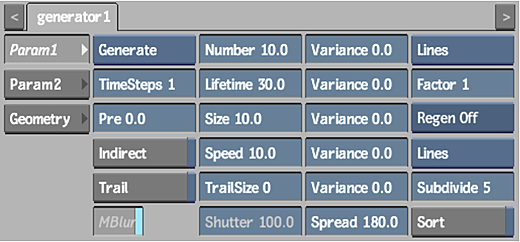
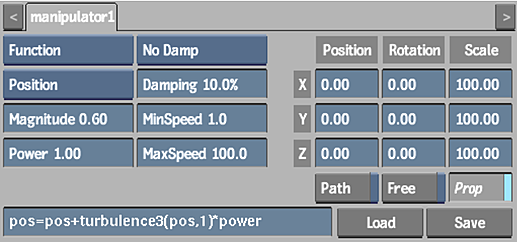
Select Function to specify your own mathematical expressions to be used as a particle manipulator. You can use the channels from the Particle Manipulator and Particle Generator menus in your expressions, as well as arithmetic operations, mathematical conventions, functions, and constants.
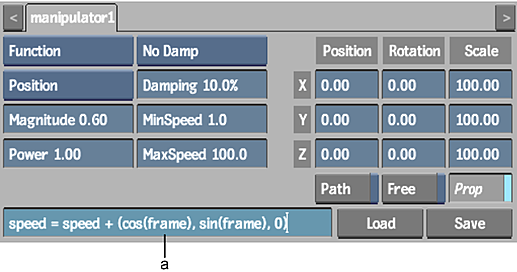
(a) Expression field
The arithmetic operators, conventions, constants, and functions that you can use in your expressions are listed in the following sections. Before writing your own expressions, you should understand the following:
- A vector is a 3D coordinate written using the convention (x, y, z) where x, y, and z are separate values.
For example, pos represents the position of each particle. If you want to increase the Y position of each particle with each pass, use the expression pos = pos + (0,1,0).
- Make sure assigned values and vector values are within an acceptable range. For example, transparency (opacity of each particle) is a value between 0 and 1. The expression transparency = size does not work unless size (particle size from the PartGen menu) falls between 0.0 and 1.0.
To make transparency dependent on size, size must be divided by an appropriate value. For example, if size is between 1 and 10, use the expression transparency = size / 10.
- Some functions return scalars and other functions return vectors. Make sure that when you use a function, it returns the right value and that this value is within an acceptable range.
For example, rgb is a vector of values between 0.0 and 1.0. The expression rgb = (0, 0, noise3(pos)) gives an error because noise3 returns a vector. The expression rgb = (0, 0, frame) does not give an error, but frame is the frame number and it is never less than 1. This means the blue channel is always set to full blue (1).
- You can specify more than one function by separating each with a semicolon.
For example, to place the two expressions in the Expression field, you would type:
Expression field operators are listed in the following table.
| Operator | Description |
|---|---|
| = | Equals |
| + | Addition |
| - | Subtraction |
| * | Multiplication |
| / | Division |
| % | Percentage |
| (x,y,z) | Vector where x, y, z may also be the results of functions |
| == | Equivalence |
| != | Not equal to |
| < | Less than |
| <= | Less than or equal to |
| > | Greater than |
| >= | Greater than or equal to |
Particle and manipulator variables that you can use in the Expression field are listed in the following table.
| Particle Symbol | Description |
|---|---|
| pos | Position, a vector (x,y,z). |
| speed | Speed, a vector (x,y,z). |
| rgba | Red, green, blue, and alpha colour channels for each particle, expressed as a 4D vector (r,g,b,a). Each component is a value between 0 and 1. |
| rgb | Red, green, and blue colour channel, expressed as a vector (r,g,b). Each component is a value between 0 and 1. |
| red | Red channel, a value between 0 and 1. |
| green | Green channel, a value between 0 and 1. |
| blue | Blue channel, a value between 0 and 1. |
| transparency | Transparency of each particle (surface or geometry), a value between 0 and 1. |
| lifetime | Lifetime of each particle, in frames. |
| lifetimeI | A value between 1.0 and 0.0 where 1.0 is when a particle is first generated and 0.0 is when it ends. |
| mass | Mass of each particle. |
| size | Size of each particle, in pixels. |
| tailSize | Width of the particle's tail, a value between 0 and 1. |
The following variables are read only. You cannot change them in the Expression field, but you can use them in your calculations.
| Manipulator Symbol | Description |
|---|---|
| frame | Current frame |
| magnitude | Value from the Magnitude field |
| power | Value from the Power field |
| damping | Value from the Damping field |
| minSpeed | Value from the MinSpeed field |
| maxSpeed | Value from the MaxSpeed field |
Single argument arithmetic functions are listed in the following table.
