ライティング インタフェース
プラグイン エフェクトを使用して、またはレンダリング ループをオーバーライドして実装する場合、API ではサポートされているライト パラメータ/アトリビュートにアクセスできます。これには、各ライト タイプの基本的なアトリビュートおよびシャドウ マップ アクセスが含まれます。
情報は、描画コンテキスト(MDrawContext)の一部として提供されます。コンテキストは粒状性の可能な限り最低のレベルで利用できます。レンダリングに向けたハードウェア シェーダ設定の直前のポイントです。必要に応じて、シェーダを呼び出す前に、ライト パラメータ データを使用してシェーダ パラメータを更新できます。
インタフェースは使用上の制限がないデータ プロバイダでしかないので、必要に応じて、固定機能シェーディングにライトとシャドウの情報を使用できます。
ライト プロパティ情報を返す基本的な構造は MLightParameterInformation です。
これらのリストは、シーン内のアクティブなライトのセットを表します。どのライトがアクティブかを判別するには、インタラクティブ レンダリングの 3D ビューポート パラメータと、バッチ レンダリングのレンダー グローバル設定を考慮します。数も、表示されると考えられるシーン内のライトの数およびアクティブな GPU デバイスによってサポートできるライトの数によって制限されます。
アンビエント ライトは、ディレクショナル プロパティを持たない単一のグローバル周囲光とみなされます。これはレンダリング フレームワークのプロパティであり、この API のプロパティではありません。
ライト情報のインタフェースは、シェーダ インスタンスの場合と同様にパラメータ ベースです。すべてのライトが同じプロパティを共有するのではなく、ライトのタイプによって異なるパラメータにアクセスできます。セマンティックはパラメータ値の背後にある意味を提供します。
レンダリング フレームワークによって生成されるシャドウ マップにアクセスできます。これらはテクスチャ(MTexture)として返されます。適切な変換によるテクスチャのルックアップに使用されるマトリックスが、パラメータの 1 つとして提供されます。テクスチャのサンプラはサンプラの説明として返されます。シャドウ マップは、ビューポートまたはバッチ レンダー設定およびライトごとの設定に基づいて返されます(たとえば、シャドウ マッピングがライトに対して有効である場合)。
次の図は、レンダリング時に MDrawContext が MPxShaderOverride、MSceneRender、MUserOperation の各オペレーションおよび MShaderInstance インスタンスで使用できることを示します。
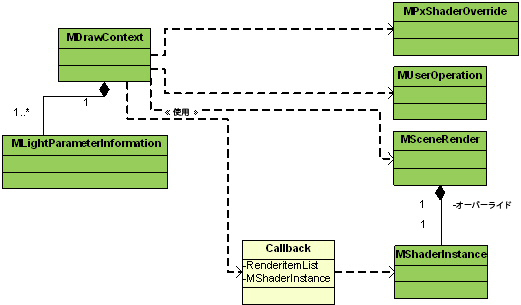
図 68: ライティング情報へのアクセスは、描画コンテキストへのアクセスに基づきます。
- dx11Shader SDK プラグインには、HLSL ファイルからセマンティックを解析するサンプル コードがあります。ライト パラメータを更新するとき、コードは提供された MDrawContext でライト情報にアクセスし、適切なパラメータを指定された HLSL シェーダのライト パラメータにバインドします。
- hwPhongShader の MPxShaderOverride には、ライト情報を照会する方法を示す簡単なコードがあります。
- gpuCacheDrawOverride の MPxDrawOverride は、パラメータ ベースではないさらに簡単なインタフェースを使用して、固定機能ライティングを設定するためにライト情報を使用する方法を示します。
次のサンプルコードでは、OpenGL で使用するためにシャドウ マップ パラメータを抽出する方法を示します。
// Get the number of active lights
unsigned int lightCount = context.numberOfActiveLights();
for (unsigned int i=0; i<lightCount; i++)
{
// Get light parameter information for a given light
MHWRender::MLightParameterInformation *lightParam =
context.getLightParameterInformation( i );
if (lightParam) {
MStringArray params;
lightParam->parameterList(params);
// Scan through all the parameters for this light. They may be differ for different
// light types.
