|
Access: |
Ribbon:
CAM tab
 2D Milling panel
2D Milling panel
 Face
Face

|
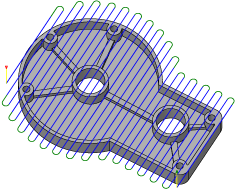
The Facing strategy is designed for quick part facing to prepare the raw stock for further machining, but can also be used for clearing flat areas in general.
 Tool tab settings
Tool tab settings

Coolant:
The type of coolant used with the tool.
Spindle speed:
The rotational speed of the spindle.
Surface speed:
The spindle speed expressed as the speed of the tool on the surface.
Ramp spindle speed:
The rotational speed of the spindle when performing ramp movements.
Cutting feedrate:
Feed used in cutting moves.
Feed per tooth:
The cutting feedrate expressed as the feed per tooth.
Lead-in feedrate:
Feed used when leading in to a cutting move.
Lead-out feedrate:
Feed used when leading out from a cutting move.
Ramp feedrate:
Feed used when doing helical ramps into stock.
Plunge feedrate:
Feed used when plunging into stock.
Feed per revolution:
The plunge feedrate expressed as the feed per revolution.
 Geometry tab settings
Geometry tab settings
Stock Contours
Enable to specify the perimeter of the stock that needs to be faced.
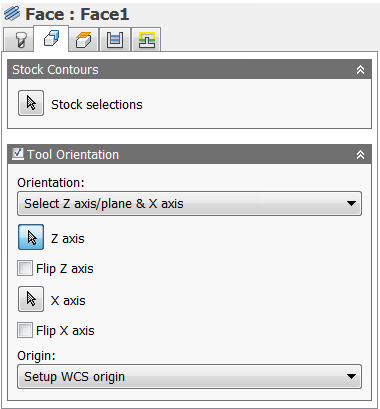
Tool Orientation
Specifies how the tool orientation is determined using a combination of triad orientation and origin options.
The Orientation drop-down menu provides the following options to set the orientation of the X, Y, and Z triad axes:
- Setup WCS orientation - Uses the workpiece coordinate system (WCS) of the current setup for the tool orientation.
- Model orientation - Uses the coordinate system (WCS) of the current part for the tool orientation.
- Select Z axis/plane & X axis - Select a face or an edge to define the Z axis and another face or edge to define the X axis. Both the Z and X axes can be flipped 180 degrees.
- Select Z axis/plane & Y axis - Select a face or an edge to define the Z axis and another face or edge to define the Y axis. Both the Z and Y axes can be flipped 180 degrees.
- Select X & Y axes - Select a face or an edge to define the X axis and another face or edge to define the Y axis. Both the X and Y axes can be flipped 180 degrees.
- Select coordinate system - Sets a specific tool orientation for this operation from an Inventor User Coordinate System (UCS) in the model. This uses both the origin and orientation of the existing coordinate system. Use this if your model does not contain a suitable point & plane for your operation.
The Origin drop-down menu offers the following options for locating the triad origin:
- Setup WCS origin - Uses the workpiece coordinate system (WCS) origin of the current setup for the tool origin.
- Model origin - Uses the coordinate system (WCS) origin of the current part for the tool origin.
- Selected point - Select a vertex or an edge for the triad origin.
- Stock box point - Select a point on the stock bounding box for the triad origin.
- Model box point - Select a point on the model bounding box for the triad origin.
 Heights tab settings
Heights tab settings
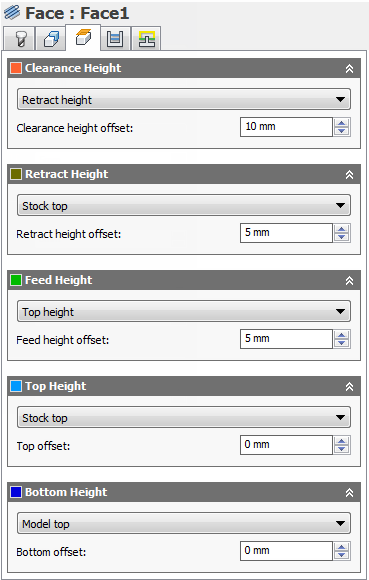
Clearance Height
The Clearance height is the first height the tool rapids to on its way to the start of the tool path.

