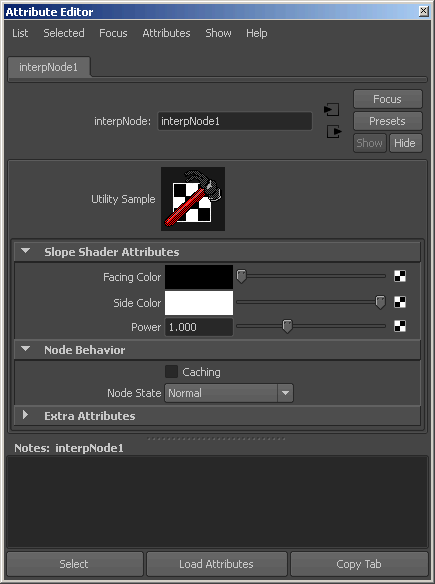
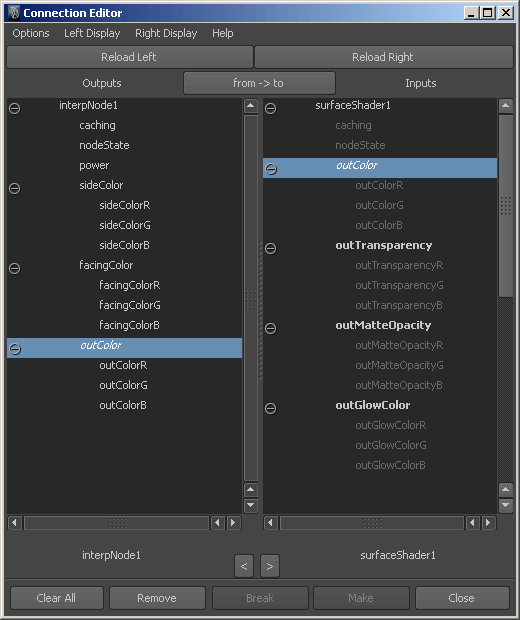
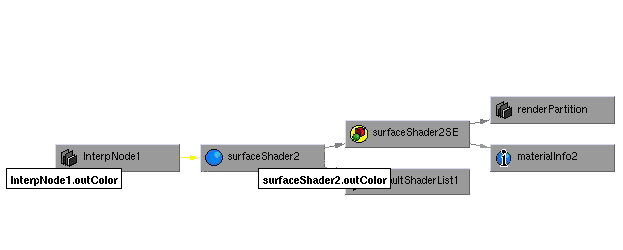
InterpNode コード サンプルの概説
シェーディング ノード プラグインは、複合アトリビュート(Compound Attributes)と単純なアトリビュート(Simple Attributes)の使用に依存します。レンダリング サンプラとシェーディング ネットワーク間のデータ マッピングは、アトリビュート名で行います。この方法は直接的で習得しやすく、十分に一般的で、現在のレンダリング要件と将来の拡張に対処できます。
プラグインが必要とするすべてのレンダリング アトリビュートは、現在のサンプリングの前に計算されています。プラグインの compute() メソッドに渡される「datablock」引数には、ノードが要求するレンダリング アトリビュート情報が含まれています。ディペンデンシー グラフによってプラグインが評価されると、評価する特定アトリビュートの「plug」引数も渡されます。評価を最適化するには、プラグイン内で定義した出力アトリビュートのみをチェックします。
このプラグイン ノードの例には、id アトリビュート以外に 20 個のアトリビュートが含まれています。
- 赤、緑、青を表す、3 つの float 型アトリビュートから複合アトリビュートとして作成される、2 つのカラー入力アトリビュート(合計 8 個のアトリビュート)。
- 赤、緑、青を表す、3 つの float 型アトリビュートから複合アトリビュートとして作成される、1 つのカラー出力アトリビュート(合計 4 個のアトリビュート)。
- X、Y、Z のベクトル コンポーネントを表す、3 つの float 型アトリビュートから複合アトリビュートとして作成される、サーフェス法線のアトリビュート(合計 4 個のアトリビュート)。
- X、Y、Z の現在のサンプル ポイントを表す、3 つの float 型アトリビュートから複合アトリビュートとして作成される、カメラ スペース内におけるジオメトリの位置のアトリビュート(合計 4 個のアトリビュート)。
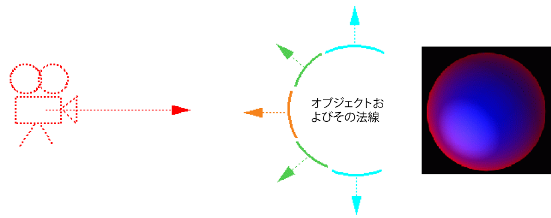
このノードは、データ ブロックから取得したサーフェス法線の方向に基づいて 2 つのカラー間を補間し、そのクラスの compute() メソッドを使用して、出力カラー アトリビュートに配置するカラーを派生させます。
派生
class InterpNode : public MPxNode { public: InterpNode(); virtual ~InterpNode(); virtual MStatus compute( const MPlug&, MDataBlock& ); static void * creator(); static MStatus initialize(); static MTypeId id; protected: static MObject InputValue; static MObject color1R,color1G,color1B,color1; static MObject color2R,color2G,color2B,color2; static MObject aNormalCameraX, aNormalCameraY, aNormalCameraZ, aNormalCamera; static MObject aPointCameraX, aPointCameraY, aPointCameraZ, aPointCamera; static MObject aOutColorR, aOutColorG, aOutColorB, aOutColor; }; MObject InterpNode::InputValue; MObject InterpNode::color1R; MObject InterpNode::color1G; MObject InterpNode::color1B; MObject InterpNode::color1; MObject InterpNode::color2R; MObject InterpNode::color2G; MObject InterpNode::color2B; MObject InterpNode::color2; MObject InterpNode::aNormalCameraX; MObject InterpNode::aNormalCameraY; MObject InterpNode::aNormalCameraZ; MObject InterpNode::aNormalCamera; MObject InterpNode::aPointCameraX; MObject InterpNode::aPointCameraY; MObject InterpNode::aPointCameraZ; MObject InterpNode::aPointCamera; MObject InterpNode::aOutColorR; MObject InterpNode::aOutColorG; MObject InterpNode::aOutColorB; MObject InterpNode::aOutColor;
initializePlugin/uninitializePlugin
MStatus initializePlugin( MObject obj ) { const MString UserClassify( "utility/general" ); MFnPlugin plugin( obj, "Autodesk", "1.0", "Any"); plugin.registerNode( "Interp", InterpNode::id, InterpNode::creator, InterpNode::initialize, MPxNode::kDependNode, &UserClassify); return MS::kSuccess; } MStatus uninitializePlugin( MObject obj) { MFnPlugin plugin( obj ); plugin.deregisterNode( InterpNode::id ); return MS::kSuccess; }
