In a Stress analysis, a load, or force, can be applied to the part, and the resulting deflections are measured. Volume loading can be used to simulate the effects of gravity in a Stress analysis.
Volume loading
You can apply a uniform load to selected elements in the model, expressed as a volume load (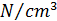 or
or 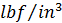 ). You need to specify the magnitude of the volume load and the direction in which it acts (only global directions supported).
). You need to specify the magnitude of the volume load and the direction in which it acts (only global directions supported).
The volume load, 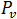 , is given by the following equation:
, is given by the following equation:
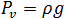
where
-
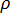 is the material density.
is the material density. -
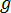 is the gravitational constant.
is the gravitational constant.
Density, in units of 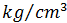 , multiplied by the gravitational constant in units of
, multiplied by the gravitational constant in units of 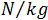 , gives the volume load in units of
, gives the volume load in units of 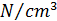 , as is required by this function.
, as is required by this function.
For example: A material with a density of 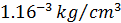 would experience a volume load of
would experience a volume load of 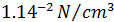 due to the effect of gravity (
due to the effect of gravity (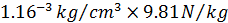 ).
).