
You can use the rendering buttons in the Status line (toolbar), or use the buttons in the Render View toolbar to perform various operations.
Some tools are renderer specific. For example, the IPR tools appear only for Maya software and mental ray rendering.
For more information on Render View, see About render view rendering.
- Redo Previous Render
-
Renders the same view you rendered last. If you rendered a region the last time, Redo Previous Render renders the entire image.
Right-click this button to select a camera. All cameras, default and user-defined, are available.
- Render Region
-
Renders only the region with a marquee. This is useful if you’ve made a change to part of the surface on which you want to perform a quick test render. See Render a region of your scene for details.
- Snapshot
-

 Right-click this button to select a camera. A wireframe snapshot is taken of the view you select and loaded as a background into
Render View. The renderer used in the snapshot is the renderer you use in your current workspace:
Viewport 2.0 or
Legacy Default Viewport.
Right-click this button to select a camera. A wireframe snapshot is taken of the view you select and loaded as a background into
Render View. The renderer used in the snapshot is the renderer you use in your current workspace:
Viewport 2.0 or
Legacy Default Viewport.
You can then marquee a region to render in front of the snapshot’s background and click the Render region icon.
Right-click this button to select a camera. All cameras, default and user-defined, are available.
Note: This option does not work when IPR rendering. - Redo Previous IPR Render
-
IPR renders the same view last IPR rendered.
Right-click this button to select a camera. All cameras, default and user-defined, are available.
- Refresh the IPR Image
-

Completely updates the entire image based on all changes you have made. The refresh occurs a bit at a time—loading all the samples for the entire image may use large amounts of memory.
- Open Render Settings Window
-
Opens the Render Settings window.
- Display RGB Channels
-

Displays the image with RGB channels. This is the default display mode.
Right-click this button to select individual channels. Each channel has a corresponding icon:
Channel Icon RGB Channels

Red
Green
Blue
Luminance

- Display Alpha Channel
-
Displays the image’s alpha channel only. See Use Background and Matte Opacity for a few examples of how the alpha channel is used.
- Display Real Size
-
Displays the image at its exact pixel resolution. See also Test render a low-res still or frame.
- Keep Image
-

Keeps the current image so you can view it later. When you keep more than one image, a slider displays at the bottom of the window. Drag this slider to view a previously “kept” image.

You can also keep rendered images with any annotation you’ve added. Right-click the Keep Image button, and select the Keep Image with Comment option. When the Custom Comment dialog box appears, enter your text into the field, and click OK. Custom comments appear at the bottom of the image.
Note:The stored (“kept”) images are lost when you end your session.
Remove Current Image / Remove All Images
Right-click the icon to select either the Remove Current Image or Remove All Images option.
These options can also be selected using the File > Remove Image from Render View and File > Remove All Images from Render View in the Render View window. See Render View menu bar for more information.
- Remove Current Image
-
Releases the current image (and the memory it uses) from Render View. Select the image you want to remove using the slider at the bottom of the window.
- Remove All Images
-
Releases all images (and the memory these images use) from Render View so that only the most recently rendered image remains.
If you are viewing one of the saved images in the Render View window, this option still removes all saved images, including the currently displayed image. Only the most recently rendered image is kept.
Tip:Only “kept” images can be removed. If you are viewing a newly rendered image in the Render View window that has not been kept, selecting this option will display an error message that the current image cannot be removed.
- Renderer
-
Select a renderer from the drop-down list: Maya Software, Maya Hardware, Maya Hardware 2.0, Maya Vector, mental ray and any additional 3rd party renderers you have installed.
- Exposure
-
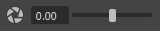
Adjust the brightness for display. Lowering the exposure allows you to view detail that is not visible in highlights by default.
You can set a value in the usual ways by using the slider, by typing in the numeric box, or by clicking in the numeric box and dragging with Ctrl + Middle mouse button. In addition, you can:- Click the icon to toggle between the default and modified values.
- Press Ctrl + Minus to decrease by fine increments.
- Press Ctrl + Alt + Minus to decrease by coarse increments.
- Press Ctrl + = to increase by fine increments.
- Press Ctrl + Alt + = to increase by coarse increments.
This is a diagnostic option that is not saved in the scene. It is not applied to the rendered output, although you can save a color-managed image from the Render View using .
- Gamma
-
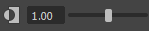
Adjust the contrast, or brightness of the midtones in the image for display. Increasing the gamma allows you to see details in the shadows of your image.
You can set a value in the usual ways by using the slider, by typing in the numeric box, or by clicking in the numeric box and dragging with Ctrl + Middle mouse button. In addition, you can:- Click the icon to toggle between the default and modified values.
- Press Ctrl + ; to decrease by fine increments.
- Press Ctrl + Alt + ; to decrease by coarse increments.
- Press Ctrl + ' to increase by fine increments.
- Press Ctrl + Alt + ' to increase by coarse increments.
This is a diagnostic option that is not saved in the scene. In particular, you do not need to set it to 2.2 to emulate sRGB.It is not applied to the rendered output, although you can save a color-managed image from the Render View using .
- View Transform
-
 Control the view transform that converts colors from the working color space for display. This is useful, for example, if you want to quickly check the raw color values. The available color spaces that you can choose depend on whether you are using an OCIO configuration file for color management.
Control the view transform that converts colors from the working color space for display. This is useful, for example, if you want to quickly check the raw color values. The available color spaces that you can choose depend on whether you are using an OCIO configuration file for color management.- Click the icon to toggle the view transform off temporarily, and back on again.
- Use the drop-down list to select a different view transform.
They are not available unless color management is enabled. See Color Management.
They are diagnostic options that are not saved in the scene. They are not applied to the rendered output, although you can save a color-managed image from the Render View using .
- Lock/unlock render layer and render pass rendering
-
Toggle between rendering all upstream images used by the compositing graph or rendering only the 2d compositing graph.
 /
/
Keep button unlocked
 to render all dependencies. For example, if your render target uses a render pass, the layer containing that pass is re-rendered. if the render target uses the result of other render targets, those render targets are re-rendered, along with their own dependencies.
to render all dependencies. For example, if your render target uses a render pass, the layer containing that pass is re-rendered. if the render target uses the result of other render targets, those render targets are re-rendered, along with their own dependencies.
When working with a compositing graph, lock button
 to render only the 2d compositing graph.
to render only the 2d compositing graph.
When making a change to the scene, unlock this button and render. If you have a render target selected in the Render View, the result of that render target is displayed after you render. After you have finished making your scene changes, lock this button to work with your compositing graph and render your render target without waiting for re-rendered passes.
Caution: If you rename the nodes in your graph, for example, a render layer node, you must unlock this button before re-rendering your render target.
Note: This button only appears if the renderer you have selected supports render targets (in other words, the mental ray renderer). If you have selected mental ray as your renderer but your scene has no render targets; or, you have selected in your Render View menu bar, this button exists but is disabled and greyed out
before re-rendering your render target.
Note: This button only appears if the renderer you have selected supports render targets (in other words, the mental ray renderer). If you have selected mental ray as your renderer but your scene has no render targets; or, you have selected in your Render View menu bar, this button exists but is disabled and greyed out .
Note: This option is currently not supported for batch rendering and IPR.
.
Note: This option is currently not supported for batch rendering and IPR. - Pause IPR Tuning
-

Pauses the updating of the selected IPR region in the Render View.
- Close IPR File and Stop Tuning
-
Closes the current IPR file and ends the current IPR session.