初期化
MStatus InterpNode::initialize() { MFnNumericAttribute nAttr; // Inputs and Attributes // // User defined attributes require a long-name and short- // name that are required to be unique within the node. // (See the compound attribute color1 named "Sides".) // // Rendering attributes that your node wants to get from // the sampler require them to be defined given the pre- // defined unique long-name.(See the compound attribute // aNormalCamera named "normalCamera".) // // User defined Attributes are generally something that you // want to store in the Maya file. The setStorable(true) // method enables an attribute to be stored into the Maya // scene file. // // Rendering attributes are primarily data that is // generated per sample and not something that you want to // store in a file. To disable an attribute from being // recorded to the Maya scene file use the // setStorable(false) method. // // Simple attributes that represent a range of values can // enable a slider on the Attribute Editor by using the // methods setMin() and setMax(). // (See the simple attribute InputValue named "Power".) // // Compound attributes that represent a vector of 3 floats // can enable a color swatch on the Attribute Editor that // will launch a color picker tool by using the method // setUsedAsColor(true). // (See the compound attribute color1 name "Sides".) // // Both Simple and Compound attributes can be initialized // with a default value using the method setDefault(). // // Attributes by default show up in the Attribute Editor // and in the Connection Editor unless they are specified // as being hidden by using the method setHidden(true). // // Attributes by default have both read/write access in the // dependency graph. To change an attributes behaviour you // can use the methods setReadable() and setWritable(). The // method setReadable(true) indicates that the attribute // can be used as the source in a dependency graph // connection. The method setWritable(true) indicates that // the attribute can be used as the destination in a // dependency graph connection. // (See the compound attribute aOutColor named "outColor" // below. It has been marked as a read-only attribute since // it is the computed result of the node, it is not stored // in the Maya file since it is always computed, and it is // marked as hidden to prevent it from being displayed in // the user interface.) // // // User defined input value InputValue = nAttr.create( "Power", "pow", MFnNumericData::kFloat); nAttr.setDefault(1.0f); nAttr.setMin(0.0f); nAttr.setMax(3.0f); nAttr.setStorable(true); // User defined color attribute