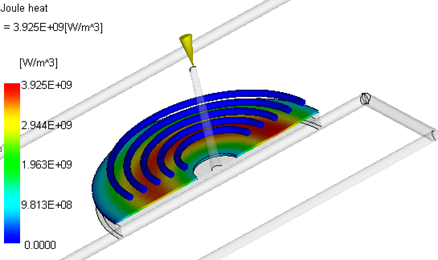
Induction heating has been added to the suite of heating options for simulating rapid heating and cooling analyses, for dual domain and 3D meshed models.
Induction heating is a very complex technology and is very dependent upon the correct choice of mold materials. The strategic placement of highly magnetic inserts on the part where heating is desired, is very important, as well the placement of metal inserts with poor magnetic properties in the mold to enhance the magnetic field near the part. The placement and exact geometry of the induction coils are also very important and need to be modeled in exact detail.
When simulating induction heating, you will need to specify mold materials for the entire mold, because the accuracy of the induction solution depends entirely upon the relative magnetic permeability and electrical resistivity in the mold. You will also need to specify the thermal conductivity, density and specific heat. Only specific mold materials can be used for induction heating in order to get the full benefit of the technology; ordinary mold materials are not highly magnetic and will not be very efficient in induction heating applications.
Accurately model the exact geometry of the entire mold, including the induction coils, to get optimum induction heating at the part's surface. Once in the simulation environment, set the property of the induction coils CAD body to Induction coil (3D). The high and low potential terminals on this coil body are set as boundary conditions. On the high potential terminal, specify the source current, or the voltage, applied to the terminal. Set the frequency of the alternating current applied to the coil, on the Induction coil (3D) body itself.
- Joule heat,
- Magnetic vector potential,
- induced current density,
- source current density,
- source electric potential,
- magnetic flux density,