for (unsigned int p=0; p<params.length(); p++) {
MHWRender::MSamplerStateDesc samplerDesc;
if (ptype == MHWRender::MLightParameterInformation::kTexture2) {
// OpenGL specific extraction of the GPU handle for a shadow map texture
void *handle = lightParam->getParameterTextureHandle( pname );
if (handle)
int openGLHandle = *((int *)handle));
break;
}
else if (ptype == MHWRender::MLightParameterInformation::kSampler) {
// Get a sampler description.
lightParam->getParameter( pname, samplerDesc );
}
}
}
}
シャドーイング コントロール
MPassContext の情報は、シャドウ マップ作成の間にプラグインがレンダリング用に呼び出されるときに示す十分な情報を提供します。MPxShaderOverride および MPxDrawOverride インタフェースはこの情報を使用して複雑なレンダリングを実行できます。既定では、レンダラ自体が既定の状態および/または使用する既定のシェーダを設定します。
MPxDrawOverride の場合、描画コードを最適化して、カラー パス レンダリングにのみ必要なコードを実行しないようにすることができます。たとえば、すべてのブレンド操作を無効にできます。
MPxShaderOverride の場合、カラー パス シェーダが何らかの種類のデフォメーションまたはテッセレーションを実行する場合、描画コードでカスタム シャドウ シェーダの使用を選択できます。
便宜上、MShaderInstance はどちらのプラグイン インタフェースでも使用できます。MPxShaderOverride 内から使用する場合、冗長なシェーダの変更を減らすため、バインドおよびバインド解除は、キーのアクティブ化および非アクティブ化のときに行う必要があります。MPxDrawOverride 内から使用する場合、バインドおよびバインド解除は描画呼び出しの中で行う必要があります。
結果のシャドウ マップは、内部レンダリングに使用され、プラグインのビューティ パス描画に使用できます。
次に示すのは、MPxShaderOverride のカスタム シャドウ投影および描画を設定するためのサンプル コードです。「ビューティ パス」では、MLightParameterInformation インスタンスから使用できるシャドウ マップおよび関連付けられたマトリックスを使用します。
class hwPhongShaderOverride : public MHWRender::MPxShaderOverride { protected: // Color shader MHWRender::MShaderInstance *fColorShaderInstance; // Shadow shader MHWRender::MShaderInstance *fShadowShaderInstance; public: void createShaderInstance() { MHWRender::MRenderer *renderer = MHWRender::MRenderer::theRenderer(); const MHWRender::MShaderManager* shaderMgr = renderer->getShaderManager(); // If no shadow shader instance created yet acquire one. Use // the stock shadow shader provided. if (!fShadowShaderInstance) { fShadowShaderInstance = shaderMgr->getStockShader( MHWRender::MShaderManager::k3dShadowerShader ); } // If no color shader instance created yet acquire one. For // now it's just using an internal shader for convenience but // a custom shader could be written here as well. if (!fColorShaderInstance) { fColorShaderInstance = shaderMgr->getStockShader( MHWRender::MShaderManager::k3dBlinnShader ); } } /* virtual */ void activateKey(MHWRender::MDrawContext& context, const MString& key) { // Bind color or shadower shader as appropriate if (fInColorPass) fColorShaderInstance->bind( context ); else if (fInShadowPass) { // Update the parameters on the shadow shader. Use the view projection // matrix from the active context MMatrix viewProj = context.getMatrix(MHWRender::MDrawContext::kViewProjMtx); fShadowShaderInstance->setParameter("shadowViewProj", viewProj ); fShadowShaderInstance->bind( context ); } } // Example of using MShaderInstace