color1R = nAttr.create( "color1R", "c1r", MFnNumericData::kFloat); color1G = nAttr.create( "color1G", "c1g", MFnNumericData::kFloat); color1B = nAttr.create( "color1B", "c1b", MFnNumericData::kFloat); color1 = nAttr.create( "Sides", "c1", color1R, color1G, color1B); nAttr.setStorable(true); nAttr.setUsedAsColor(true); nAttr.setDefault(1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f); color2R = nAttr.create( "color2R", "c2r", MFnNumericData::kFloat); color2G = nAttr.create( "color2G", "c2g", MFnNumericData::kFloat); color2B = nAttr.create( "color2B", "c2b", MFnNumericData::kFloat); color2 = nAttr.create( "Facing", "c2", color2R, color2G, color2B); nAttr.setStorable(true); nAttr.setUsedAsColor(true); nAttr.setDefault(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f); // Surface Normal supplied by the render sampler aNormalCameraX = nAttr.create( "normalCameraX", "nx", MFnNumericData::kFloat); nAttr.setStorable(false); nAttr.setDefault(1.0f); aNormalCameraY = nAttr.create( "normalCameraY", "ny", MFnNumericData::kFloat); nAttr.setStorable(false); nAttr.setDefault(1.0f); aNormalCameraZ = nAttr.create( "normalCameraZ", "nz", MFnNumericData::kFloat); nAttr.setStorable(false); nAttr.setDefault(1.0f); aNormalCamera = nAttr.create( "normalCamera","n", aNormalCameraX, aNormalCameraY, aNormalCameraZ); nAttr.setStorable(false); nAttr.setHidden(true); // Point on surface in camera space, will be used to compute view vector aPointCameraX = nAttr.create( "pointCameraX", "px", MFnNumericData::kFloat); nAttr.setStorable(false); nAttr.setDefault(1.0f); aPointCameraY = nAttr.create( "pointCameraY", "py", MFnNumericData::kFloat); nAttr.setStorable(false); nAttr.setDefault(1.0f); aPointCameraZ = nAttr.create( "pointCameraZ", "pz", MFnNumericData::kFloat); nAttr.setStorable(false); nAttr.setDefault(1.0f); aPointCamera = nAttr.create( "pointCamera","p", aPointCameraX, aPointCameraY, aPointCameraZ); nAttr.setStorable(false); nAttr.setHidden(true); // Outputs aOutColorR = nAttr.create( "outColorR", "ocr", MFnNumericData::kFloat); aOutColorG = nAttr.create( "outColorG", "ocg", MFnNumericData::kFloat); aOutColorB = nAttr.create( "outColorB", "ocb", MFnNumericData::kFloat); aOutColor = nAttr.create( "outColor", "oc", aOutColorR, aOutColorG, aOutColorB); nAttr.setStorable(false); nAttr.setHidden(false); nAttr.setReadable(true); nAttr.setWritable(false); addAttribute(InputValue); addAttribute(color1R); addAttribute(color1G); addAttribute(color1B); addAttribute(color1); addAttribute(color2R); addAttribute(color2G); addAttribute(color2B); addAttribute(color2); addAttribute(aNormalCameraX); addAttribute(aNormalCameraY); addAttribute(aNormalCameraZ); addAttribute(aNormalCamera); addAttribute(aPointCameraX); addAttribute(aPointCameraY); addAttribute(aPointCameraZ); addAttribute(aPointCamera); addAttribute(aOutColorR); addAttribute(aOutColorG); addAttribute(aOutColorB); addAttribute(aOutColor); attributeAffects (InputValue, aOutColor); attributeAffects (color1R, color1); attributeAffects (color1G, color1); attributeAffects (color1B, color1); attributeAffects (color1, aOutColor); attributeAffects (color2R, color2); attributeAffects (color2G, color2); attributeAffects (color2B, color2); attributeAffects (color2, aOutColor); attributeAffects (aNormalCameraX, aOutColor); attributeAffects (aNormalCameraY, aOutColor); attributeAffects (aNormalCameraZ, aOutColor); attributeAffects (aNormalCamera, aOutColor); attributeAffects (aPointCameraX, aOutColor); attributeAffects (aPointCameraY, aOutColor); attributeAffects (aPointCameraZ, aOutColor); attributeAffects (aPointCamera, aOutColor); return MS::kSuccess; }
compute メソッド
MStatus InterpNode::compute( const MPlug& plug, MDataBlock& block ) { int k=0; float gamma,scalar; k |= (plug == aOutColor); k |= (plug == aOutColorR); k |= (plug == aOutColorG); k |= (plug == aOutColorB); if (!k) return MS::kUnknownParameter; MFloatVector resultColor(0.0,0.0,0.0); MFloatVector& Side = block.inputValue( color1 ). asFloatVector(); MFloatVector& Face = block.inputValue( color2 ). asFloatVector(); MFloatVector& surfaceNormal = block. inputValue( aNormalCamera ). asFloatVector(); MFloatVector& viewVector = block. inputValue( aPointCamera ). asFloatVector(); float power = block.inputValue( InputValue ).asFloat(); // Normalize the view vector double d = sqrt((viewVector[0] * viewVector[0]) + (viewVector[1] * viewVector[1]) + (viewVector[2] * viewVector[2])); if (d != (double)0.0) { viewVector[0] /= d; viewVector[1] /= d; viewVector[2] /= d; } // find dot product float scalarNormal = ((viewVector[0]*surfaceNormal[0]) + (viewVector[1]*surfaceNormal[1]) + (viewVector[2]*surfaceNormal[2])); // take the absolute value if (scalarNormal < 0.0) scalarNormal *= -1.0; // Use InputValue to change interpolation // power == 1.0 linear // power >= 0.0 use gamma function // if (power > 0.0) { gamma = 1.0 / power; scalar = pow(scalarNormal,gamma); } else { scalar = 0.0; } // Interpolate the colors MFloatVector interp(0.0,0.0,0.0); interp[0] = scalar * (Face[0] - Side[0]); interp[1] = scalar * (Face[1] - Side[1]); interp[2] = scalar * (Face[2] - Side[2]); resultColor[0] = Side[0] + interp[0]; resultColor[1] = Side[1] + interp[1]; resultColor[2] = Side[2] + interp[2]; // set ouput color attribute MDataHandle outColorHandle = block. outputValue( aOutColor ); MFloatVector& outColor = outColorHandle. asFloatVector(); outColor = resultColor; outColorHandle.setClean(); return MS::kSuccess; }