Use render proxies to manage large scenes with complex geometry. If your scene includes a complex piece of geometry, you can first export the object as a mental ray assembly file, and then replace it in your scene with a placeholder object that references this file. When you render, the exported object is loaded into memory and rendered with the rest of your scene. The overall translation is instantaneous, since there are virtually no geometries being passed to mental ray. Translation time and memory usage are therefore drastically reduced, allowing mental ray for Maya to render large scenes.
The use of render proxies can cut down translation time and memory usage in several ways. First of all, complex geometry is never loaded into Maya. It is only loaded into mental ray if necessary. If the proxy is occluded or behind another object or behind the camera, then it is not loaded. Also, the texture file associated with the render proxy is not loaded unless the proxy is. Furthermore, mental ray for Maya can also unload the entire render proxy during rendering in order to reduce memory consumption.
Create a render proxy as follows:
- Export your geometry by selecting File > Export Selection >
 . See File > Export All, Export Selection (mental ray) for more information.Note:
. See File > Export All, Export Selection (mental ray) for more information.Note:When you export your render proxy using the default settings, you also export its shading network. Therefore, shading that you apply to the placeholder does not take effect. To change this behavior, customize your export options by selecting File > Export Selection >
 .
. - Under the General Options section, File type attribute, select mentalRay.
- Under the File Type Specific Options section, Export selection output: attribute, select Render Proxy (Assembly).Note:
When creating your render proxy, do not compress your .mi header file because Maya needs to read the bounding box data from the .mi file.
- Click Export Selection, and save your object as a .mi file.Note:
Place your proxy object at the origin before exporting it to a .mi file. For example, if your proxy is at x=10 during the export, the placeholder item will also be moved by 10.

Rendering your scene using a render proxy
- Create a simple base geometry as a placeholder for your more complex geometry.
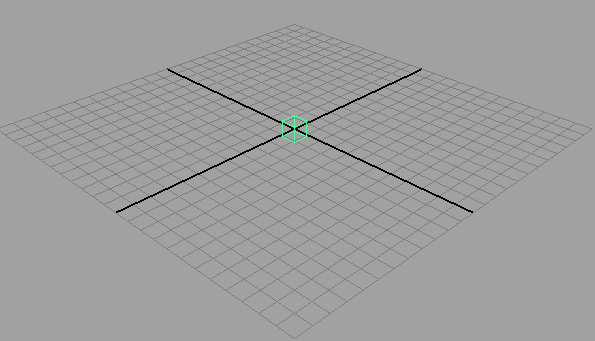
- In the base geometry's shape node, expand the mental ray section. In the Render Proxy section, select your render proxy .mi file. Your base geometry is now resized so that it fits the original render proxy object.

- In the base geometry's transform node, expand the mental ray section. In the Render proxy section, ensure that Renderable is enabled to render the proxy instead of your base geometry.
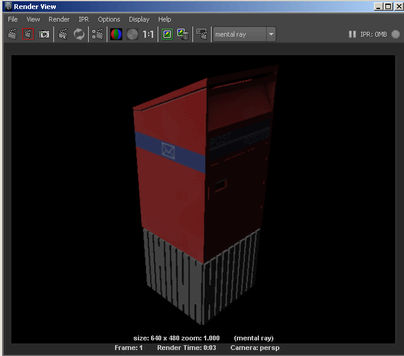
- Render your scene. Your base geometry is replaced by your render proxy in the render view.
Assign the proxy file before animating the placeholder. The Freeze Transformations operation fails if the transformation has incoming connections. Therefore, you should animate the placeholder after assigning to it the proxy file.