Clearance Height
- Retract height: incremental offset from the Retract Height.
- Feed height: incremental offset from the Feed Height.
- Top height: incremental offset from the Top Height.
- Bottom height: incremental offset from the Bottom Height.
- Model top: incremental offset from the Model Top.
- Model bottom: incremental offset from the Model Bottom.
- Stock top: incremental offset from the Stock Top.
- Stock bottom: incremental offset from the Stock Bottom.
- Selected contour(s): incremental offset from a Contour selected on the model.
- Selection: incremental offset from a Point (vertex), Edge or Face selected on the model.
- Origin (absolute): absolute offset from the Origin that is defined in either the Setup or in Tool Orientation within the specific operation.
Clearance height offset:
The Clearance height offset is applied and is relative to the Clearance height selection in the above drop-down list.
Retract Height
Retract height sets the height that the tool moves up to before the next cutting pass. Retract height should be set above the Feed height and Top. Retract height is used together with the subsequent offset to establish the height.
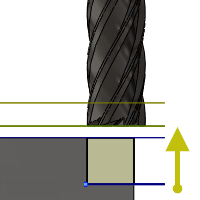
Retract Height
- Clearance height: incremental offset from the Clearance Height.
- Feed height: incremental offset from the Feed Height.
- Top height: incremental offset from the Top Height.
- Bottom height: incremental offset from the Bottom Height.
- Model top: incremental offset from the Model Top.
- Model bottom: incremental offset from the Model Bottom.
- Stock top: incremental offset from the Stock Top.
- Stock bottom: incremental offset from the Stock Bottom.
- Selected contour(s): incremental offset from a Contour selected on the model.
- Selection: incremental offset from a Point (vertex), Edge or Face selected on the model.
- Origin (absolute): absolute offset from the Origin that is defined in either the Setup or in Tool Orientation within the specific operation.
Retract height offset:
Retract height offset is applied and is relative to the Retract height selection in the above drop-down list.
Feed Height
Feed height sets the height that the tool rapids to before changing to the feed/plunge rate to enter the part. Feed height should be set above the Top. A drilling operation uses this height as the initial feed height and the retract peck height. Feed height is used together with the subsequent offset to establish the height.
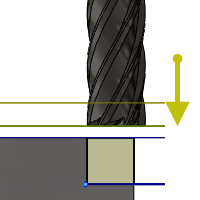
Feed Height
- Clearance height: incremental offset from the Clearance Height.
- Retract height: incremental offset from the Retract Height.
- Disabled: Disabling the Feed Height causes the tool to rapid down to the lead-in.
- Top height: incremental offset from the Top Height.
- Bottom height: incremental offset from the Bottom Height.
- Model top: incremental offset from the Model Top.
- Model bottom: incremental offset from the Model Bottom.
- Stock top: incremental offset from the Stock Top.
- Stock bottom: incremental offset from the Stock Bottom.
- Selected contour(s): incremental offset from a Contour selected on the model.
- Selection: incremental offset from a Point (vertex), Edge or Face selected on the model.
- Origin (absolute): absolute offset from the Origin that is defined in either the Setup or in Tool Orientation within the specific operation.
Feed height offset:
Feed height offset is applied and is relative to the Feed height selection in the above drop-down list.
Top Height
Top height sets the height that describes the top of the cut. Top height should be set above the Bottom. Top height is used together with the subsequent offset to establish the height.

Top Height
- Clearance height: incremental offset from the Clearance Height.
- Retract height: incremental offset from the Retract Height.
- Feed height: incremental offset from the Feed Height.
- Bottom height: incremental offset from the Bottom Height.
- Model top: incremental offset from the Model Top.
- Model bottom: incremental offset from the Model Bottom.
- Stock top: incremental offset from the Stock Top.
- Stock bottom: incremental offset from the Stock Bottom.
- Selected contour(s): incremental offset from a Contour selected on the model.
- Selection: incremental offset from a Point (vertex), Edge or Face selected on the model.