to draw. Terminate // the shader instance here. /* virtual */ void terminateKey(MHWRender::MDrawContext& context, const MString& key) { if (fInColorPass) fColorShaderInstance->unbind( context ); else if (fInShadowPass) fShadowShaderInstance->unbind( context ); } /* virtual */ bool draw(MHWRender::MDrawContext& context, const MHWRender::MRenderItemList& renderItemList) const { // Draw for color pass with a blend state change if (fInColorPass) { stateMgr->setBlendState(sBlendState); unsigned int passCount = fColorShaderInstance->getPassCount( context ); for (unsigned int i=0; i<passCount; i++) { fColorShaderInstance->activatePass( context, i ); MHWRender::MPxShaderOverride::drawGeometry(context); } stateMgr->setBlendState(pOldBlendState); } // Draw for shadow pass else if (fInShadowPass) { unsigned int passCount = fShadowShaderInstance->getPassCount( context ); for (unsigned int i=0; i<passCount; i++) { fShadowShaderInstance->activatePass( context, i ); MHWRender::MPxShaderOverride::drawGeometry(context); } } } }
「無制限」のライト情報アクセス
オンデマンドまたは無制限のライト情報を要求するには、最初に MRenderer::needEvaluateAllLights()を呼び出す必要があります。
詳細については、「Maya 2016 Extension の新機能: ライティング」を参照してください。
内部シェーディングに使用されるライトの数はレンダラのライトの制限数クランプによって制限されますが、ライト情報にアクセスするための API インタフェースを使用すると、このライトの制限数の設定を無視するかどうかを指定できます。
以下のインタフェースには、ライトの制限数をバイパスするための LightFilter パラメータを指定するオプションがあります。
「必要に応じた」シャドウ/ライティングの更新
オンデマンドまたは無制限のライト情報を要求するには、最初に MRenderer::needEvaluateAllLights()を呼び出す必要があります。
詳細については、「Maya 2016 Extension の新機能: ライティング」を参照してください。
- 特定のライト DAG オブジェクトのシャドウ マップがビューポート 2.0 レンダラのライトの制限数設定を超えている場合でも、それらのシャドウ マップの計算を要求することができます。MRenderer::setLightRequiresShadows() メソッドを使用すると、このような要求をキューに入れたりキューから除去したりできます。このメソッドは、特定のシャドウ マップの計算を強制することも、リフレッシュまたは新規レンダーの実行を強制することもありません。シャドウ マップ更新の必要性のチェックをトリガします。MRenderer::setLightsAndShadowsDirty() (変更管理を参照)を使用すると、必要に応じて強制的に計算することができます。
- このメソッドがフレームのレンダリング内から呼び出された場合、シャドウ マップ計算の更新はすべて、次のシーンの更新時に行われます。たとえば、ハードウェア シェーダ プラグイン(MPxShaderOverride)内から呼び出された場合、更新は次のフレーム(リフレッシュ)で実行されます。レンダー オーバーライド操作から呼び出された場合、次のシーン レンダーによって更新がトリガされます。シーン レンダーは、オーバーライド内から呼び出された次の MSceneRender か、レンダー オーバーライドがない場合にレンダラによって内部的に呼び出された次のシーン レンダーのいずれかです。
-
このインタフェースを使用したコード例は、dx11Shader (MPxShaderOverride)プラグインおよび viewRenderOverrideShadows (MRenderOverride)プラグインにあります。dx11Shader プラグインには、ライトのバインドが変更されたときの追加リフレッシュの呼び出しを示すコードがあります。
- 通常、ライト情報はシーン レンダー(MSceneRender)中にのみ更新されます。シャドウ要求がカスタム レンダー オーバーライドのユーザ操作(MUserRenderOperation)内から実行された場合は、最後の使用可能なライト情報のみを使用できます。ユーザ操作にライト情報が必要な場合は、新しい仮想メソッド MUserRenderOperation::requiresLightData() をオーバーライドして、true を返すように設定できます。
- レンダー オーバーライドでのシーン レンダーが更新後にシャドウ マップなどの情報にアクセスできるようにするために、2 つのメソッド MSceneRender::preSceneRender() と MSceneRender::postSceneRender() を使用できます。これらのメソッドは、シャドウ マップの更新またはシーンのレンダリングの前か後のいずれかに呼び出されます。この時点で、現在の描画コンテキスト、したがってライティング/シャドーイング情報(MLightParameterInformation)が利用できます。
