Analysis Characteristics
- Steady-state
- axisymmetric
- 2D internal
- Turbulent
- Compressible
- Adiabatic
Reference
White, F.M., Fluid Mechanics, McGraw-Hill, New York, 1979
Problem Description
Compressible flow through a converging-diverging nozzle is a classic fluid mechanics problem. For ideal flow (no friction), shockless and choked conditions, there are analytical expressions for determining the exit Mach number, pressure and temperature.
For this verification analysis, the inlet conditions are set so that the flow is choked and the Mach number at the throat is 1.0 for ideal flow conditions. Friction is included in the analysis, so the interaction between the boundary layer and the supersonic flow in the diverging portion is apparent.
Outlet conditions predicted by Autodesk Simulation CFD are compared to values predicted using ideal flow theory.
Geometry and Boundary Conditions
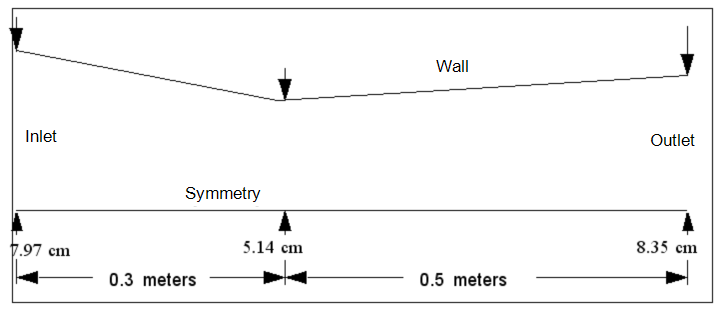
- Outlet Area to Throat Area Ratio = 2.64
- Inlet Area to Throat Area Ratio = 2.40
- Inlet Conditions: u = 111.5 m/s, p= 90.183 kPa - gage (Ma = 0.25)
- Stagnation temperature = 500 K
- Outlet Conditions: unknown
Results
Comparison of exit conditions:
| Benchmark | 2014: Build 20130102 | % Error | 2015: Build 20131223 | % Error | |
| Exit Mach Number | 2.5 | 2.484 | 0.621 | 2.483 | 0.656 |
| Exit Velocity | 747 m/s | 745.03 | 0.264 | 744.91 | 0.280 |
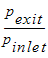
|
0.061 | 0.0691 | 13.22 | 0.06907 | 13.23 |