- Origin (absolute): absolute offset from the Origin that is defined in either the Setup or in Tool Orientation within the specific operation.
Top offset:
Top offset is applied and is relative to the Top height selection in the above drop-down list.
Bottom Height
Bottom height determines the final machining height/depth and the lowest depth that the tool descends into the stock. Bottom height needs to be set below the Top. Bottom height is used together with the subsequent offset to establish the height.

Bottom Height
- Clearance height: incremental offset from the Clearance Height.
- Retract height: incremental offset from the Retract Height.
- Feed height: incremental offset from the Feed Height.
- Top height: incremental offset from the Top Height.
- Model top: incremental offset from the Model Top.
- Model bottom: incremental offset from the Model Bottom.
- Stock top: incremental offset from the Stock Top.
- Stock bottom: incremental offset from the Stock Bottom.
- Selected contour(s): incremental offset from a Contour selected on the model.
- Selection: incremental offset from a Point (vertex), Edge or Face selected on the model.
- Origin (absolute): absolute offset from the Origin that is defined in either the Setup or in Tool Orientation within the specific operation.
Bottom offset:
Bottom offset is applied and is relative to the Bottom height selection in the above drop-down list.
 Passes tab settings
Passes tab settings
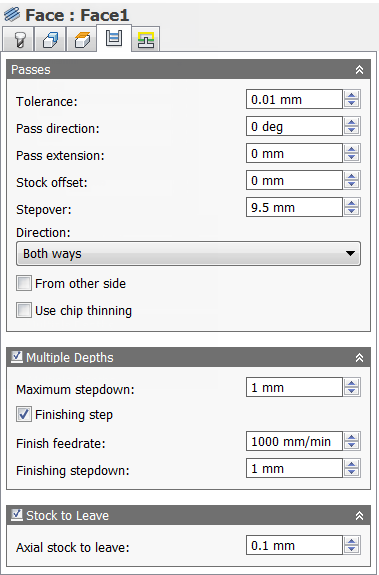
Tolerance:
The tolerance used when linearizing geometry such as splines and ellipses. The tolerance is taken as the maximum chord distance.
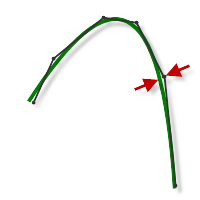
Loose Tolerance .100
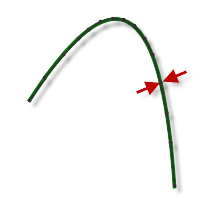
Tight Tolerance .001
CNC machine contouring motion is controlled using line G1 and arc G2 G3 commands. To accommodate this, CAM approximates spline and surface toolpaths by linearizing them creating many short line segments to approximate the desired shape. How accurately the toolpath matches the desired shape depends largely on the number of lines used. More lines result in a toolpath that more closely approximates the nominal shape of the spline or surface.
Data Starving
It is tempting to always use very tight tolerances, but there are trade-offs including longer toolpath calculation times, large G-code files, and very short line moves. The first two are not much of a problem because Inventor HSM calculates very quickly and most modern controls have at least 1MB of RAM. However, short line moves, coupled with high feedrates, may result in a phenomenon known as data starving.
Data starving occurs when the control becomes so overwhelmed with data that it cannot keep up. CNC controls can only process a finite number of lines of code (blocks) per second. That can be as few as 40 blocks/second on older machines and 1,000 blocks/second or more on a newer machine like the Haas Automation control. Short line moves and high feedrates can force the processing rate beyond what the control can handle. When that happens, the machine must pause after each move and wait for the next servo command from the control.
Pass direction:
Specifies the direction of the passes.
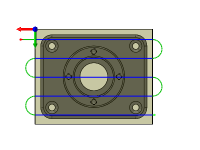
Pass direction @ 0°
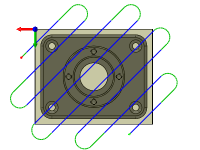
Pass direction @ 45°
Pass extension:
Distance to extend the passes beyond the machining boundary.
