The Geometry panel of the Import Options dialog controls how 3ds Max derives AutoCAD primitives and whether 3ds Max uses the scene material definitions when linking to or reloading the AutoCAD drawing. It also presents options for geometry translation and for toggling inclusion of certain elements in the DWG or DXF file.
Model Scale group
- Incoming file units
- This drop-down list lets you specify the base units in the incoming file. Available only when Rescale is on.
- Rescale
- Allows rescaling the incoming geometry by a factor corresponding to the most common unit type used. The importer tries to detect the units of the DWG file being imported, compares those units with the 3ds Max system units, and then provides the appropriate conversion factor.
For example, if a drawing file is built in millimeters and 3ds Max has its System Units set to inches, the AutoCAD DWG/DXF Import Options dialog automatically has Rescale on and the Incoming File Units set to millimeters.
When there is a scale disparity, It's generally advisable to rescale an incoming drawing to more realistic units to account for the precision limitations of 3ds Max compared to AutoCAD. For instance, if you import an airport designed in millimeters in AutoCAD, set Incoming File Units to Feet or Meters.
Note: If the units are unspecified in the drawing, the drop-down list is blank. In this case, if you click OK to perform the import with Rescale on, you are prompted to select a value for Incoming File Units, and are then returned to the AutoCAD DWG/DXF Import Options dialog. - Resulting model size
- Incoming geometry is evaluated to determine its bounding box size. This field displays the scene extents based on three factors:
- Incoming file units
- System units in 3ds Max
- Display units in 3ds Max
Note: If 3ds Max cannot determine the size, the field shows “(Drawing Extents Not Known)”.
Derive AutoCAD Primitives By group
This group box contains options for translating the geometry in the DWG or DXF file to 3ds Max format.
- [derivation method]
- Choose the method for deriving imported AutoCAD primitives from this drop-down list. The options are as follows:
- Layer, Blocks as Node Hierarchy All objects on a given layer in the AutoCAD drawing that aren't in blocks are combined into a single Editable Mesh or Editable Spline object when imported into 3ds Max. The name of each imported object is based on the AutoCAD object's layer. The imported object name has a “Layer:” prefix and is followed by the layer name. For example, all AutoCAD objects residing on the layer Walls become part of the Editable Mesh named Layer:Walls after they are imported to 3ds Max.
Each block is imported separately as a hierarchy, with the block itself as the parent object and its constituent parts as child objects. The child objects of the block are combined by layer.
- Layer, Blocks as Node Hierarchy, Split by Material This works the same as the Layer, Blocks as Node Hierarchy option, with the following additional functionalities: the combination of non-block objects by layer, followed by material and support for multiple materials assigned to ACIS solid and polymesh geometry.
- Non-block layer combination
For example, take an AutoCAD file with six objects in layer A: three have a Brick material and three have a Stone material. Using this option, this file would be imported in the form of two objects, or nodes, one containing the Brick material and the other with the Stone material.
Each block is imported separately as a hierarchy, with the block itself as the parent object and its constituent parts as child objects. The child objects of the block are combined by layer.
- Multiple material support
On import, ACIS solids and polymesh geometry can support multiple materials. For polymesh geometry, one material is supported per face. For an ACIS solid, if the solid has more than one material associated with it, a multi/sub object material is created that contains the materials used. If the solid has only one material associated with it, a standard/architectural material is assigned instead.
Note: Multiple material support for ACIS solids applies to DWG files imported or file linked from Revit Architecture 2008 or AutoCAD Architecture (formerly Architectural Desktop or ADT) 2007 and later.Note: This derivation method is intended for use with AutoCAD 2007 (and later) format files. Using this method with DWG files created with previous versions of AutoCAD may result in data loss. - Entity, Blocks as Node Hierarchy Every imported object not in a block is represented as a separate object in the 3ds Max scene, without regard to layers. The nodes are then placed on scene layers that correspond to the drawing layers. Each block is imported separately as a hierarchy, with the block itself as the parent object and its constituent parts as child objects. The child objects of the block are combined by layer.
One benefit of this option is that you can apply instanced animation controllers to block subcomponents and thus, by transforming a single member, transform all members at once. For example, in a scene containing a conference table with six chairs around it, you could move all of the chairs simultaneously by moving a single chair.
Another advantage is that all geometry is instanced, so edited UVs and normals and other modifications need be done only once.
Multiple materials per object are supported with this option, if needed. If the object is an ACIS solid, and has more than one material associated with it, a multi/sub object material is created containing the materials that can be edited in the Materials Editor. If the solid has only one material associated with it, a standard/architectural material is assigned instead. If the object is a Polymesh, one material per face is supported.
Note: Multiple material support for ACIS solids applies on the DWG files imported or file linked from Revit Architecture 2008 or AutoCAD Architecture (formerly Architectural Desktop or ADT) 2007 and later.Note: This derivation method setting might cause unreliable material propagation when importing drawings containing dynamic blocks. Materials may propagate to some block instances and not to others.Warning: This option has the potential to create an enormous number of objects in your scene. - Layer Imported objects are combined in 3ds Max according to their layer. Objects in each of the associated application's layers are combined into one object, with the exception of blocks, each of which is represented as an individual VIZBlock (not a hierarchy). Multiple inserts of the same block are represented using instances in the scene. Material assignments are lost but material IDs are preserved.
- Color Imported AutoCAD objects are combined in 3ds Max according to their color. All objects of the same color are combined into one object, with the exception of blocks, each of which is represented as an individual VIZBlock (not a hierarchy). Multiple inserts of the same block are represented using instances in the scene. Material assignments are lost but material IDs are preserved. Note: Blocks can contain objects with different colors. However, when sorting, 3ds Max considers only the color of the block itself. Also, 3ds Max objects can only display one color, unless a material is applied.
- Color and Material Imported AutoCAD objects are combined in 3ds Max according to their material color. All objects with the same material color are combined into one object, with the exception of blocks, each of which is represented as an individual VIZBlock (not a hierarchy). Multiple inserts of the same block are represented using instances in the scene. Material assignments are not lost, and material IDs are preserved.
- Entity Provides a one-to-one correspondence between AutoCAD objects and 3ds Max objects. For each imported object or block in the imported file, the importer creates an independent object or VIZBlock, respectively, in the scene. Material assignments are lost but material IDs are preserved. Warning: This option has the potential to create an enormous number of objects in your scene.Note: When working with drawings exported from Revit, it is recommended that you do not use this setting.
- One Object All imported objects are combined into a single VIZBlock. Material assignments are lost but material IDs are preserved.
- Layer, Blocks as Node Hierarchy All objects on a given layer in the AutoCAD drawing that aren't in blocks are combined into a single Editable Mesh or Editable Spline object when imported into 3ds Max. The name of each imported object is based on the AutoCAD object's layer. The imported object name has a “Layer:” prefix and is followed by the layer name. For example, all AutoCAD objects residing on the layer Walls become part of the Editable Mesh named Layer:Walls after they are imported to 3ds Max.
- Use Extrude modifier to represent thickness
- When on, objects with thickness receive an Extrude modifier to represent the thickness value. You can then access the parameters of this modifier and change the height segments, capping options, and height value. Unavailable with the Layer, Blocks As Node Hierarchy option.
When off, objects with thickness (and closed capped objects) are converted directly to mesh objects.
- Create one scene object for each ADT object
- AutoCAD Architecture (formerly Architectural Desktop or ADT) objects are imported as a single object instead of being separated into their constituent components. This means that if you import an ADT door object, the door is represented as one object instead of three (frame, step, door). Turning on this switch makes importing faster and the scene size smaller. Note: This switch presents several modeling concerns that you should be aware of:
- Material assignments from ADT are not translated during the import process..
- If you want to assign materials to these objects, use Multi/Sub-Object materials. The assigned material IDs match the color indices specified in ADT (red=1, white=7, and so on).
- Depending on the Texture Mapping option you choose, UVW coordinates are translated correctly.
- Use scene material definitions
- When on, 3ds Max checks the current scene for any currently used materials with the exact same name as a material name in the incoming DWG file. If a match is found, the importer does not translate the drawing's material, but instead uses the material defined in the scene.
When off, the File Link Manager always uses the material definitions contained in the DWG file, and will overwrite scene materials with the same name, regardless of which objects the material is applied to. All material definitions stored in the DWG file are reloaded (even when using a selective reload). If you make changes to a linked material, in Autodesk VIZ, then reload, those changes will be lost (if the switch is off).
Geometry Options group
- Weld nearby vertices
- Sets whether coincident vertices of converted objects are welded, according to the Weld Threshold setting. Welding smoothes across seams and unifies normals of objects with coincident vertices.
- Weld threshold
- Sets the distance that determines whether vertices are coincident. If the distance between two vertices is less than or equal to the Weld Threshold, the vertices are welded together.
- Auto-smooth adjacent faces
- Assigns smoothing groups according to the Smooth Angle value. Smoothing groups determine whether faces on an object render as a smooth surface or display a seam at their edges, creating a faceted appearance.
- Smooth-angle
- Controls whether smoothing occurs between two adjacent faces. If the angle between the two face normals is less than or equal to the smooth angle, the faces are smoothed.
