光線投影でジオメトリを検索する
ReferenceIntersector
このクラスを使用すると、アプリケーションで Revit の選択ツールを使用して、要素とジオメトリを検索できます。このクラスは点から指定した方向への光線を使用し、光線が当たるジオメトリを見つけ出します。
このクラスは 3D ジオメトリのみと交差し、作成時には 3D ビューが必要です。断面ボックスによって切り取られた 3D ビューや、ビュー固有のジオメトリとグラフィックス オプション セットを持つ 3D ビューを使用することができ、切り取りやトリミングしていない 3D モデルでは見つからない交差を見つけることができます。
ReferenceIntersector クラスは、要素や参照のタイプを基準とする出力のフィルタリングをサポートしています。メソッドを呼び出して光線投影を実行する前に、使用するコンストラクタを基準にして出力をカスタマイズしたり、クラスのメソッドやプロパティを使用して出力をカスタマイズすることができます。
コンストラクタには次の 4 つがあります。
|
名前 |
説明 |
|
ReferenceIntersector(View3D) |
すべての要素から、すべての参照ターゲットのタイプを表す交差を返すように設定された ReferenceIntersector を作成します。 |
|
ReferenceIntersector(ElementFilter, FindReferenceTarget, View3D) |
フィルタを通過する任意の要素の交差を返すように設定された ReferenceIntersector を作成します。 |
|
ReferenceIntersector(ElementId, FindReferenceTarget, View3D) |
単一のターゲット要素のみの交差を返すように設定された ReferenceIntersector を作成します。 |
|
ReferenceIntersector(ICollection<ElementId>, FindReferenceTarget, View3D) |
任意のターゲット要素のセットの交差を返すように設定された ReferenceIntersector を作成します。 |
FindReferenceTarget 列挙には、要素、メッシュ、エッジ、曲線、面、すべてのオプションがあります。
光線を投影するためのメソッドは 2 つあり、その両方とも入力として光線の始点とその方向をとります。Find()メソッドは、ReferenceIntersector の基準に一致する ReferenceWithContext オブジェクトのコレクションを返します。このオブジェクトには交差する参照が含まれますが、光線が交差する要素とジオメトリ参照の両方が対象となります。返される要素の参照の一部は、同様に交差する付随したジオメトリ オブジェクトを持ちます(たとえば、壁の開口部を通過する光線は壁および開口部要素と交差します)。実際の物理的な交差のみ必要な場合は、参照が要素タイプとなっているすべての参照はアプリケーションによって破棄されます。
FindNearest()メソッドは Find()メソッドと同様の動作をしますが、光線の始点に最も近い交差する参照のみを返します。
ReferenceWithContext の戻り値には近接パラメータが含まれます。これは、光線の始点と交点の間の距離です。アプリケーションはこの距離を使用することで、特定のジオメトリ解析の基準点から距離が離れすぎている項目を除外することができます。さらに、アプリケーションは、モデル内のジオメトリの解析を含む興味深い問題に取り組む際にもこの距離を使用することができます。
- このメソッドにより、光線の前にある要素に対して両方の参照が検索されて返されることが分かります。
- このメソッドは、リンク ファイル内の交点を返しません。
- このメソッドは、アクティブなデザイン オプションにない要素との交点を返しません。
要素の近くにある要素を検索する
このツールの主な用途の 1 つに、他の要素に近接する要素の検索があります。それにより、アプリケーションがこのツールを自らの「目」として使用し、組み込みの関係性をまだ持っていない要素同士の関係性を判断することができます。
たとえば、レイトレース機能を使用すれば、壁に埋め込まれた柱を検索することができます。柱と壁は関係を直接的に保持していないため、このクラスを使用することで、壁の範囲のちょうど外側の光線をトレースして、柱との交差を探すことで、候補となり得る対象を検索することができます。
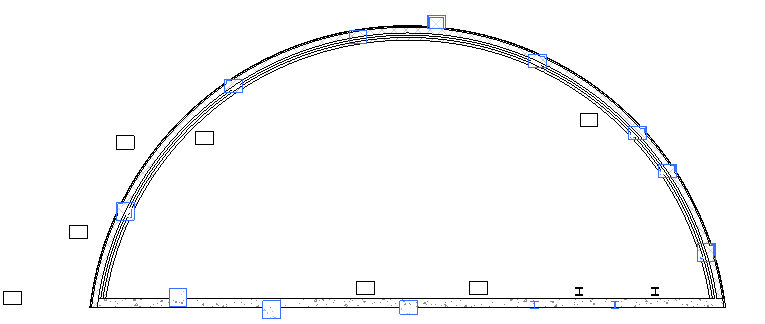
例: 壁に埋め込まれている列を検索
距離を計測する
このクラスを使用しても天窓から直近の床までの垂直距離を計測できます。
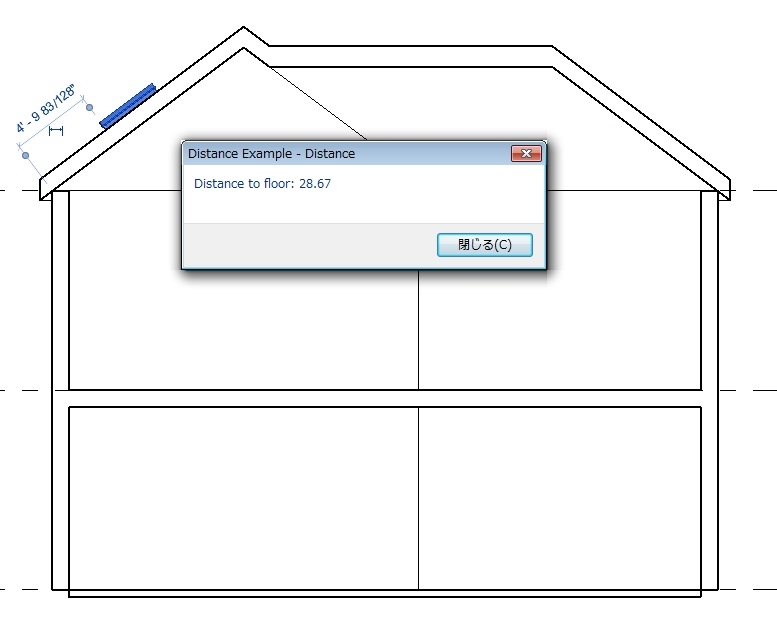
例: ReferenceIntersector.FindNearest()を使用して計測
|
コード領域: 光線投影を使用した距離の計測 |
public class RayProjection : IExternalCommand
{
public Result Execute(ExternalCommandData revit, ref string message, ElementSet elements)
{
Document doc = revit.Application.ActiveUIDocument.Document;
