| Long name (short name) |
Argument types |
Properties |
|
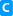
-absolute(-a)
|
|
|
|
preserve existing world object transformations
(overall object transformation is preserved
by modifying the objects local transformation)
If the object to parent is a joint, it will
alter the translation and joint orientation of
the joint to preserve the world object
transformation if this suffices. Otherwise, a
transform will be inserted between the joint
and the parent for this purpose. In this case,
the transformation inside the joint is not
altered.
[default]
|
|
-addObject(-add)
|
|

|
|
preserve existing local object transformations
but don't reparent, just add the object(s) under
the parent. Use -world to add the world as
a parent of the given objects.
|
|
-noConnections(-nc)
|
|

|
|
The parent command will normally generate
new instanced set connections when adding instances.
(ie. make a connection to the shading engine for
new instances) This flag suppresses this behaviour
and is primarily used by the file format.
|
|
-noInvScale(-nis)
|
|

|
|
The parent command will normally connect
inverseScale to its parent scale on joints.
This is used to compensate scale on joint.
The connection of inverseScale will occur if both child and parent are joints and no connection is present on child's inverseScale.
In case of a reparenting, the old inverseScale will only get broken if the old parent is a joint. Otherwise connection will remain intact.
This flag suppresses this behaviour.
|
|
-relative(-r)
|
|

|
|
preserve existing local object transformations
(relative to the parent node)
|
|
-removeObject(-rm)
|
|

|
|
Remove the immediate parent of every object specified. To remove only
a single instance of a shape from a parent, the path to the shape
should be specified.
Note: if there is a single parent then the object is effectively deleted from
the scene. Use -world to remove the world as a parent of the given object.
|
|
-shape(-s)
|
|

|
|
The parent command usually only operates on
transforms. Using this flags allows a shape
that is specified to be directly parented under
the given transform. This is used to instance
a shape node. (ie. "parent -add -shape" is
equivalent to the "instance" command).
This flag is primarily used by the file format.
|
|
-world(-w)
|
|

|
|
unparent given object(s) (parent to world)
|
|