Theoretically, cooling time is proportional to the square of the heaviest part wall thickness and the largest runner diameter raised to the power of 1.6, and inversely proportional to the thermal diffusivity of the polymer melt.
Cooling time
These relationships are given by:
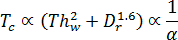
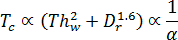
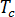 is the cooling time,
is the cooling time, 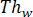 is the thickness at the thickest part of the part wall,
is the thickness at the thickest part of the part wall, 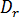 is the diameter of the largest runner, and
is the diameter of the largest runner, and 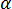 is the thermal diffusivity.
is the thermal diffusivity.
In other words, doubling the wall thickness quadruples the cooling time.
The thermal diffusivity of polymer melt is defined as:
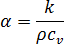
where:
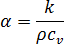
where:
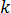 is the thermal conductivity
is the thermal conductivity 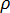 is the density
is the density 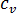 is the specific heat constant volume
is the specific heat constant volume
Reynolds number and coolant flow
The type of coolant flow can be determined by the Reynolds number, 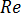 , as listed in the following table.
, as listed in the following table.
Reynolds number (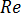 ) ) |
Type of flow |
|---|---|
10,000 < 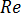 |
Turbulent |
2,300 < 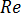 < 10,000 < 10,000 |
Transition |
100 < 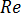 < 2,300 < 2,300 |
Laminar |
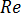 < 100 < 100 |
Stagnated |
The Reynolds number is defined as:
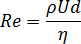
where:
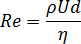
where:
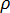 is the density of the coolant
is the density of the coolant 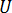 is the averaged velocity of the coolant
is the averaged velocity of the coolant 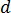 is the diameter of the cooling channel
is the diameter of the cooling channel 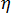 is the dynamic viscosity of the coolant
is the dynamic viscosity of the coolant