ICollection<ElementId> selectedIds = revit.Application.ActiveUIDocument.Selection.GetElementIds();
// If skylight is selected, process it.
FamilyInstance skylight = null;
if (selectedIds.Count == 1)
{
foreach (ElementId id in selectedIds)
{
Element e = doc.GetElement(id);
if (e is FamilyInstance)
{
FamilyInstance instance = e as FamilyInstance;
bool isWindow = (instance.Category.Id.IntegerValue == (int)BuiltInCategory.OST_Windows);
bool isHostedByRoof = (instance.Host.Category.Id.IntegerValue == (int)BuiltInCategory.OST_Roofs);
if (isWindow && isHostedByRoof)
{
skylight = instance;
}
}
}
}
if (skylight == null)
{
message = "Please select one skylight.";
return Result.Cancelled;
}
// Calculate the height
Line line = CalculateLineAboveFloor(doc, skylight);
// Create a model curve to show the distance
Plane plane = revit.Application.Application.Create.NewPlane(new XYZ(1, 0, 0), line.GetEndPoint(0));
SketchPlane sketchPlane = SketchPlane.Create(doc, plane);
ModelCurve curve = doc.Create.NewModelCurve(line, sketchPlane);
// Show a message with the length value
TaskDialog.Show("Distance", "Distance to floor: " + String.Format("{0:f2}", line.Length));
return Result.Succeeded;
}
/// <summary>
/// Determines the line segment that connects the skylight to the nearest floor.
/// </summary>
/// <returns>The line segment.</returns>
private Line CalculateLineAboveFloor(Document doc, FamilyInstance skylight)
{
// Find a 3D view to use for the ReferenceIntersector constructor
FilteredElementCollector collector = new FilteredElementCollector(doc);
Func<View3D, bool> isNotTemplate = v3 => !(v3.IsTemplate);
View3D view3D = collector.OfClass(typeof(View3D)).Cast<View3D>().First<View3D>(isNotTemplate);
// Use the center of the skylight bounding box as the start point.
BoundingBoxXYZ box = skylight.get_BoundingBox(view3D);
XYZ center = box.Min.Add(box.Max).Multiply(0.5);
// Project in the negative Z direction down to the floor.
XYZ rayDirection = new XYZ(0, 0, -1);
ElementClassFilter filter = new ElementClassFilter(typeof(Floor));
ReferenceIntersector refIntersector = new ReferenceIntersector(filter, FindReferenceTarget.Face, view3D);
ReferenceWithContext referenceWithContext = refIntersector.FindNearest(center, rayDirection);
Reference reference = referenceWithContext.GetReference();
XYZ intersection = reference.GlobalPoint;
// Create line segment from the start point and intersection point.
Line result = Line.CreateBound(center, intersection);
return result;
}
}
|
光線の反射/解析
ReferenceIntersector.Find()が返す参照には、ジオメトリ上の交点が含まれます。面上の交点、面のマテリアル、光線の方向が分かれば、アプリケーションで建物内の反射と屈折を解析することができます。次の図は、交点を使用してモデル要素が交差する光線を反射させる方法を表しています。各光線のパスを表すためにモデル曲線が追加されています。
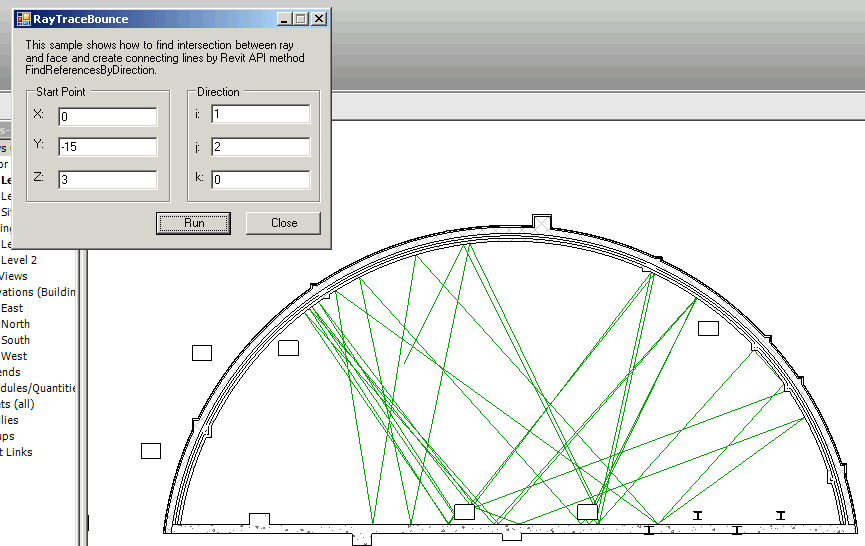
例: 交差する面で反射する光線
交点/衝突を検索する
ReferenceIntersector クラスの別の使用方法としては、特定の梁または配管の中心線と交差/干渉する交差(梁や配管など)の検索があります。
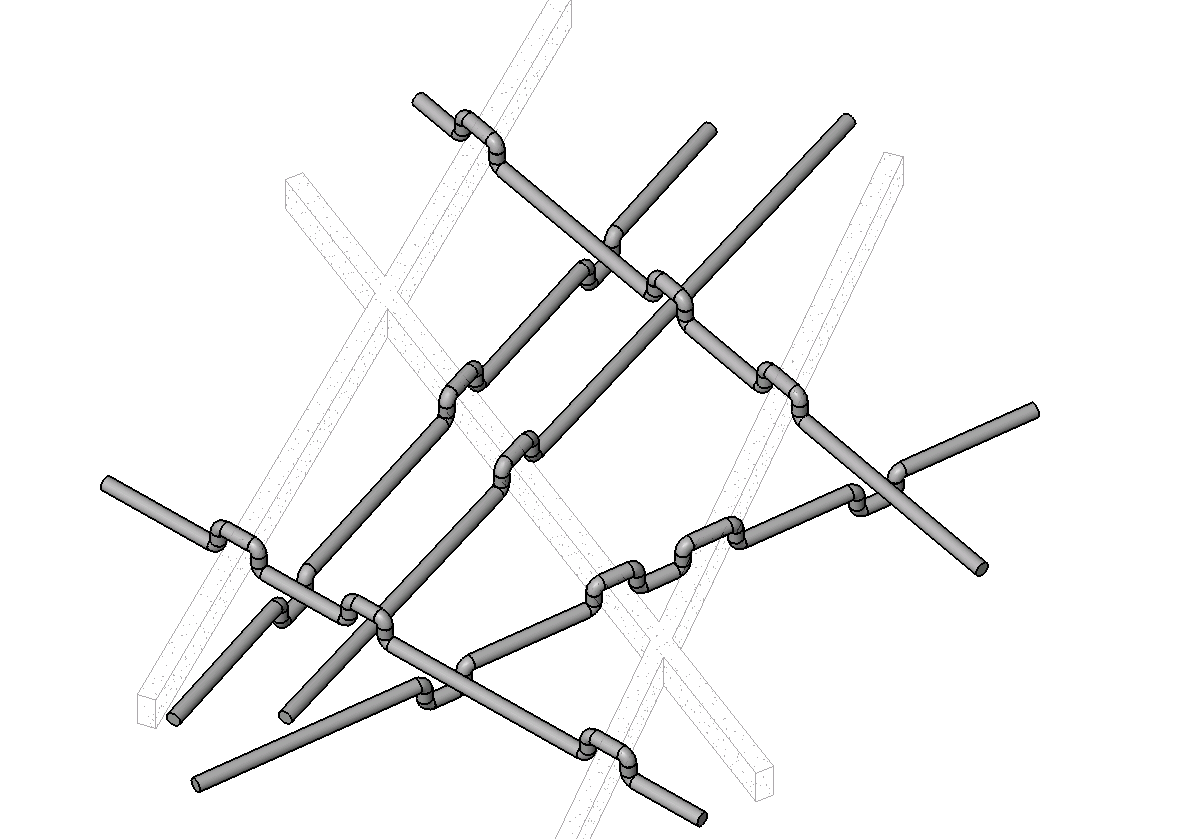
例: 干渉周辺の要素の経路を変更