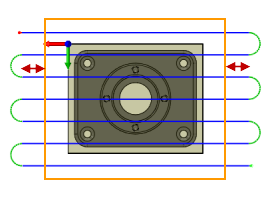
Pass extension
Stock offset:
Specifies the distance to offset the stock contour outwards.
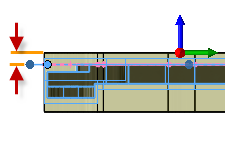
Stock offset
Stepover:
Specifies the horizontal stepover between passes. By default this value is 95% of the cutter diameter less the tool corner radius.
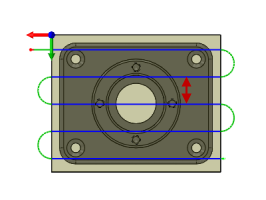
Horizontal stepover
Direction:
The Direction option lets you control if Inventor HSM should try to maintain either Climb or Conventional milling.
Climb
Select Climb to machine all the passes in a single direction. When this method is used, Inventor HSM attempts to use climb milling relative to the selected boundaries.
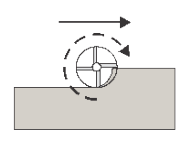
Climb
Conventional
This reverses the direction of the toolpath compared to the Climb setting to generate a conventional milling toolpath.
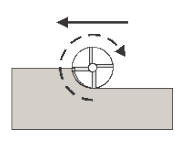
Conventional
From other side
Specifies that the toolpath starts on the other side of the part.
Unselected
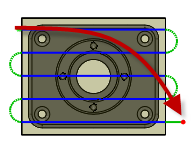
Selected
Use chip thinning
Enable to use a roll-on cut to keep the chips thin.
Multiple Depths
Specifies that multiple depths should be taken.
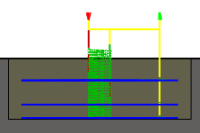
With Multiple Depth cuts
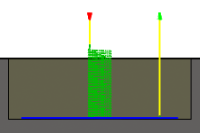
Without Multiple Depth cuts
Maximum stepdown:
Specifies the maximum stepdown between Z-levels for roughing.
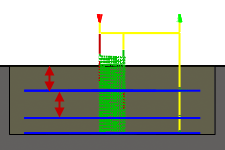
Maximum stepdown - shown without finishing stepdowns
Finishing step
Specifies that a finishing step should be taken.
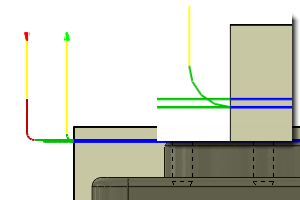
Finishing step
Finish feedrate:
Feedrate used for the final finishing pass.
Finishing stepdown:
The size of each stepdown in the finishing passes.
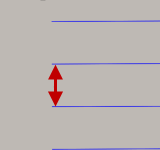
Finishing stepdown
Stock to Leave
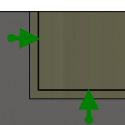
Positive
Positive Stock to Leave - The amount of stock left after an operation to be removed by subsequent roughing or finishing operations. For roughing operations, the default is to leave a small amount of material.
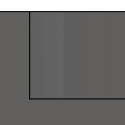
None
No Stock to Leave - Remove all excess material up to the selected geometry.
Negative
Negative Stock to Leave - Removes material beyond the part surface or boundary. This technique is often used in Electrode Machining to allow for a spark gap, or to meet tolerance requirements of a part.
Axial (floor) stock to leave
The Axial stock to leave parameter controls the amount of material to leave in the axial (along the Z-axis) direction, i.e. at the end of the tool.
Axial stock to leave
Both radial and axial stock to leave
Specifying a positive axial stock to leave results in material being left on the shallow areas of the part.
For surfaces that are not exactly horizontal, Inventor HSM interpolates between the axial and radial (wall) stock to leave values, so the stock left in the axial direction on these surfaces might be different from the specified value depending on surface slope and the radial stock to leave value.
Changing the radial stock to leave automatically sets the axial stock to leave to the same amount, unless you manually enter the axial stock to leave.
For finishing operations, the default value is 0 mm / 0 in, i.e. no material is left.
