AreaReinforcement と PathReinforcement
AreaReinforcementCurves を表す ElementId の IList を返す GetBoundaryCurveIds()メソッドを呼び出して、AreaReinforcement の AreaReinforcementCurves を検索します。
オーバーロードされた AreaReinforcement.Create()メソッドには、ホスト境界または曲線の配列複写に基づいた、新しい AreaReinforcement を作成するための 2 つの方法があります。面に配筋の主筋方向は、オーバーロードされた Create()メソッドのいずれかを使用して新しい AreaReinforcement を作成するときに設定できますが、AreaReinforcment.Direction プロパティは読み込み専用です。
|
コード領域 29-3: 面に配筋を作成 |
AreaReinforcement CreateAreaReinforcementInWall(Wall wall, Autodesk.Revit.DB.Document document)
{
// Get the wall analytical profile whose curves will define the boundary of the the area reinforcement
AnalyticalModel analytical = wall.GetAnalyticalModel() as AnalyticalModel;
if (null == analytical)
{
throw new Exception("Can't get AnalyticalModel from the selected wall");
}
IList<Curve> curves = analytical.GetCurves(AnalyticalCurveType.ActiveCurves);
//define the Major Direction of AreaReinforcement,
//we get direction of first Line on the Wall as the Major Direction
Line firstLine = (Line)(curves[0]);
XYZ majorDirection = new XYZ(
firstLine.GetEndPoint(1).X - firstLine.GetEndPoint(0).X,
firstLine.GetEndPoint(1).Y - firstLine.GetEndPoint(0).Y,
firstLine.GetEndPoint(1).Z - firstLine.GetEndPoint(0).Z);
// Obtain the default types
ElementId defaultRebarBarTypeId = document.GetDefaultElementTypeId(ElementTypeGroup.RebarBarType);
ElementId defaultAreaReinforcementTypeId = document.GetDefaultElementTypeId(ElementTypeGroup.AreaReinforcementType);
ElementId defaultHookTypeId = ElementId.InvalidElementId;
// Create the area reinforcement
AreaReinforcement rein = AreaReinforcement.Create(document, wall, curves, majorDirection, defaultAreaReinforcementTypeId, defaultRebarBarTypeId, defaultHookTypeId);
return rein;
}
|
AreaReinforcement.GetBoundaryCurveIds()メソッドは、AreaReinforcementCurves を表す ElementId のセットを返します。これには Curve を返すプロパティがありますが、PathReinforcement.GetCurveElementIds()メソッドは、ModelCurves を表す ElementId の集合を返します。PathReinforcement.Create()メソッドを使用して作成する以外の方法では、PathReinforcement をフリップすることはできません。PathReinforcment は曲線の配列複写を使用することでのみ作成できます。
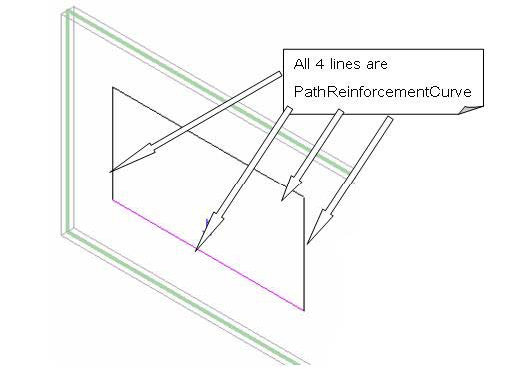
図 155: 編集モードの PathReinforcement ModelCurves
|
コード領域 29-4: パス配筋を作成 |
PathReinforcement CreatePathReinforcement(Autodesk.Revit.DB.Document document, Wall wall)
{
// Create a geometry line in the selected wall as the path
List<Curve> curves = new List<Curve>();
LocationCurve location = wall.Location as LocationCurve;
XYZ start = location.Curve.GetEndPoint(0);
XYZ end = location.Curve.GetEndPoint(1);
curves.Add(Line.CreateBound(start, end));
// Obtain the default types
ElementId defaultRebarBarTypeId = document.GetDefaultElementTypeId(ElementTypeGroup.RebarBarType);
ElementId defaultPathReinforcementTypeId = document.GetDefaultElementTypeId(ElementTypeGroup.PathReinforcementType);
ElementId defaultHookTypeId = ElementId.InvalidElementId;
// Begin to create the path reinforcement