- Orient normals of adjacent faces consistently
- Analyzes the face normals of each object and flips normals to make their directions consistent. If the imported geometry is not properly welded, or if 3ds Max can’t determine the object's center, normals might be oriented in the wrong direction. Use the Edit Mesh or Normal modifiers to flip normals.
When this option is off, 3ds Max calculates normals according to the face vertex order in the drawing file. Face normals for solid objects are already unified. Make sure this option is off when importing drawings containing solid objects.
You should also make sure this option is off when working with AutoCAD Architecture files.
AutoCAD solids will never have their normals unified, regardless of the setting of this import toggle. Solids generate faces and normals correctly.
- Cap closed splines
- Applies an Extrude modifier to all closed objects, and turns on the Cap Start and Cap End options of the modifier. The Extrude modifier Amount value for a closed entity with no thickness is set to 0. Capping makes closed entities with thickness appear solid and closed entities without thickness appear flat. When Cap Closed Objects is turned off, the Extrude modifier Cap Start and Cap End options for closed entities with thickness are turned off. No modifiers are applied to closed entities without thickness, except for Circle, Trace, and Solid. Note: If Use Extrude Modifier to Represent Thickness is off, 3ds Max does not apply an Extrude modifier to closed objects.
- Texture mapping
- The texture mapping settings affect the loading time of models that have many objects with stored UVW Coordinates for texture mapped materials. Note: This setting only applies to geometry that is stored as a mesh in the scene. Spline shapes marked as renderable have separate controls for UVW coordinate generation on the Spline Rendering panel.
- No mapping coordinates When No Mapping Coordinates is used, 3ds Max does not generate texture coordinates for the mesh objects that are imported.
When drawings are imported, objects are added to the scene as Editable Mesh objects that do not have UVW coordinate assignments. Before assigning materials to imported objects, you'll need to apply a UVW Map modifier to add texture coordinates. When you then apply the material and the material or texture map is set to Show Map in Viewport, the texture map is displayed if the viewport is set to Smooth + Highlights. If the UVW Map modifier is not applied, the object turns gray and you'll see a Missing Map Coordinates dialog when you render the scene.
This option gives you faster loading speed, but no UVW coordinate generation.
- Generate coordinates for all objects This option forces all objects to have UVW coordinates generated when the drawing is imported.
This option tells the DWG/DXF Importer to create UVW coordinates, but loading time is increased while the coordinate generation occurs.
- No mapping coordinates When No Mapping Coordinates is used, 3ds Max does not generate texture coordinates for the mesh objects that are imported.
- Curve steps
- Adjusts how smoothly an arc or curve appears when the drawing is imported. Larger numbers result in smoother curves. Default=10.
- Maximum surface deviation for 3D solids
- Specifies the maximum allowable distance from the 3ds Max surface mesh to the parametric 3D solid surface. Small numbers produce more accurate surfaces with a greater number of faces. Large numbers produce less accurate surfaces with fewer faces. In most cases, the default value suffices. Default=1.0.
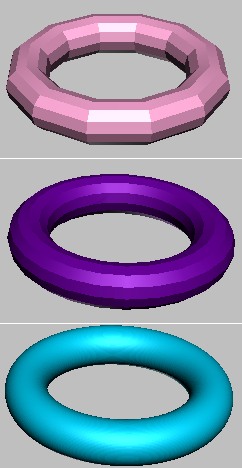
Imported 3D solid with different Surface Deviation settings
Top: Surface Deviation=10.0
Center: Surface Deviation=1.0 (the default)
Bottom: Surface Deviation=0.1
Include group
This group allows you to toggle the inclusion of specific parts of a drawing file during the import process.
- External References (xrefs)
- Imports xrefs attached to the drawing file.
- Lights
- Imports lights from pre-AutoCAD 2007 drawing files.
- Sun and Sky
- Imports Sun and Shadows position from the drawing file (AutoCAD / AutoCAD Architecture 2008 and Revit 2008 only). Note: You must set mental ray as the active renderer for you to see the Sun and Sky effect.
- Hatches
- Imports hatches from the drawing file. Warning: This stores each line or dot in the hatch pattern as a separate component of the VIZBlock that defines the hatch; this can create a very large number of objects in your scene.
- Views and Cameras
- Imports named views and cameras from the drawing file, and converts named views to 3ds Max cameras. Note: Orthographic views do not translate correctly in imported DWG files. However, there are no problems with Perspective views.
- Points
- Imports points from the drawing file. Note: The imported point objects are represented in 3ds Max as Point Helper objects.
- UCSs (grids)
- Imports user coordinate systems (UCS) from the drawing file and converts them to 3ds Max grid objects.