For roughing operations, the default is to leave a small amount of material that can then be removed later by one or more finishing operations.
Negative stock to leave
When using a negative stock to leave the machining operation removes more material from your stock than your model shape. This can be used to machine electrodes with a spark gap, where the size of the spark gap is equal to the negative stock to leave.
Both the radial and axial stock to leave can be negative numbers. However, when using a ball or radius cutter with a negative radial stock to leave that is greater than the corner radius, the negative axial stock to leave must be less than or equal to the corner radius.
 Linking tab settings
Linking tab settings
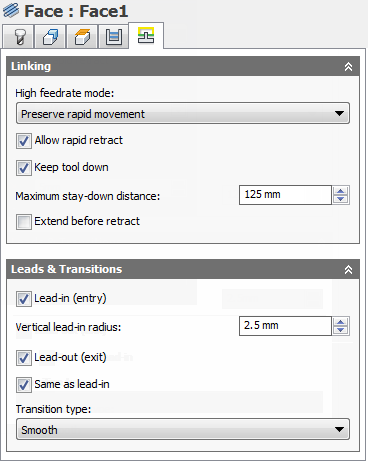
High feedrate mode:
Specifies when rapid movements should be output as true rapids (G0) and when they should be output as high feedrate movements (G1).
- Preserve rapid movement - All rapid movements are preserved.
- Preserve axial and radial rapid movement - Rapid movements moving only horizontally (radial) or vertically (axial) are output as true rapids.
- Preserve axial rapid movement - Only rapid movements moving vertically.
- Preserve radial rapid movement - Only rapid movements moving horizontally.
- Preserve single axis rapid movement - Only rapid movements moving in one axis (X, Y or Z).
- Always use high feed - Outputs rapid movements as (high feed moves) G01 moves instead of rapid movements (G0).
This parameter is usually set to avoid collisions at rapids on machines which perform "dog-leg" movements at rapid.
High feedrate:
The feedrate to use for rapids movements output as G1 instead of G0.
Allow rapid retract
When enabled, retracts are done as rapid movements (G0). Disable to force retracts at lead-out feedrate.
Keep tool down
When enabled, the strategy avoids retracting when the distance to the next area is below the specified stay-down distance.
Maximum stay-down distance:
Specifies the maximum distance allowed for stay-down moves.
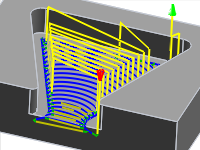
1" Maximum stay-down distance
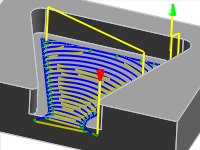
2" Maximum stay-down distance
Extend before retract
Enable to extend the cutting pass beyond the stock before retracting.
Lead-in (entry)
Enable to generate a lead-in.
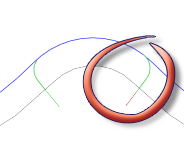
Lead-in
Vertical lead-in radius:
The radius of the vertical arc smoothing the entry move as it goes from the entry move to the toolpath itself.
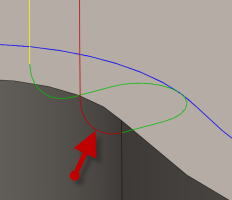
Vertical lead-in radius
Lead-out (exit)
Enable to generate a lead-out.
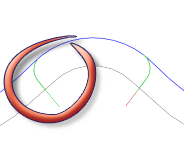
Lead-out
Same as lead-in
Specifies that the lead-out definition should be identical to the lead-in definition.
Vertical lead-out radius:
Specifies the radius of the vertical lead-out.
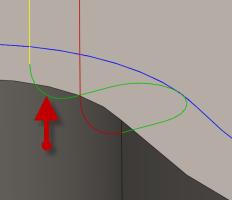
Vertical lead-out radius
Transition type:
Specifies the type of connection done between passes.
- No contact - Sidesteps are not connected with each other on the same Z-level, but connected with a retract move.
- Straight line - Simpler, direct connections using straight lines.
- Shortest path - The shortest possible path between machining areas - typically a move in a straight line.
- Smooth - Use smooth tangential movements using true arcs where appropriate.