How to scale objects proportionally, non-proportionally, and around a rotational pivot.
Scale objects proportionally
- Choose Transform > Scale
 .
. - Drag to scale the object uniformly along all axes, or type a scaling value.
Scale objects non-proportionally
- Choose Transform > Non-p Scale
 .
. - Drag the mouse buttons to scale along the different axes, or type scale values for the X, Y, and Z directions.
How do the different mouse buttons work in the different windows?
| Drag... | In Window Type... | To Do This |
|---|---|---|
|
|
Orthographic | Scale freely in the view axes. 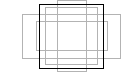 |
| Perspective | Scale along X axis. 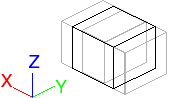 |
|
|
|
Orthographic | Scale horizontally. 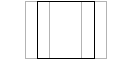 |
| Perspective | Scale along Y axis. 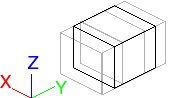 |
|
|
|
Orthographic | Scale vertically.  |
| Perspective | Scale along Z axis.  |
Scale objects around a rotational pivot
- Select Transform > Modify > Rotational Scale
 or click its icon.
or click its icon. You can pick and unpick geometry in the Object Lister by clicking the DAG nodes.
- The system prompts you to enter the first pivot point.
Define the pivot point for the deformation by typing an X, Y, Z location or by using the mouse. A cross-hair, the pivot point, appears to mark the center of the rotational scale.
Note:The system calculates the best fit for the model according to the deformation values you request. For the most accurate fit, enter values using the keyboard rather than the mouse.
- The system prompts you to enter another pivot point. The two pivot points define the axis for deformation.
The geometry deforms about the pivot point and toward or away from this second point.
Define the second point by typing an X, Y, Z location, or using the mouse. Another cross-hair appears. The selected curves and surfaces rotate around this axis point.
- If no objects are picked, the system prompts you to select geometry.
If you hold down Shift, you can select several objects. You can continue selecting and deselecting geometry during the function.
- The system tells you the current scale and prompts you to adjust the scale factor.
Select more objects by holding down
 and clicking with the
and clicking with the  .
. - Type a new scale value or use the
 to adjust the scale by moving the object.
to adjust the scale by moving the object. This new value can be a new scale or a new number of divisions, depending upon the Type of input mode that you chose in the Rotate Options window.
Scale a picked object using the universal transform manipulator
- Choose Transform > Transform
 .
. - To scale the object along an axis, drag a cube.
To scale the object uniformly, click a cube, then drag the cube. at the center of the manipulator.
Rotational scale example
To create an eight-spoked wheel by rotationally scaling a spoke of a five-spoked wheel:

- Select the geometry for one of the spokes, and toggle the rest of the model invisible or templated, or delete it. (You can use intersecting planes to "slice" out a section of the wheel.)
- Select Transform > Modify > Rotational Scale

 or double-click its icon in the tool palette.
or double-click its icon in the tool palette. - In the option box, set the input mode to Number of divisions.
- Place the pivot point at the center of the wheel and the second point along the spoke to set the axis of rotation.
- Now enter how many divisions were in the original model. (Type 5 for this example.)
- Enter the new number of divisions. (For this example, type in 8.) The element is scaled to its new angle.
- You are now finished deforming the model. To complete the new wheel, create seven additional copies of this spoke, each rotated by the correct amount.
To make these copies, use Edit > Duplicate > Object
 . In this example, the wheel was in the X - Z plane, so the rotation is about the Y axis. Set the following options in the Duplicate Object Options window:
. In this example, the wheel was in the X - Z plane, so the rotation is about the Y axis. Set the following options in the Duplicate Object Options window: - Rotation – Y 45
- Number of duplicates – 7
- Geometry type – instance
A new wheel is created, with eight spokes:
