Dans le logiciel Robot, la définition de la position du centre de gravité et du centre géométrique de la structure se fait comme suit :
Centre géométrique
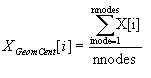 i = x,y,z
i = x,y,z
Centre de gravité
- Pour une structure 3D :
La charge permanente agit dans la direction Z
Xc[0] = Somme(My(0,0,0))/Somme(Pz)
La charge permanente agit dans la direction Z
Xc[1] = -Somme(Mx(0,0,0))/Somme(Pz)
La charge permanente agit dans la direction X
XC [2] = -Somme(My (0,0,0)) /Somme(px)
- Pour les plaques et grillages :
La charge permanente agit dans la direction Z
Xc[0] = Somme(My(0,0,0))/Somme(Pz)
La charge permanente agit dans la direction Z
Xc[1] = -Somme(Mx(0,0,0))/Somme(Pz)
Xc[2] = 0
- Pour les images et les treillis 2D ainsi que pour les structures de contrainte plane/de déformations :
La charge permanente agit dans la direction Z
Xc[0] = Somme(My(0,0,0))/Somme(Pz)
XC [1] = 0
La charge permanente agit dans la direction X
XC [2] = -Somme(My (0,0,0)) /Somme(px)
- Pour les structures axisymétriques :
La charge permanente agit dans la direction Y
XC [0] = 0
XC [1] = 0
La charge permanente agit dans la direction X
XC [2] = -Somme(My (0,0,0)) /Somme(px)