants and three independent thermal expansion coefficients.
Using this result
These results are recorded for each tetrahedral element in the model at the end of the analysis and are used in the thermal loading calculation of subsequent Stress analyses.