The PDB feature checks a DCL file for errors the first time you load it. If a syntax error, a misuse of attributes, or any other error is encountered (such as failure to specify a key attribute for an active tile), the PDB does not load the DCL file.
When an error is encountered, one or more dialog boxes alerting you to the error are displayed, or a list of errors are written to a text file named acad.dce. If the error messages are written to acad.dce, it alerts you to this with a message similar to the following:
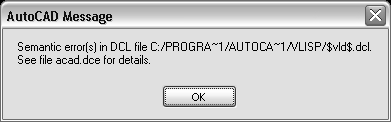
You can inspect the contents of acad.dce to find the problem. The acad.dce file is placed in the current working directory. When a DCL file is read successfully, the acad.dce file is deleted.
If your application uses multiple DCL files, the acad.dce file is overwritten (or deleted if no errors occur) when each new file is loaded. When you test the program, acad.dce shows errors (if any) from only the DCL file most recently read. You can also load and debug each file manually in AutoCAD with the load_dialog function. The following load_dialog function loads the DCL file hellofile.dcl:
Command: (load_dialog "hellofile")
3
If the dialog box loads successfully, load_dialog returns a positive integer that identifies the DCL file. You pass this value to the new_dialog function to initialize individual dialog boxes in the file.
The new_dialog function returns T if it succeeds; otherwise it returns nil. If new_dialog returns T, call the start_dialog function to display the dialog box.
Once you have debugged each DCL file, you can load your program and test the dialog boxes in combination. If your program calls a restricted function between the start_dialog and done_dialog calls, AutoCAD terminates all dialog boxes and displays the following error message:
AutoCAD rejected function