- 新しいインタフェースを使用する例としては、新しい viewRenderOverrideShadows レンダー オーバーライド プラグインがあります。このプラグインは、ユーザ操作を実行してシャドウ要求をキューに格納した後、カスタム シーン レンダーでそのシャドウ要求を使用します。プリシーン レンダー メソッドは、要求されたシャドウ マップを抽出するようにオーバーライドされます。これにより、カスタム シェーダがシーンのレンダリング中にこのシャドウ マップを使用できるようになります。ライトの制限数を超えるライトおよびシャドウ情報にアクセスできます。
ライト情報をワールドから固定関数ライティングのビュー空間に変換する
ライトを設定する場合は、ライト情報はビュー空間ではなくワールド空間に返されることに注意することが重要です。MFrameContext::kViewMtx パラメータを MDrawContext::getMatrix()メソッドの入力パラメータとして使用し、トランスフォームを表示するワールドを取得することができます。
プログラミングが可能なシェーダで、ビュー空間を使用することができます。固定関数 OpenGL のライティングではビュー空間を使用します。(固定関数 DirectX のライティングは存在しません)。OpenGL の場合は、ライティングの設定時にワールドとビューの行列をロードする必要があります。
固定関数のライティングでライティング インタフェースを使用する例については、gpuCache MPxDrawOverride Developer Kit サンプル(gpuCacheDrawOverride.cpp ファイル)を参照してください。
サンプル コードに基づいたサンプルの設定を次に示します。すべてのライティングの状態をプラグインによって設定する必要があります。既定では、プログラミング可能なパイプラインには目的がないため、実行時に固定関数のライティングは設定されません。
コードの最初の部分では、ライトが 8 個という OpenGL の制限を超えていないか確認し、ワールドとビューの行列を設定しています。gGLFT 変数は MGLFunctionTable のポインタであり、コンテキスト変数はプラグインに渡される MDrawContext であることに注目してください。
MStatus status; // Take into account only the 8 lights supported by the basic // OpenGL profile. const unsigned int nbLights = std::min(context.numberOfActiveLights(&status), 8u); if (status != MStatus::kSuccess) return false; if (nbLights > 0) { // Lights are specified in world space and needs to be // converted to view space. const MMatrix worldToView = context.getMatrix(MHWRender::MFrameContext::kViewMtx, &status); gGLFT->glLoadMatrixd(worldToView.matrix[0]);
残りの一般的な設定でライティングを有効化し、両面ライティングのチェックなどのパラメータを設定します。この例では、アンビエントおよびスペキュラは 0 に設定されます。
gGLFT->glEnable(MGL_LIGHTING);
gGLFT->glColorMaterial(MGL_FRONT_AND_BACK, MGL_AMBIENT_AND_DIFFUSE);
gGLFT->glEnable(MGL_COLOR_MATERIAL) ;
gGLFT->glEnable(MGL_NORMALIZE) ;
{
const MGLfloat ambient[4] = { 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f };
const MGLfloat specular[4] = { 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f };
gGLFT->glMaterialfv(MGL_FRONT_AND_BACK, MGL_AMBIENT, ambient);
gGLFT->glMaterialfv(MGL_FRONT_AND_BACK, MGL_SPECULAR, specular);
gGLFT->glLightModelfv(MGL_LIGHT_MODEL_AMBIENT, ambient);
// Check for two sided lighting in VP2.0.
if (context.getDisplayStyle() & MHWRender::MFrameContext::kTwoSidedLighting) {
gGLFT->glLightModeli(MGL_LIGHT_MODEL_TWO_SIDE, 1);
}
else {
gGLFT->glLightModeli(MGL_LIGHT_MODEL_TWO_SIDE, 0);
}
}
コードの最後の部分では、各ライトをループし、適切なライト単位の情報を設定しています。ここでは、パラメータ ベースのメソッドを使用することもできますが、要件は固定関数のライティングであるため、より単純な MDrawContext::getLightInformation()メソッドを使用しています。
for (unsigned int i=0; i<nbLights; ++i)
{
MFloatPointArray positions;
MFloatVector direction;
float intensity;
MColor color;
bool hasDirection;
bool hasPosition;
// Use simple interface to get basic lighting information for the
// current light.