PathReinforcement rein = PathReinforcement.Create(document, wall, curves, true, defaultPathReinforcementTypeId, defaultRebarBarTypeId, defaultHookTypeId, defaultHookTypeId);
if (null == rein)
{
throw new Exception("Create path reinforcement failed.");
}
// Give the user some information
TaskDialog.Show("Revit","Create path reinforcement succeed.");
return rein;
}
|
要素のジオメトリの取得の詳細は、「ジオメトリ」を参照してください。
[面に配筋とパス配筋]に関連するプロジェクト全体の設定は、ReinforcementSettings クラスからアクセスできます。鉄筋
Rebar クラスは、コンクリート梁、柱、スラブ、基礎などの適した要素を補強するために使用する鉄筋を表します。
3 つの静的な Rebar メソッドのいずれかを使用して、鉄筋オブジェクトを作成できます。
|
名前 |
説明 |
public static Rebar Rebar.CreateFromCurves(
Document doc,
RebarStyle style,
RebarBarType rebarType,
RebarHookType startHook,
RebarHookType endHook,
Element host,
XYZ norm,
IList<Curve> curves,
RebarHookOrientation startHookOrient,
RebarHookOrientation endHookOrient,
bool useExistingShapeIfPossible,
bool createNewShape
);
|
プロジェクトの鉄筋要素の新しいインスタンスを作成します。すべての曲線は法線と基準点によって定義された平面に属している必要があります。 |
public static Rebar Rebar.CreateFromRebarShape(
Document doc,
RebarShape rebarShape,
RebarBarType rebarType,
Element host,
XYZ origin,
XYZ xVec,
XYZ yVec
);
|
RebarShape のインスタンスとして、新しい Rebar を作成します。このインスタンスには、RebarShape からの既定の形状パラメータがあり、その位置はシェイプ定義のシェイプの境界ボックスに基づいています。フックは境界ボックスを計算する前に、シェイプから削除されます。適切なフックがドキュメントで見つからない場合は、任意に割り当てられます。 |
public static Rebar Rebar.CreateFromCurvesAndShape(
Document doc,
RebarShape rebarShape,
RebarBarType rebarType,
RebarHookType startHook,
RebarHookType endHook,
Element host,
XYZ norm,
IList<Curve> curves,
RebarHookOrientation startHookOrient,
RebarHookOrientation endHookOrient
);
|
プロジェクトの鉄筋要素の新しいインスタンスを作成します。このインスタンスには、RebarShape からの既定の形状パラメータがあります。すべての曲線は法線と基準点によって定義された平面に属している必要があります。 |
最初のバージョンは、鉄筋を記述する曲線の配列から鉄筋を作成し、2 番目のバージョンは、RebarShape と位置に基づいて Rebar オブジェクトを作成します。3 番目のバージョンは、RebarShape に基づいて曲線の配列から鉄筋を作成します。
CreateFromCurves()または CreateFromCurvesAndShape()メソッドを使用している場合は、パラメータ RebarHookType がドキュメントの RebarBarTypes および RebarHookTypes プロパティで使用できます。
次のコードでは、特定のレイアウトで鉄筋を作成する方法を示します。
|
コード領域 29-8: 特定のレイアウトで鉄筋を作成 |
Rebar CreateRebar(Autodesk.Revit.DB.Document document, FamilyInstance column, RebarBarType barType, RebarHookType hookType)
{
// Define the rebar geometry information - Line rebar
LocationPoint location = column.Location as LocationPoint;
XYZ origin = location.Point;
XYZ normal = new XYZ(1, 0, 0);
// create rebar 9' long
XYZ rebarLineEnd = new XYZ(origin.X, origin.Y, origin.Z + 9);
Line rebarLine = Line.CreateBound(origin, rebarLineEnd);
// Create the line rebar
IList<Curve> curves = new List<Curve>();
curves.Add(rebarLine);
Rebar rebar = Rebar.CreateFromCurves(document, Autodesk.Revit.DB.Structure.RebarStyle.Standard, barType, hookType, hookType,
column, origin, curves, RebarHookOrientation.Right, RebarHookOrientation.Left, true, true);
if (null != rebar)
{
// set specific layout for new rebar as fixed number, with 10 bars, distribution path length of 1.5'
// with bars of the bar set on the same side of the rebar plane as indicated by normal
// and both first and last bar in the set are shown
