Topological Design Variable
Description: Defines a topology design region for topology optimization.
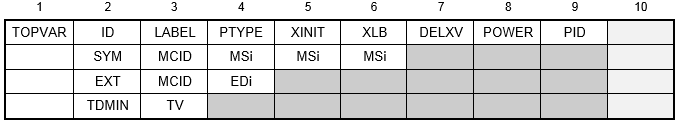
Format:
Example:
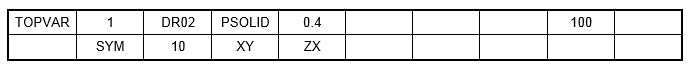
| Field | Definition | Type | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
| ID | Topology design region identification number. | Integer > 0 | Required |
| LABEL | Label associated with design region used for output headings. | Character | |
| PTYPE | Property type. Used with PID to identify the elements to be designed, one of the following character variables: PSOLID, PSHELL, or PCOMP. | Character | Required |
| XINIT | Initial value for design variable. Typically XINIT is defined to match the mass target constraint, so the initial design does not have violated constraints. | XLB ≤ XINIT | 0.5 |
| XLB | Lower bound for design variable to prevent the singularity of the stiffness matrix. | Real > 0.0 | 1.0E-03 |
| DELXV | Fractional change allowed for the design variable during design iteration. See Remark 2. | Real > 0.0 | 0.2 |
| POWER | A penalty factor used in the relation between topology design variables and element Young's modulus. The range between 2.0 ≤ POWER ≤ 5.0 is recommended. See Remark 3. | Real > 1.0 | 3.0 |
| PID | Property identification number. Must be unique with respect to the PID values specified in other TOPVAR entries as design regions cannot share the same element. | Integer > 0 | Required |
| SYM | Symbol indicating that this line defines symmetry constraints. | Character | |
| MCID | Coordinate system identification number used to define manufacturing constraints. See Remark 3. | Integer > 0 or blank | 0 |
| MSi | Mirror symmetry planes, one of the following character variables: XY, YZ, or ZX. See Remark 3. | Character | Required |
| EXT | Symbol indicating that this line defines extrusion constraints (i.e., enforced constant cross-section) | Character | |
| EDi | Extrusion direction, one of the following character variables: X, Y, or Z. See Remarks 3, 4, and 5. | Character | Required |
| TDMIN | Symbol indicating that minimum member size is specified. | Character | |
| TV | Minimum member size. See Remark 6. | Character | Required |
Remarks:
- The topologically designable element properties include PSHELL, PCOMP, and PSOLID. Multiple TOPVAR entries are allowed in a single file. Those elements whose PID is not specified in TOPVAR entries are considered to be non-designable elements; that is, they are considered to be fully filled by the material and are not changed during topology optimization.
- When X is the topology design variable of an element, the Young's modulus of the element is calculated by:
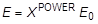
where,
E0 is Young's modulus of the material.
- One, two, or three different mirror symmetry planes can be present (such as MS1 = XY, MS2 = YZ, and MS3 = ZX). When the mesh is regular and parallel to the coordinate system MCID, all elements on the positive coordinate side are considered to have independent design variables, and elements on the negative side are considered dependent design. When the mesh is not regular or not parallel to the coordinate system MCID, an element in the negative coordinate side is considered dependent if the element is moved to the mirror plane and if there is an independent element on the positive side within the distance specified by the model parameter TOPTELEMSYMTOL (see Section 5, Parameters, for more information on TOPTELEMSYMTOL).
- The EXT (extrusion) manufacturability constraint is only applicable when PTYPE = PSOLID.
- Some symmetry constraint types can be combined with extrusion constraints. The referenced coordinate system CID must be the same for the combined constraints. Some possible combinations are: (EDi = X, MSi = XY, and/or ZX), (EDi = Y, MSi = YZ, and/or XY), (EDi = Z, MSi = ZX, and/or YZ).
- TDMIN is a dimensional quantity with a guideline that it be set to at least three times a representative element dimension. Without a TDMIN continuation line, the minimum member size is set to 3 levels of adjacent elements. Minimum member size constraints can be used with all other constraint types.