status = context.getLightInformation(
i, positions, direction, intensity, color,
hasDirection, hasPosition);
プラグインは、すべての情報を取得した後に、設定する必要があるライトのタイプを判別します。最初に、ディレクショナル ライトをチェックします。ディレクショナル ライトは位置を持つことができるため、スポットライトとして解釈することができます。ここではいくつかの情報をハードコードしていますが、パラメータ ベースのインタフェースから抽出することもできることに注目してください。
// Handle lights which have a direction:
if (hasDirection)
{
if (hasPosition)
{
// Set up a “spot light” as we have direction and position
MFloatPoint position;
position[0] = positions[0][0];
position[1] = positions[0][1];
position[2] = positions[0][2];
const MGLfloat ambient[4] = { 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f };
const MGLfloat diffuse[4] = { intensity * color[0],
intensity * color[1],
intensity * color[2],
1.0f };
const MGLfloat pos[4] = { position[0],
position[1],
position[2],
1.0f };
const MGLfloat dir[3] = { direction[0],
direction[1],
direction[2]};
gGLFT->glLightfv(MGL_LIGHT0+i, MGL_AMBIENT, ambient);
gGLFT->glLightfv(MGL_LIGHT0+i, MGL_DIFFUSE, diffuse);
gGLFT->glLightfv(MGL_LIGHT0+i, MGL_POSITION, pos);
gGLFT->glLightfv(MGL_LIGHT0+i, MGL_SPOT_DIRECTION, dir);
// Just using default value's for spot lights.
// Could use the parameter interface to get more information.
gGLFT->glLightf(MGL_LIGHT0+i, MGL_SPOT_EXPONENT, 0.0);
gGLFT->glLightf(MGL_LIGHT0+i, MGL_SPOT_CUTOFF, 20.0);
}
else
{
// Set up a “directional” light which has a 180 degree cone.
const MGLfloat ambient[4] = { 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f };
const MGLfloat diffuse[4] = { intensity * color[0],
intensity * color[1],
intensity * color[2],
1.0f };
const MGLfloat pos[4] = { -direction[0],
-direction[1],
-direction[2],
0.0f };
gGLFT->glLightfv(MGL_LIGHT0+i, MGL_AMBIENT, ambient);
gGLFT->glLightfv(MGL_LIGHT0+i, MGL_DIFFUSE, diffuse);
gGLFT->glLightfv(MGL_LIGHT0+i, MGL_POSITION, pos);
gGLFT->glLightf(MGL_LIGHT0+i, MGL_SPOT_CUTOFF, 180.0);
}
}
// Handle setting up a point light:
else if (hasPosition)
{
MFloatPoint position;
position[0] = positions[0][0];
position[1] = positions[0][1];
position[2] = positions[0][2];
const MGLfloat ambient[4] = { 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f };
const MGLfloat diffuse[4] = { intensity * color[0],
intensity * color[1],
intensity * color[2],
1.0f };
const MGLfloat pos[4] = { position[0],
position[1],
position[2],
1.0f };
gGLFT->glLightfv(MGL_LIGHT0+i, MGL_AMBIENT, ambient);
gGLFT->glLightfv(MGL_LIGHT0+i, MGL_DIFFUSE, diffuse);
gGLFT->glLightfv(MGL_LIGHT0+i, MGL_POSITION, pos);
gGLFT->glLightf(MGL_LIGHT0+i, MGL_SPOT_CUTOFF, 180.0);
}
最終チェックは、「アンビエント ライト」と解釈されるアンビエント期間のチェックです。
// Handle setting up an ambient light for the ambient term:
else
{
const MGLfloat ambient[4] = { intensity * color[0],
intensity * color[1],
intensity * color[2],
1.0f };
const MGLfloat diffuse[4] = { 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f };
const MGLfloat pos[4] = { 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f };
gGLFT->glLightfv(MGL_LIGHT0+i, MGL_AMBIENT, ambient);
gGLFT->glLightfv(MGL_LIGHT0+i, MGL_DIFFUSE, diffuse);
gGLFT->glLightfv(MGL_LIGHT0+i, MGL_POSITION, pos);
gGLFT->glLightf(MGL_LIGHT0+i, MGL_SPOT_CUTOFF, 180.0);
}
// Enable the light
gGLFT->glEnable(MGL_LIGHT0+i);
}
}
プラグインのサンプルは、ライトを無効化する対応サンプル コードも提供します。詳細については、Developer Kit サンプルを参照してください。
