
In the Content Browser, you can navigate through folders in different locations, search for files in the Content panel, and then import those files.
Navigating the folders
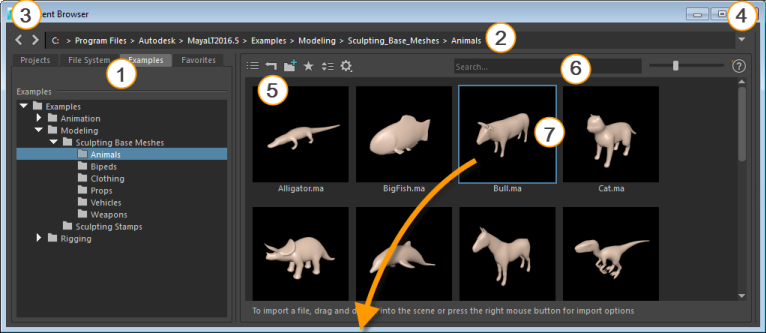
Expand the folder structure in the browsing panel on the left and select a folder to display its contents in the Content panel on the right.
|
Element in Content Browser |
Lets you do this |
|---|---|
|
1: Tabs in the browsing panel |
Find the location of the data you want to load, then expand the folder structure and select a folder to display its contents in the Content panel:
|
|
2: Path bar |
Select or enter an absolute path to find content:
|
|
3: Back/forward arrows |
Navigate among the previous and next locations you have already visited. |
|
4: Navigation arrow |
Open a menu that displays the recent navigation history. Select a location to go to it. |
|
5: Go Up One Directory Level icon |
Click the
|
|
6: Search field |
Search the contents that are currently displayed in the Content panel - see below for details. |
|
7: File |
Import a file into your scene in different ways, such as by dragging and dropping it into a view panel. |
Searching for files
You can search for files in the contents of the current folder using the Search field at the top of the Content panel:
- Start typing a string to find files that match. The files are automatically filtered to match the string as you type.
- Use wildcards (*), such as *ee, to find any file whose name contains that string.
- Enter a file type extension (such as .ma or .jpg) to find all files of that type.
To clear the Search field, click the X at the right end of it, or select the contents and press the Delete or Backspace keys.
Importing files into the scene
To import one or more files
- Double-click a single file.
- Drag and drop one or more selected files into the view panel.
- Right-click one or more selected .mlt, .ma, .mb, or .fbx files and choose
Import.
You can also click the
 icon to open
Import Options.
icon to open
Import Options.
- For .mel files, right-click and choose Source mel file.
 For .py files, drag and drop them into the scene to automatically execute their
onMayaDroppedPythonFile method.
For .py files, drag and drop them into the scene to automatically execute their
onMayaDroppedPythonFile method.
- For sculpting stamps, right-click and choose Use selected stamp - see Stamps for more information.
- For image files, right-click an icon and choose one of these options:
- Open file as normal file texture: For normal textures, Maya LT applies a texture map according to the geometry characteristics—textures are placed onto polygons based on UV information or placed onto NURBS surfaces based on parameterized information.
- Open file as projected file texture: To create projection textures, Maya LT applies a texture map to the surface of a 3D object by projecting a 2D texture into 3D space—in other words, Maya LT projects the texture maps independently of the geometry characteristics.
- Open file as stencilled file texture: Lets you place an image file or texture on a surface and manipulate its placement and size to look like a label. You can use masking techniques to hide unwanted parts of the image.
 icon in the Content panel to open the directory above the current folder and display its content in the Content panel.
icon in the Content panel to open the directory above the current folder and display its content in the Content panel.