rebar.SetLayoutAsFixedNumber(10, 1.5, true, true, true);
}
return rebar;
}
|
次の表は、パラメータ REBAR_ELEM_LAYOUT_RULE の整数値の一覧です。
表 59: 鉄筋レイアウト規則
|
値 |
0 |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
|
説明 |
なし |
固定数 |
最大間隔 |
間隔と数 |
最小間隔 |
RebarHostData と RebarCoverType
かぶり厚は、有効な鉄筋ホストの各面に関連付けられています。Autodesk.Revit.Elements.RebarHostData オブジェクトから、ホストのかぶり設定にアクセスできます。同じ設定に簡単、強力にアクセスできるメカニズムがパラメータから提供されます。
かぶりは、要素 Autodesk.Revit.DB.Structure.RebarCoverType としてモデリングされた、名前の付いたオフセット距離によって定義されます。
番号付け
鉄筋は、Revit API を介して番号付けをコントロールできる要素のカテゴリの 1 つです。NumberingSchema クラスと NumberingSchemaType クラスを使用すると、番号付けまたはタグ付けのために鉄筋要素を整理する方法を定義することができます。各 NumberingSchema は、特定のタイプの要素の番号付けをコントロールします。また、NumberingSchema のインスタンスも要素であり、各 Revit ドキュメント内に常にいずれかのタイプのうち 1 つのみが存在します。すべての組み込みの番号付けスキーマのうちで、使用可能なタイプが NumberingSchemaTypes クラスに列挙されます。
特定のスキーマ(NumberingSchemaTypes.StructuralNumberingSchemas.Rebar など)に属している要素(鉄筋など)が順番に整理され、番号付けされます。順番は、同じ番号付けパーティションを共有する要素の集合です。パーティションは、それぞれの Partition パラメータ(NUMBER_PARTITION_PARAM)の値によって定義されます。番号付けの順番には少なくとも 1 つの要素が含まれている必要があります。すなわち、(同じ番号付けスキーマの)他の要素と異なるパーティション パラメータの値を持つ要素がある場合に、順番が作られることになります。最後の要素が除外されると(削除された、または別の順番に移動された)、空になった順番は存在しなくなります。
要素は(現在の番号付けパーティションの値に基づいて)その作成時に順番に割り当てられる他、要素の Partition パラメータを明示的に修正したり、AssignElementsToSequence()メソッドを使用するなどして順番に割り当てることができます。変更したパラメータは現在のトランザクションが終了した後に有効になるのに対して、AssignElementsToSequence()メソッドは順番と要素番号を即座に適用するため、Partition パラメータを明示的に変更する場合よりも、AssignElementsToSequence()メソッドの方が優先されます。
直接または間接的に要素の Partition パラメータを変更する他に、NumberingSchema クラスのメソッドを使用して番号付けの順番を整理しなおすことができます。MoveSequence()メソッドは、既存の順番のすべての要素を、スキーマ内に存在しない新しい順番に移動します。そうすることで、影響を受けるすべての要素の Partition パラメータの名前を効率的に変更できます。AppendSequence()メソッドは、ある順番からすべての要素を除外し、一致ポリシーを適用して、既存の別の順番の要素に追加します。MergeSequences()メソッドは、指定されたすべての順番の要素を取得し、新しく作成された順番にすべて移動します。合成したすべての要素は、必要に応じて、一致アルゴリズムに基づいた再番号付け、マッチングが行われます。
下の例は、MoveSequence()メソッドを使用して、2 つの番号付けの順番にある鉄筋の番号を入れ替えます。
| コード領域: 番号を入れ替え |
|---|
/// <summary>
/// This method uses multiple moving operations to swap numbers
/// for Rebars in two numbering sequences. The sequences are
/// identified by the names of two numbering partitions.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="document">Document to modify</param>
/// <param name="part1">Name of the partition of one numbering sequence</param>
/// <param name="part2">Name of the partition of another numbering sequence</param>
private void SwapNumberingSequences(Document document, string part1, string part2)
{
// Obtain a schema object for a particular kind of elements
NumberingSchema schema = NumberingSchema.GetNumberingSchema(document,NumberingSchemaTypes.StructuralNumberingSchemas.Rebar);
using (Transaction transaction = new Transaction(document))
{
// Changes to numbering sequences must be made inside a transaction
transaction.Start("Swap Numbering Sequences");
// We will use a temporary partition for the swap operation,
// for the move operation only works if the target partition
// does not exist yet in the same numbering schema.
