In the Change of analysis type dialog, select Buckling, and click OK, or select a Buckling analysis case in the Calculation options dialog and click Parameters to open the Buckling Analysis Parameters dialog. This defines buckling analysis parameters for a load case defined for a structure.
The problem of linear buckling analysis of a structure is formulated and solved through the problem of eigenvalues. For each required buckling mode, critical load coefficients (eigenvalues) and eigenvectors are determined.
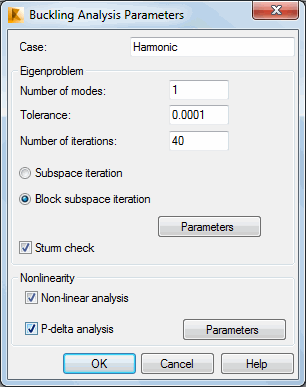
In the Buckling Analysis Parameters dialog, the following parameters are defined.
- Case - The name of a load case.
- Number of modes - The number of required buckling modes.
- Tolerance - Value of tolerance that is to be achieved during iterative analysis of a structure. The default value is 0.0001.
- Number of iterations - The maximum number of iterations. If exceeded and the required tolerance has not been achieved, calculations of the structure are stopped. The default value is 40.
- The methods of solving the problem (subspace iteration or block subspace iteration methods).The Parameters button (shift, increment) is available if Block subspace iteration method is selected.
- Sturm check - Toggles the algorithm that finds the skipped vibration modes of a structure. If the algorithm identifies a skipped vibration mode, the iterative calculations are repeated.
It is recommended to select the ICCF method (non-multilevel (single-level) or multilevel method). In case of the iterative solver the parameters other than Number of Modes, Tolerance, and Number of Iterations are disregarded.
See also: