Use the Advance Steel API and C# to create a Hello World program using the directions provided.
The Hello World walkthrough covers the following topics:
- Create a new project
- Add references
- Add code
- Register the addin with Advance Steel
- Run the addin
All operations and code in this section were created using Visual Studio 2012.
Create a new project
The first step in writing a C# program with Visual Studio is to choose a project type and create a new Class Library.
- From the File menu, select New
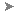 Project….
Project….
- In the Installed Templates frame, click Visual C#.
- In the right-hand frame, click Class Library (see Figure 1: Add New Project below). This walkthrough assumes that the project location is: C:\Samples.
- In the Name field, type HelloWorld as the project name.
- Verify that the selected .NET Framework is ".NET Framework 4.5".
- Click OK.
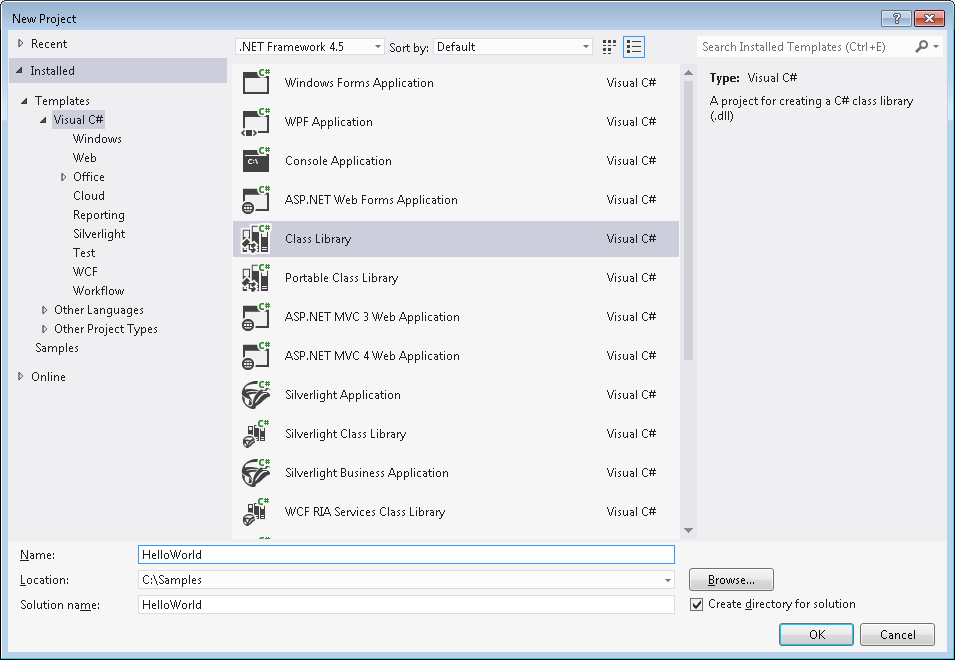
Figure 1: Add New Project
Add references
A number of components make up the Advance Steel API. They are installed with Advance Steel and can be found in subdirectories of the Advance Steel 20xx program folder, where 20xx is the version number of Advance Steel, such as 2015 or 2016. You need to add references to the following components in order to compile the project. Note that some components have different names depending on which version of Advance Steel you have installed.
| Component | Location | Description |
|
ASNetRuntime.dll |
\Advance Steel 20xx\Common\Bin |
Required to compile the Addin |
|
ASMgd.dll |
\Advance Steel 20xx\Kernel\Bin |
Main Advance Steel objects access |
|
ASCADLinkMgd.dll |
\Advance Steel 20xx\Kernel\Bin |
CAD - related objects access (database, object id, …) |
|
ASGeometryMgd64.dll or ASGeometryMgd32.dll |
\Advance Steel 20xx\Common\Bin |
Advance Steel geometry - needed to interact with Advance Steel objects |
|
ASProfilesMgd64.dll or ASProfilesMgd32.dll |
\Advance Steel 20xx\Common\Bin |
Advance Steel profiles database access |
|
ASModelerMgd64.dll or ASModelerMgd32.dll |
\Advance Steel 20xx\Common\Bin |
Advance Steel modeler access |
To add references to the required components, follow these steps:
- If the Solution Explorer window is not open, select Solution Explorer from the View menu.
- In the Solution Explorer, right-click References to display a context menu.
- From the context menu, click Add Reference. The Reference Manager window appears.
- In the Reference Manager window, click the Browse button. A window to select files appears.
- Browse to the Advance Steel 20xx installation folder, which is typically located at C:\Program Files\Autodesk\Advance Steel 20xx.
- Browse to the appropriate subfolder and select a dll listed above to add.
- Click the Add button to select the dll and close the window.
- The selected dll should now be listed in the Reference Manager with a checkmark next to it.
- Repeat steps 4-8 until all 6 components are added. Note that when selecting dlls to add, multiple dlls may be selected at one time.
- In the Reference Manager, click OK to close the window.
- The selected components will now appear in the Solution Explorer under the References folder.
- Select the newly added references and change their Copy Local property to False.
- Return to the Reference Manager window.
- Click Assemblies in the left-hand pane.
- Scroll down the list in the right-hand pane to find System.Windows.Forms.
- Click the checkbox next to System.Windows.Forms.
- Click OK to close the Reference Manager window.
Add code
There are three main steps to adding code to an Advance Steel Addin:
- Implement the IExtensionApplication interface
- Create your command class
- Edit the AssemblyInfo.cs file
Implement IExtensionApplication
A default class called Class1 should have been created with the new project.
- Right-click on Class1.cs in the Solution Explorer and select Rename from the context menu.
- Rename the file Plugin.cs.
- Replace the text in Plugin.cs with the sample code below.
|
Code Region: Implement IExtensionApplication |
using Autodesk.AdvanceSteel.Runtime;
namespace HelloWorld
{
public sealed class Plugin : IExtensionApplication
{
void IExtensionApplication.Initialize()
{
}
void IExtensionApplication.Terminate()
{
}
}
}
|

Figure 2: Use Intellisense to implement the interface
Create a command class
- Add a new class to the project called TestClass.
- Place the following code in TestClass.cs:
|
Code Region: Create a command class |
using Autodesk.AdvanceSteel.CADAccess;
using Autodesk.AdvanceSteel.DocumentManagement;
using Autodesk.AdvanceSteel.Runtime;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace HelloWorld
{
public class TestClass
{
[CommandMethodAttribute("TEST_GROUP", "HelloWorld", "HelloWorld", CommandFlags.Modal)]
public void SayHelloWorld()
{
MessageBox.Show("Hello World!");
}
}
}
|
An Advance Steel addin must have a method with the CommandMethodAttribute as shown in the sample code above. The parameters for the CommandMethodAttribute are:
- groupName - The name of the group to which the command will be added. If the group does not exist, it will be created before the command is added.
- globalName - The command name to add. This name represents the global or untranslated name.
- localizedNameId - The command name to add. This name represents the local or translated name.
- flags - Flags associated with the command.
Note that the options for CommandFlags are the same as for the AutoCAD Managed .NET API and the full list of options can be found here.
Edit the AssemblyInfo.cs file
An Advance Steel addin must include certain Informational Attribute directives. These belong in the AssemblyInfo.cs files.
- In the Solution Explorer, click on the Properties folder to expose the AssemblyInfo.cs file.
- Open the AssemblyInfo.cs file. This file already contains some assembly attributes such as the title and copyright.
- Add a using statement at the top of the file for Autodesk.AdvanceSteel.Runtime.
- Add a new informational attribute directive called ExtensionApplicationAttribute as shown below. Note that it takes as a parameter the type of the class which implements IExtensionApplication. This is what makes your .Net Framework DLL an Advance Steel addin.
Code Region: Add an ExtensionApplicationAttribute
[assembly: ExtensionApplicationAttribute(typeof(HelloWorld.Plugin))]
- Add a new informational attribute directive called CommandClassAttribute as shown below. Note that it takes as a parameter the type of the class which implements a command. This is required to be able to register the command with Advance Steel.
Code Region: Add a CommandClassAttribute
[assembly: CommandClassAttribute(typeof(HelloWorld.TestClass))]
After following these steps, the AssemblyInfo.cs file will look something like this:
|
Code Region: Sample AssemblyInfo.cs |
using Autodesk.AdvanceSteel.Runtime;
using System.Reflection;
using System.Runtime.CompilerServices;
using System.Runtime.InteropServices;
// General Information about an assembly is controlled through the following
// set of attributes. Change these attribute values to modify the information
// associated with an assembly.
[assembly: AssemblyTitle("HelloWorld")]
[assembly: AssemblyDescription("")]
[assembly: AssemblyConfiguration("")]
[assembly: AssemblyCompany("")]
[assembly: AssemblyProduct("HelloWorld")]
[assembly: AssemblyCopyright("Copyright © 2015")]
[assembly: AssemblyTrademark("")]
[assembly: AssemblyCulture("")]
[assembly: ExtensionApplicationAttribute(typeof(HelloWorld.Plugin))]
[assembly: CommandClassAttribute(typeof(HelloWorld.TestClass))]
// Setting ComVisible to false makes the types in this assembly not visible
// to COM components. If you need to access a type in this assembly from
// COM, set the ComVisible attribute to true on that type.
[assembly: ComVisible(false)]
// The following GUID is for the ID of the typelib if this project is exposed to COM
[assembly: Guid("85900596-22ee-4873-bbd6-7f970d32b5af")]
// Version information for an assembly consists of the following four values:
//
// Major Version
// Minor Version
// Build Number
// Revision
//
// You can specify all the values or you can default the Build and Revision Numbers
// by using the '*' as shown below:
// [assembly: AssemblyVersion("1.0.*")]
[assembly: AssemblyVersion("1.0.0.0")]
[assembly: AssemblyFileVersion("1.0.0.0")]
|
Register the addin
After compiling the code, you need to add a new registry key that will be used by Advance Steel to automatically load your addin on startup. The new key should be:
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Autodesk\AdvanceSteel\<Advance_Steel_Version_Number>\NETAddins\<Addin_Name>]
"InstallLocation"="<addin_dll_path>\<file_name>"
<Advance_Steel_Version_Number> will be the version of Advance Steel for the addin, such as "2016". <Addin_Name> is the name of the Advance Steel addin, and the InstallLocation points to the full pathname of the addin .dll file.
The image below shows the new registry key for the HelloWorld addin for Advance Steel 2016.
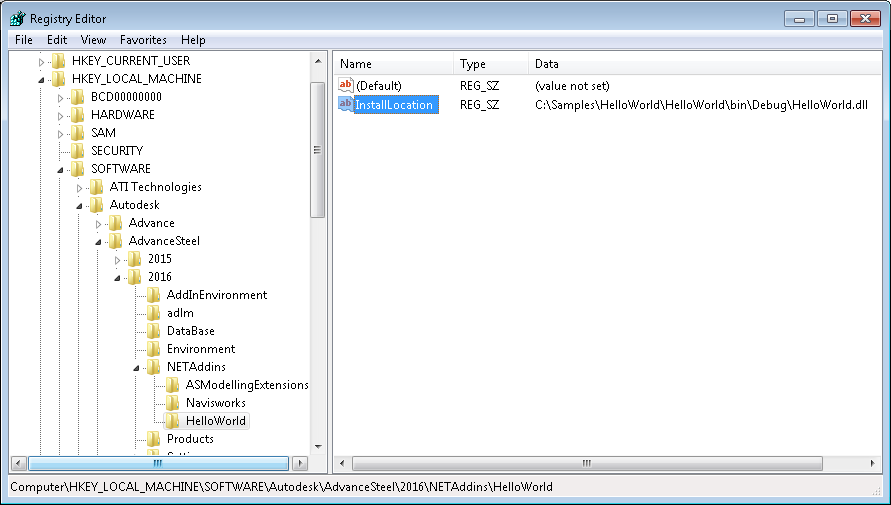
Figure 2: Add a registry key
This only needs to be done once per addin .dll. Any new commands added to the assembly designated by the " CommandMethodAttribute" attribute will be automatically recognized as a separate command that can be run when Advance Steel is loaded.
Run the addin
To run the addin command, start Advance Steel. Then simply type in the name of the command, in this case, HelloWorld, and hit enter.
If you need to debug your addin, you can follow these steps:
- Start Advance Steel.
- In Visual Studio, put a breakpoint where you would like to stop the code in your command.
- From the Debug menu, select Attach to Process...
- Select the acad.exe process.
- Run your command in Advance Steel and your breakpoint will be triggered in Visual Studio.