| One Argument | Description |
|---|---|
| sin(a) | Sine of a |
| cos(a) | Cosine of a |
| tan(a) | Tangent of a |
| asin(a) | Arcsine of a |
| acos(a) | Arccosine of a |
| atan(a) | Arctangent of a |
| exp(x) | Exponential function of x |
| expm1(x) | Equivalent to exp(x)-1 |
| log(x) | Natural logarithm of x |
| log10(x) | Base 10 logarithm of x |
| log1p(x) | Equivalent to log (1+ x) |
| sqrt(x) | Square root of x |
| abs(x) | Absolute value of x |
| trunc(x) | Integer value of x |
| floor(x) | Smallest integer greater than or equal to x |
| ceil(x) | Largest integer greater than or equal to x |
| round(x) | x rounded to the nearest integer |
| radians(a) | a converted to radians |
| degrees(r) | r converted to degrees |
| sign(x) | Returns +1 or -1 depending on the sign of x |
| length(p) | Euclidean length of point p |
| noise(v) | Noise of vector v, returns a float |
| fnoise(v) | Fractal noise vector v, returns a float |
| noise3(v) | Noise of vector v, returns a vector |
Making Particles Transparent
The following example illustrates how to make particles become transparent as they reach the end of their lifetime using the expression transparency = lifetimeI. The settings in the Particle Manipulator menu, Particle Generator menu, and the resulting effect are shown.
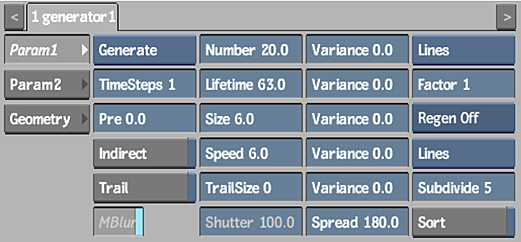
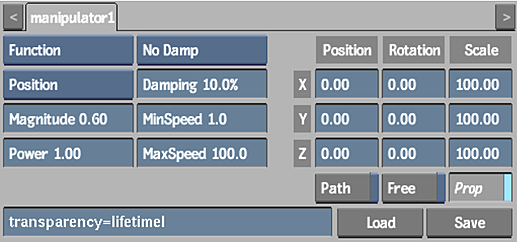
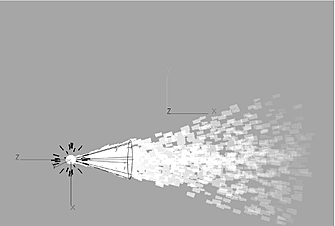
Making Particles Spin
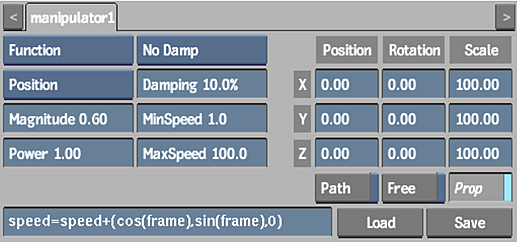
The following example illustrates how to spin particles using the expression:
The settings in the Particle Manipulator menu, Particle Generator menu, and the resulting effect are shown. Notice that the particle Timestep value is increased to improve the accuracy of the particle stream.
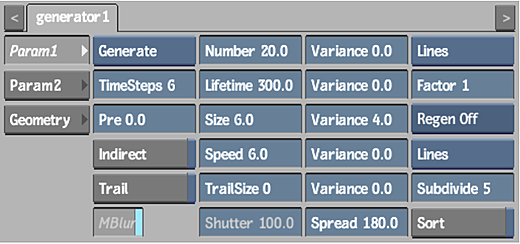

Arithmetic functions that have two or more arguments are listed in the following table.
| Symbol | Description |
|---|---|
| atan(x,y) | Arctangent of y over x |
| pow(x,y) | x to the power of y |
| mod(x,y) | Returns the remainder of dividing x by y |
| min(x,y) | Minimum value of x and y |
| max(x,y) | Maximum value of x and y |
| step(x,y) | Returns 0 if x < y, 1 if x >= y |
| dot(v1, v2) | Dot product of two vectors; returns a scalar |
| cross(v1, v2) | Cross product of two vectors; returns a vector |
| turbulence(v, o) | Turbulence of vector v and octave o; returns a float |
| turbulence3(v, o) | Turbulence of vector v and octave o; returns a vector |
| smoothstep (min,max, x) | Returns 0 if x < min, 1if x >= max; if neither are true, returns a hermite interpolation between 0 and 1 |
| clamp(x, min, max) | x clamped to the range [min,max] |
The following example illustrates how to create animated turbulence using the expression: