
Using AutoCAD Map 3D, you can create node, network, or polygon topologies.
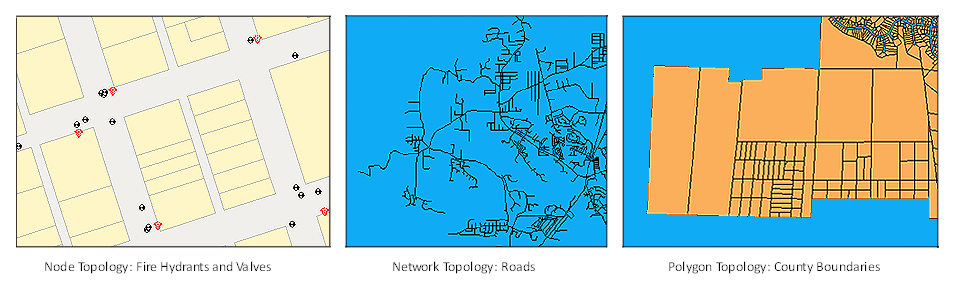
Node Topologies
- Define the interrelation of nodes (point objects).
- Are often used in conjunction with other topologies in analysis.
Network Topologies
- Connect links (lines) to form a linear network.
- Links can connect nodes.
An example of network topology is a water-distribution application that traces the flow of water from a pumping station to residences. A street network is another example. For network topologies, you can specify the direction for a link and specify the resistance for a link or node.
Polygon Topologies
- Define polygons that represent enclosed areas such as land parcels and census tracts. A single link defines the common boundary between adjacent areas.
Uses of polygon topology include tax assessment and land planning in which parcels of land are represented by polygons. Political boundaries, such as voting districts, city, state, or provincial boundaries, special districts, and school districts, are other examples of the use of polygon topology.
Notes
When you create a topology, keep the following points in mind:
- Before you create network or polygon topologies, use the drawing cleanup tools to clean up your map. Node topologies do not usually require cleanup.
- Before you create a topology, freeze all layers containing objects in paper space (Layout tab). Otherwise, these objects are included in the topology creation when you use the Select All objects option.
- MAPTOPOCREATE can create topologies on layers that are turned off. It does not affect layers that are frozen.
- When creating network or polygon topologies, if you enable the Create New Nodes option, AutoCAD Map 3D detects where lines are connected and assigns nodes to end points. It creates physical or explicit node objects at all link end points where no objects exist. If the layer you specify does not exist already, AutoCAD Map 3D creates the layer with a color of 7 and a CONTINUOUS linetype.
- You can create nodes using ACAD_POINT. To change their appearance and size, at the Command prompt, enter ddptype.
- When you create a topology, information is stored as object data on each element of the topology and is saved with the map. Each node, link, or polygon is automatically given a unique identification (ID) number. Each ID is automatically processed when you use any topology command.