// (We assume this TEMPORARY partition does not exist.)
string tempPartition = "TEMPORARY";
// Step 1
// First we move all elements from one sequence into
// a partition we know does not exist. This action will
// create the temporary partition and remove the original
// one (part1).
schema.MoveSequence(part1, tempPartition);
// Step 2
// With the sequence in partition 'part1' removed
// we can now move elements from the second sequence to it.
// This action will re-create a sequence in partition 'part1'
// and remove the sequence in partition 'part2'
schema.MoveSequence(part2, part1);
// Step 3
// Finally, we can move elements 'parked' in the temporary
// sequence to partition 'part2', for that partition was
// removed in the previous step and thus can now be created
// again. The temporary partition will be automatically
// removed upon completing this step.
schema.MoveSequence(tempPartition, part2);
transaction.Commit();
}
}
|
異なる順番の要素は独立して番号付けされます。つまり、別々の要素が、2 つの順番内で同じ番号を持つことがあります。同様に、別の番号を持つまったく同じ要素が 2 つ以上の順番に存在する場合もあります。ただし、それぞれの番号付けの順番内では、2 つの同じ要素は常に同じ番号を持ち、異なる要素が番号付けの順番内で同じ番号を持つことはありません。
可算要素は常に、作成時に自動的に番号付けされます。新しい要素には、増分された番号が付けられます。ただし、同じ順番内の既存の要素と一致する新しい要素には、割り当てられている同じ番号が付けられます。要素は、割り当てられた番号を可能な限り保持します。これは、たとえば、以前に作成した鉄筋要素が削除された場合、(同じ番号付けの順番内の)残りのすべての要素はその番号を保持しますが、それぞれの番号付けの順番にギャップが生じることがあります。ギャップが望ましくない順番に対しては、RemoveGaps()を呼び出すことでギャップをなくすことができます。
次の例では、番号付けの順番内に残っているギャップをなくし、順番内の番号が重複しないように開始番号を設定して、鉄筋要素の番号を統合します。
| コード領域: 鉄筋の番号を統合 |
|---|
private void ConsolidateRebarNumbers(Document document)
{
// Obtain a schema object for a particular kind of elements
NumberingSchema schema = NumberingSchema.GetNumberingSchema(document,NumberingSchemaTypes.StructuralNumberingSchemas.Rebar);
// Collect the names of partitions of all the numbering sequences currently contained in the schema
IList<string> sequences = schema.GetNumberingSequences();
using (Transaction transaction = new Transaction(document))
{
// Changes to numbers must be made inside a transaction
transaction.Start("Consolidate Rebar Numbers");
// First we make sure numbers in all sequences are consecutive
// by removing possible gaps in numbers. Note: RemoveGaps does
// nothing for a sequence where there are no gaps present.
// We also want to find what the maximum range of numbers is
// of all the sequences (the one the widest span of used numbers)
int maxRange = 0;
foreach (string name in sequences)
{
schema.RemoveGaps(name);
// Here we use First() from the Linq extension.
// There is always at least one range in every sequence,
// and after gaps are closed there is exactly one range.
IntegerRange range = schema.GetNumbers(name).First();
int rangeSpan = 1 + (range.High - range.Low);
if (rangeSpan > maxRange)
{
maxRange = rangeSpan;
}
}
// Next we give sequences different start numbers
// starting with 100 and then stepping by at least
// the maximum range we found in the previous step
int startNumber = 100;
// We round the range up to the closest 100
int step = 100 * (int)((maxRange + 99) / 100.0);
foreach (string name in sequences)
{
schema.ShiftNumbers(name, startNumber);
startNumber += step;
}
transaction.Commit();
}
}
|
番号は、番号付けされた各番号の要素に、番号付けパラメータの値として格納されます。パラメータの ID は、NumberingSchema.NumberingParameterId プロパティを照会することで取得できます。番号値は、番号付けされた各要素のパラメータを照会することで取得できます。値は読み込み専用のため、設定することはできません。番号は常に、番号付けパーティションでの要素の関係性と、各要素の番号付けの順番内の一致ポリシーに基づいて算出されます。
番号は、スキーマのすべての要素に自動的に割り当てられますが、ChangeNumber()メソッドを使用すれば、新たな番号が番号付けの順番内で一意である限り、プログラマが特定の番号を明示的に上書きすることができます。呼び出し側が変更する番号を指定し、新しい番号が同じ番号付けの順番内にまだ存在していない場合は、適用する新しい値を指定します。