The Max Stress Criterion identifies three possible modes of failure: Longitudinal Failure, Transverse Failure, or Shear Failure.
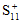 = Value of σ11 at longitudinal tensile failure
= Value of σ11 at longitudinal tensile failure
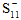 = Value of σ11 at longitudinal compressive failure
= Value of σ11 at longitudinal compressive failure
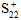 = Value of σ22 at transverse tensile failure
= Value of σ22 at transverse tensile failure
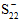 = Value of σ22 at transverse compressive failure
= Value of σ22 at transverse compressive failure
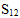 = Absolute value of σ12 at longitudinal shear failure
= Absolute value of σ12 at longitudinal shear failure
Longitudinal Failure occurs whenever 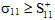 or
or 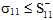
Transverse Failure occurs whenever 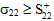 or
or 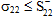
Longitudinal Shear Failure occurs whenever 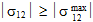
Failure Index = Max. Absolute Value of 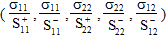
Since the failure index is a simple ratio of stresses, the failure load can be computed by simply dividing the applied load by the failure index. For example, consider a composite material subjected to a transverse normal stress of 1 psi. If the computed failure index is 0.0002, the transverse normal stress at failure is (1 psi)/0.0002 = 5000 psi.