Thermal analysis
To run the model, from a command line run:
$ pan -b 06_thermal
The analysis progress is written to file 06_thermal.out. To check progress on Linux, run:
$ tail 06_thermal.out
After the analysis completes, the last few lines of the output file 06_thermal.out should be similar to the following:
inc = 16 time = 38525.953 iter = 3 eps = 0.12810E-11 Increment end inc = 17 time = 88525.953 iter = 1 eps = 0.89174E+00 inc = 17 time = 88525.953 iter = 2 eps = 0.10202E-12 Increment end Analysis completed CPU wall= 34.96875 CPU total= 555.4205 END PROJECT PAN
Actual CPU times will differ.
Quasi-static mechanical analysis
Run the analysis from the command line:
$ pan -b 06_mechanical
After the analysis completes, the last few lines of the output file 06_mechanical.out should be similar to the following:
Substrate removal time increment inc = 16 time = 188525.95 iter = 1 eps = 0.27463E+06 inc = 16 time = 188525.95 iter = 2 eps = 0.17720E-07 Increment end Analysis completed CPU wall= 142.7695 CPU total= 2538.382 END PROJECT PAN
Actual CPU times will differ.
Results may be imported and viewed in ParaView.
Figures 6.2 shows the computed final distortion before the build plate is removed from the machine, after the build plate is removed from the machine, and after the part is removed from the build plate.
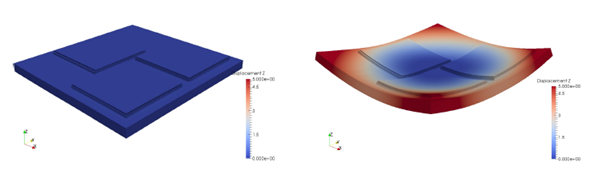
(a) After deposition and before build plate removal from the machine, and (b) After build plate removal from the machine
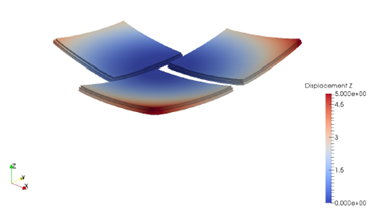
(c) After part removal from the build plate