
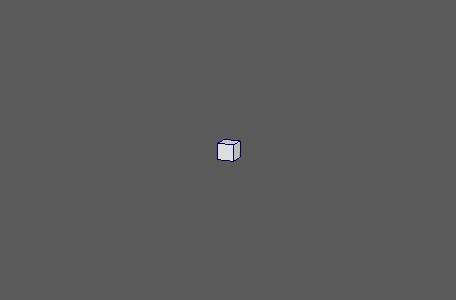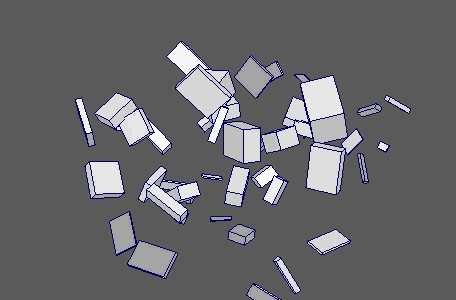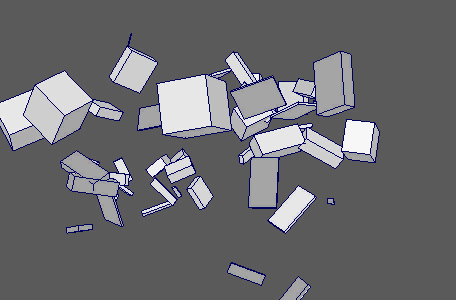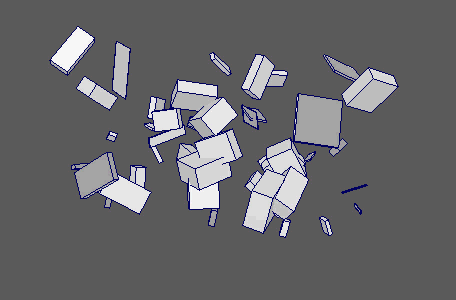
Apply various forms of animated noise to your objects' channels.
Noise Node
- Noise Type
-
Determines the type of noise generated. Options include:
- Perlin Noise: A gradient noise with an organic texture that can resemble marble, wood, clouds, fire, etc.
- Seek: Fully procedural random walk, in which points will wander from the centre of the screen in random directions. Particularly useful for simulating insect movement when used in conjunction with the Flight node.
- fBM Noise: Stands for Fractal Brownian Motion, but also known as Turbulence. Similar to Perlin Noise except objects will speed up and slow down.
- Perlin Noise (looping): A loopable version of Perlin Noise.
- Amplitude X, Amplitude Y, Amplitude Z
- Controls the strength of the noise in the respective axes.
Perlin/fBM Noise settings
- Frequency X, Frequency Y, Frequency Z
- Controls the speed of the noise in the respective axes.
Seek Noise settings
- Seek Angle (FoV)
- Determines the angle at which particles can wander.
Perlin Loop settings
- Loop time (frames)
- Determines the number of frames until the noise loops.
Strength
- Strength
- Fades the node's effect for all the objects at the same time.
- Random Strength
- Smoothly fades the node's effect on all the objects in a random order.
- Step Strength
- Turns the node's effect off one object at a time.
- Strength Map
- Determines the input file (2D texture, animated texture, etc) that controls the shape of the node's effect.
- Map Projection Axis
- Determines the axis along which the Strength Map is projected.
- Map Helper
- Displays the object being used to interactively place the
Strength Map in the scene. You can right-click the field to create a new helper object (a plane) if none exists. You can also middle-drag a mesh into this field or right-click to connect a selected mesh. If a mesh is already connected, you can also right-click to break its connection or show it in the Outliner.
Note: For the best results, assign the same texture to both the Strength Map and the Map Helper (this automatically happens when creating a new helper object).
Per Point Adjustments
- Step
- Sets the time difference between the noise given to each object. Lower values make objects look like they're following each other over the noise.
- Octaves
- Sets the number of noise octaves. Higher values produce more detailed noise.
- Random Seed
- Adjusts the randomization of the noise.
- Persistence
- The strength of each noise octave.
- Absolute Noise
- Ensures that the node returns only positive numbers.
- Whole Numbers
- Ensures that the node returns only whole numbers.
- Uniform Noise
- Noise values are scaled uniformly in the x, y, and z axes.